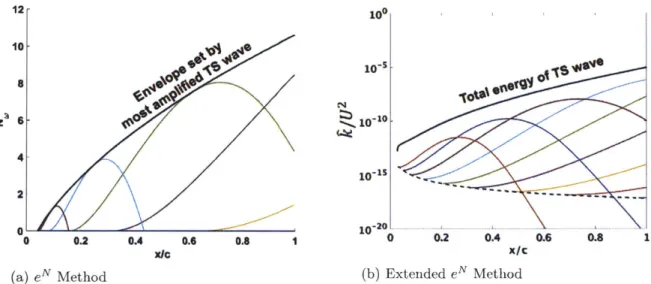
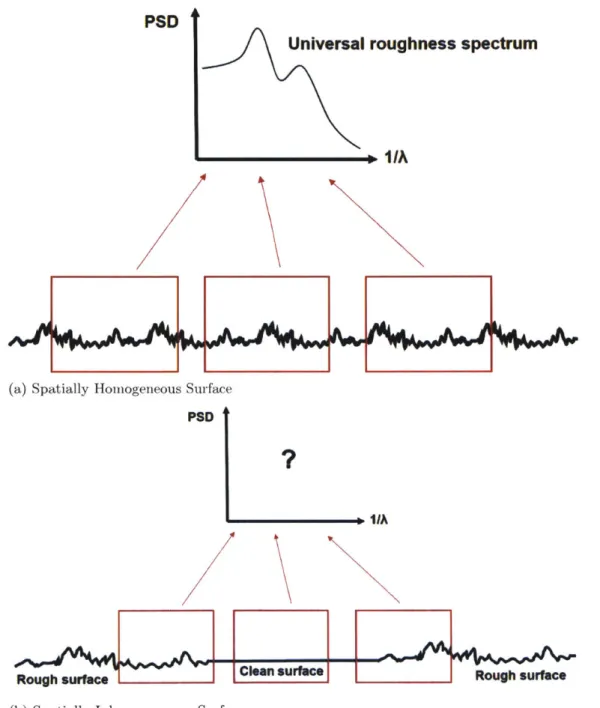
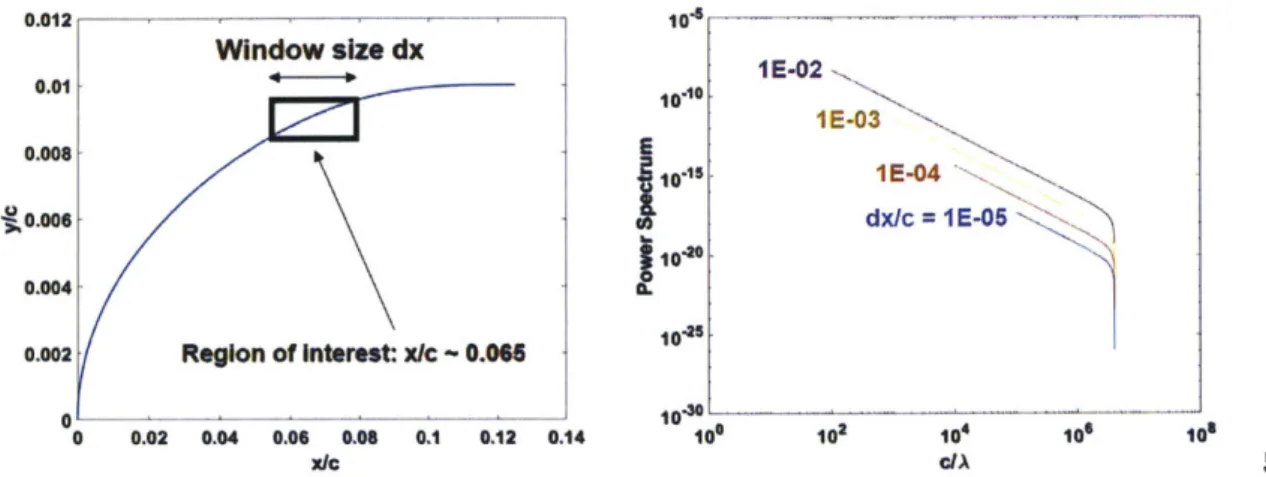
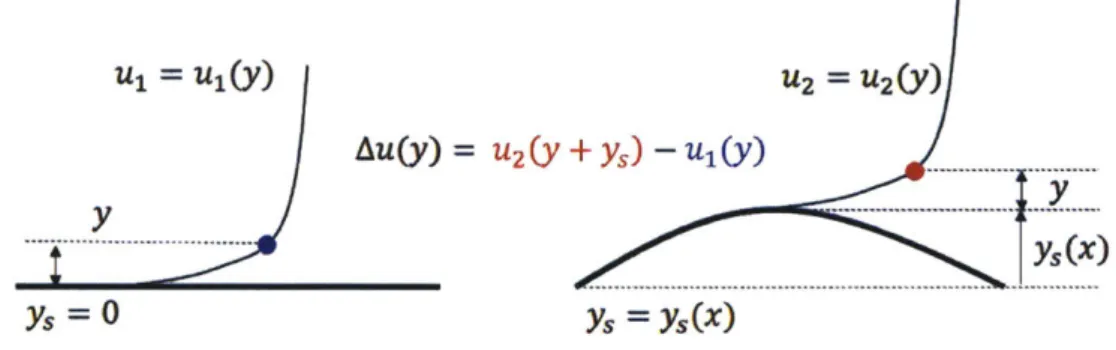Characterization and mitigation of blade waviness effects on fan performance
Texte intégral
Figure

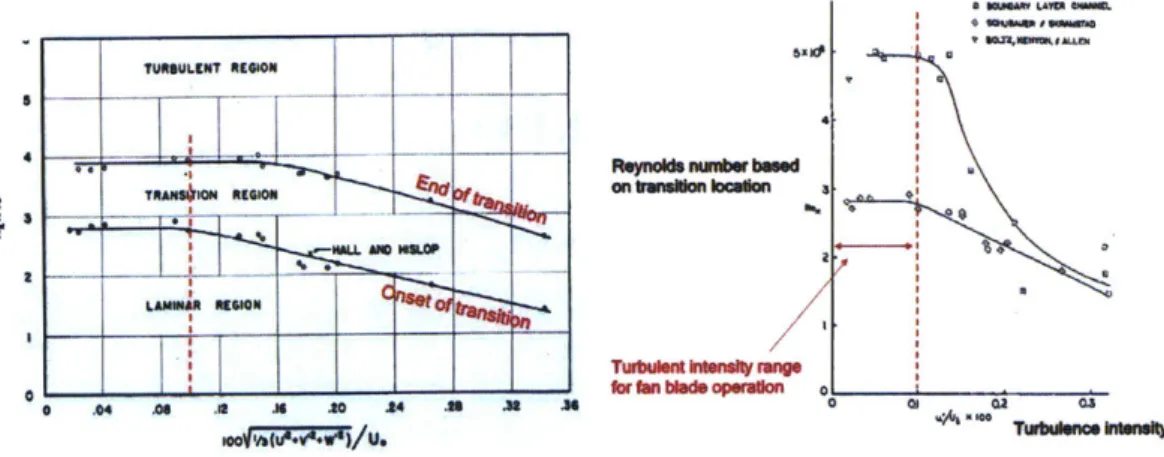
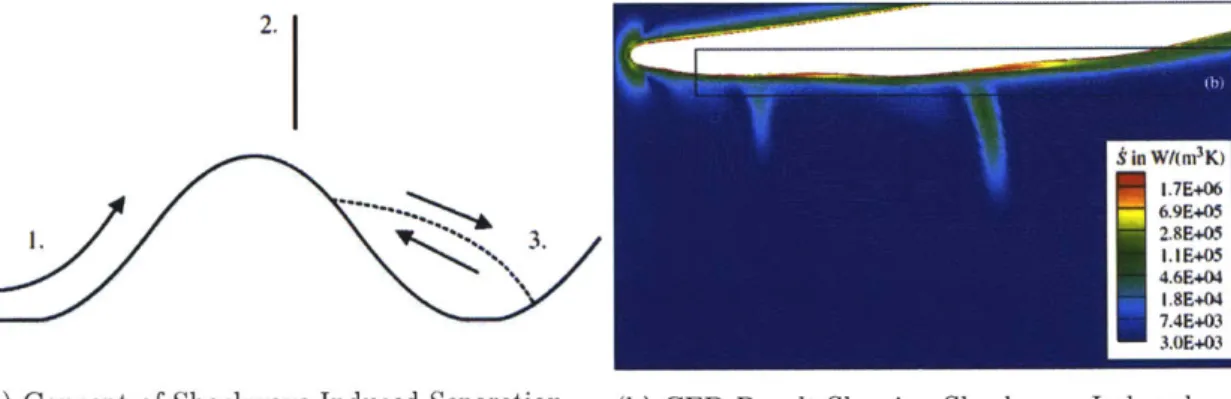

Documents relatifs
As plant roots are capable of decreasing the concentration of K + from several hundreds of micromoles per dm 3 in the bulk soil down to concentrations in the micromolar range at
Therefore, MPBNs offer a drastic reduction in the theoretical computational complexity for analyzing reachability, attractors, and reachable attractors of BNs, with
On another hand, the vibration of a conductor inside a magnetic field induced by ultrasound induces by Lo- rentz force an electrical current which is connected to the
It considers optimal resupply quantities based on ordering and inventory holding costs, product sellable shelf life, minimum packaging quantities, and a maximum order
Since, the trophic conditions control the concentration of dissolved organic matter in the surface ocean, and given the fertilizing potential of atmospheric iron, dissolved
If errors are due to perturbations in loading matrices inverse formula is better when condition number of the mode-3 loading matrix is smaller than or equal to 16. (6) was
To generate a composite spectrum for a single epoch, we first Doppler shift each template by its calculated radial velocity, interpolate the secondary spectrum to the same