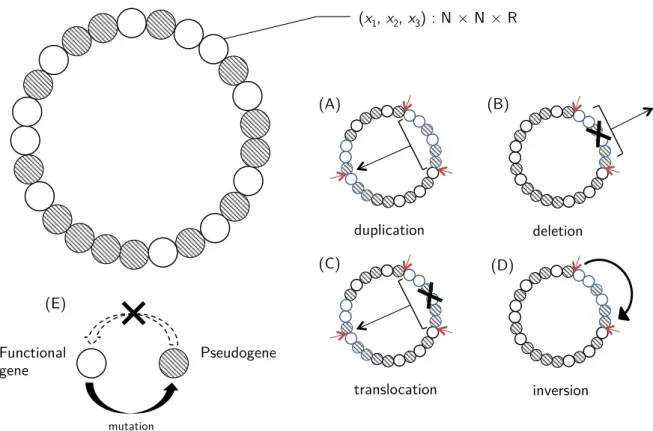
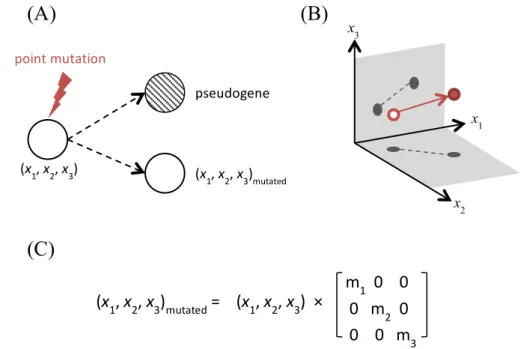
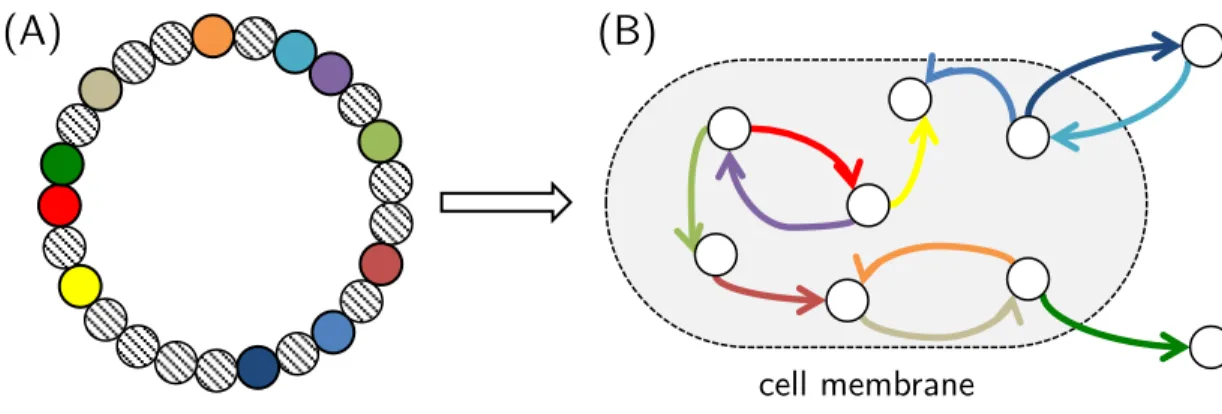
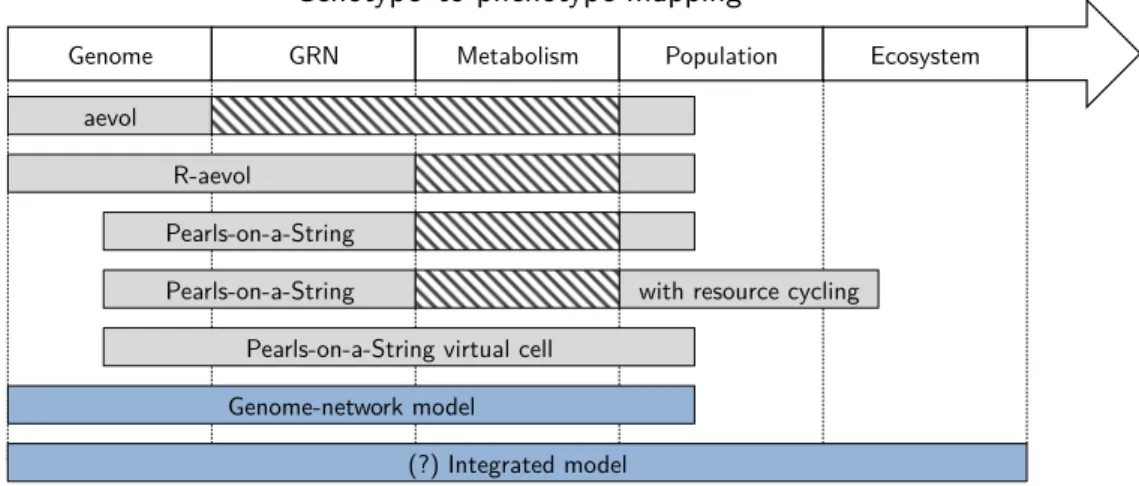
EvoEvo Deliverable 2.1: Specifications of the genome-network model
Texte intégral
Figure
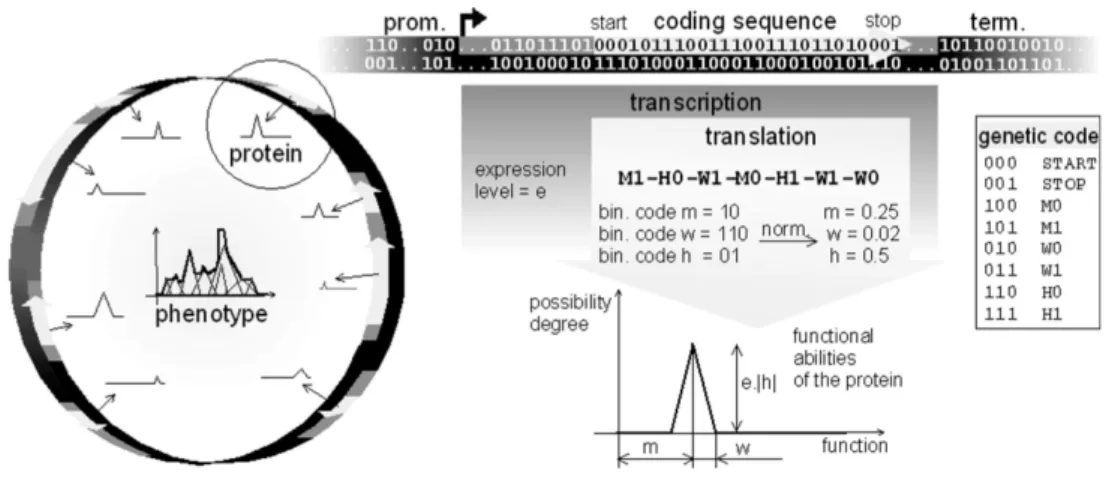

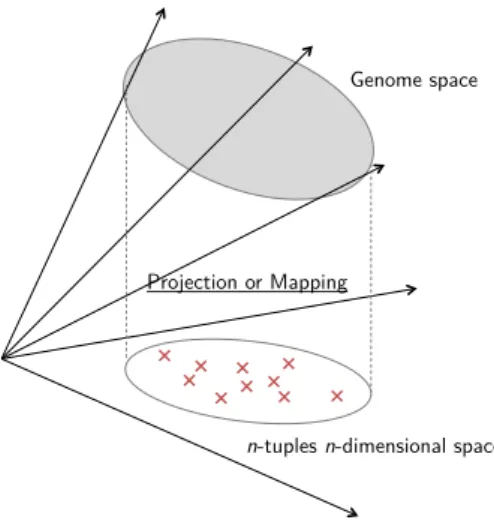
Documents relatifs
Stepanov Institute of Physics, National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, Minsk, Republic of Belarus 92 National Scientific and Educational Centre for Particle and High Energy
Abonnement : Dialogue (ISSN 0012-2173) est une revue trimestrielle publiée en mars, juin, septembre et décembre par la Cambridge University Press, 32 Avenue of the Americas, New
33 Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INR RAN), Moscow, Russia 34 Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics (SB RAS) and Novosibirsk State
depend, omitted due to copyright Figure 2-220: Bader House north Section.. 103 omitted due to copyright Figure 2-221: mid SectTon through stair omitted due to copyright Figure
The parameter of interest in this search is the signal strength, µ, defined as the ratio of the fitted signal cross section times branching fraction to the signal cross section
For 12 elements (H, Li, B, C, N, O, Mg, Si, S, Cl, Br, and Tl) having interval standard atomic-weight values the isotopic abundance of each stable isotope is given as an interval
70-100 Total raising of the vitelline envelope 80-100.. The regions where cortical granules simultaneously burst out represent a surface area much more extensive than upon
4.3 Effect of bounded cascade modeling and sparse sampling on the ARF In Chapter 3 we investigated the scaling properties of the ARF with the maximum linear size of