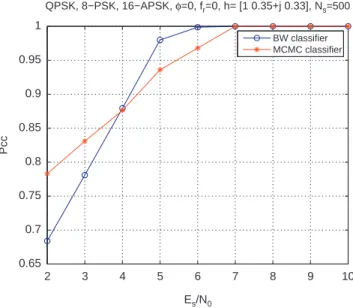
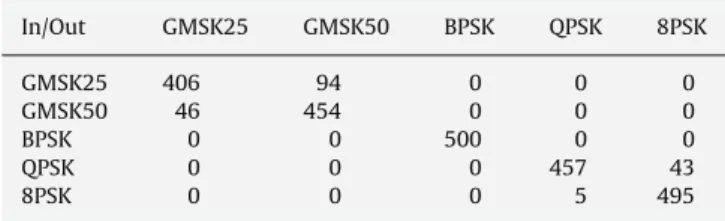
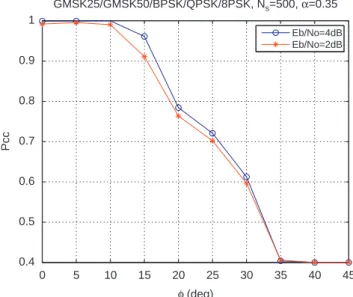
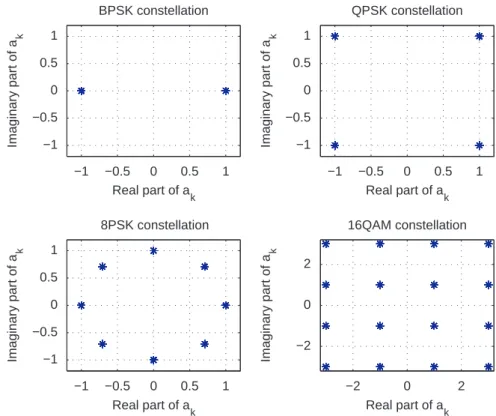
Classification of linear and non-linear modulations using the Baum–Welch algorithm and MCMC methods
Texte intégral
Figure
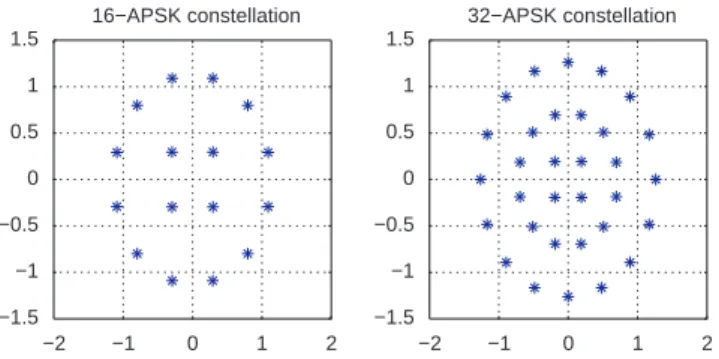
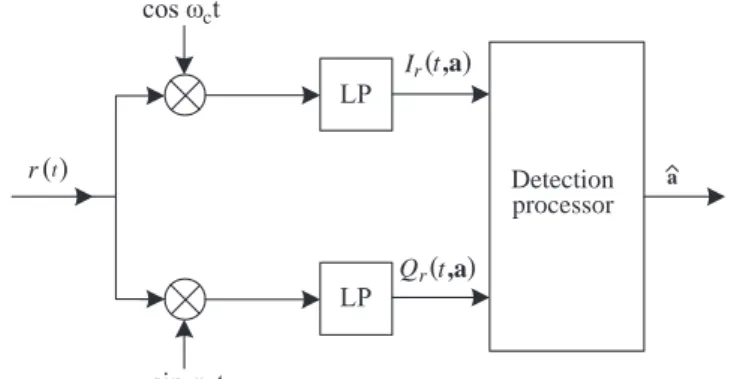
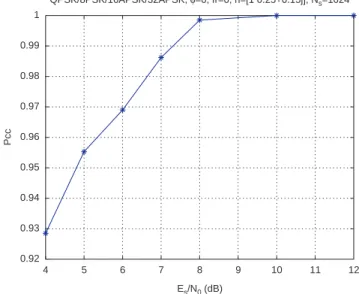
Documents relatifs
Dans ce manuscrit, nous avons défini pour trois problèmes (Stefan, Stokes, Navier-Stokes) le cadre des schémas gradients, permettant d’obtenir des résultats de convergence et
The results obtained for SCB in electric field (El = 2 and al = 0.5 for the substance) are qualitatively consistent with the theoretical predictions summarised in figures I and 2:
My current research project aims to enhance understanding of the dynamic interplay between the diet, the rumen microbiota and the ruminant animal via an interdisciplinary
/Ŷ ƚŚŝƐ ƉĂƉĞƌ͕ / ƉƌŽƉŽƐĞ ƚŽ ĚĞĐŽŵƉŽƐĞ ŶŽŶͲůŝŶĞĂƌŵŽĚĞůƐ ĚĞĚƵĐĞĚ ĨƌŽŵ Ă ůĂƚĞŶƚ
Essentially the authors in [23] demonstrate a reduction from testing freeness of the cycle matroid in a function to testing freeness of the cycle subgraph in a graph, and then
In this paper, sufficient conditions for the robust stabilization of linear and non-linear fractional- order systems with non-linear uncertainty parameters with fractional
Damages in reinforced concrete structures like friction in cracks, change in stiffness due to the alternately opening and closing of cracks under dynamic excitation or
-There exist four types of localized solutions which correspond to the four Arnold strong resonances of the dynamical system. -These solutions are weakly chaotic and the