Impact of the Via Baltica on the Urbanisation in Lithuania by Multi-level Remote Sensing Analysis
Texte intégral
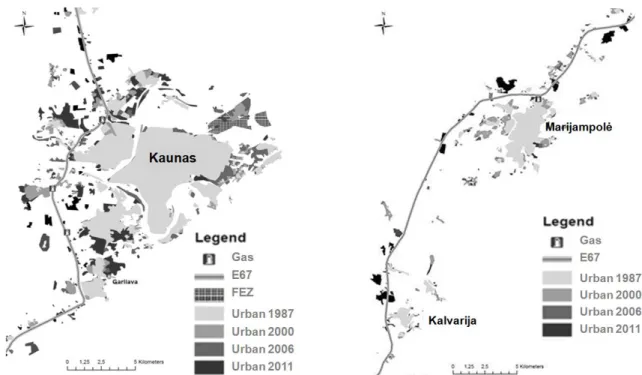
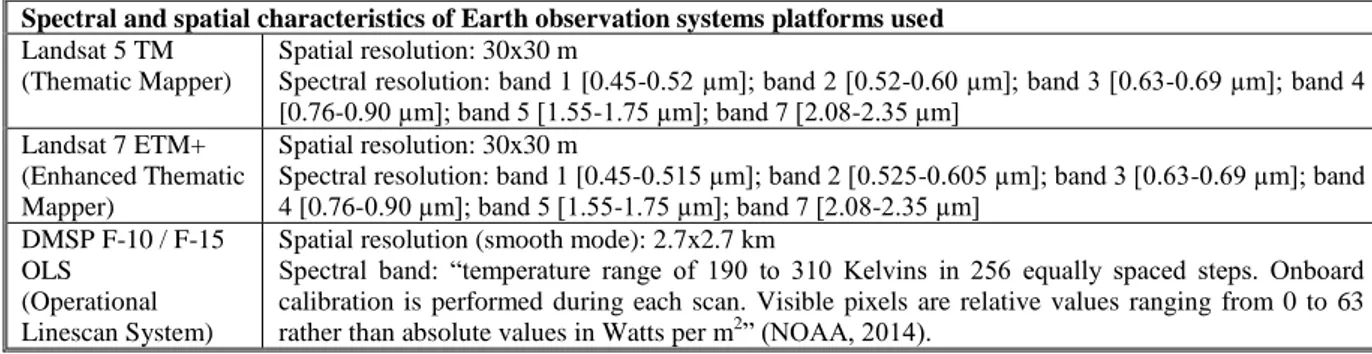
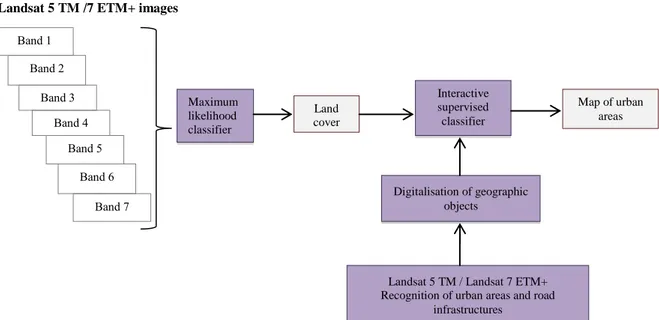
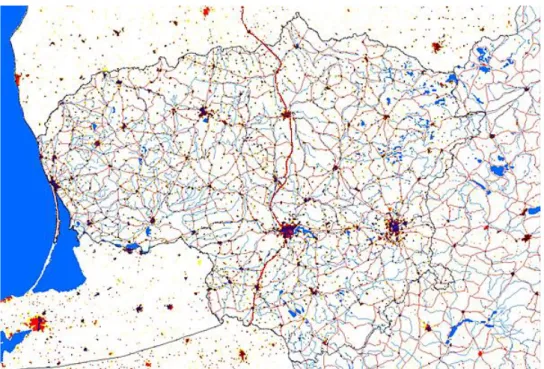
Figure

Documents relatifs
En especial, se propone este concepto –definido como un proceso interactivo y participativo de las relaciones sociales (políticas, económicas y culturales), orientado a promover
The results showed that the communication (interaction) among social network users is a main reason to actively use those services, loss of privacy is the
Economic benefits include reduced health expenditure due to less illness, the value of assumed productivity gains due to less illness and death, time savings due to less time
Beyond semimartingales and Markov processes, local time process associated with Gaussian processes may exist (c.f. [8]) as occupation densi- ties. A particular example of
was positively correlated with vascular and total species richness and negatively with moss
Using the ground-based AMS data, in addition to satellite data with high spatial resolution (MAIAC), it is possible to create an information basis for a modern system of
In summation, for the studied interconnected nonlinear systems, an interconnected observer design method is proposed by combining both actuator and process subsystem state
This can be achieved by means of indicators coupling (e.g., choosing the sensors with constraints on both the detection probability and the saturation time), by imposing a