Conservation genetics and population history of the threatened European mink Mustela lutreola, with an emphasis on the west European population.
Texte intégral
Figure

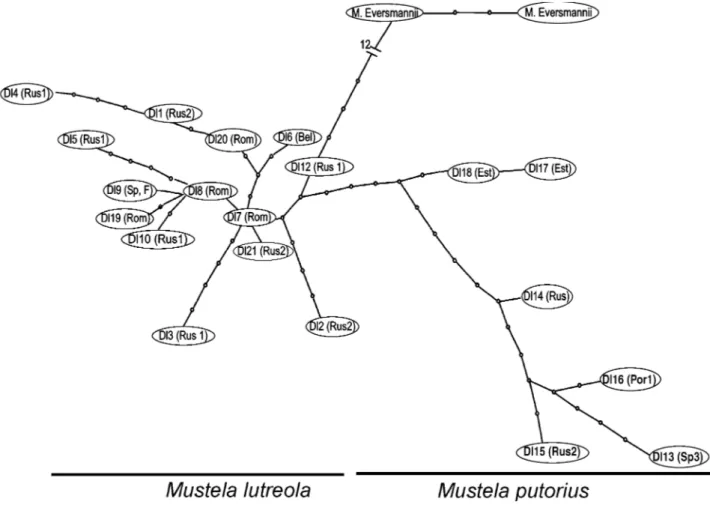

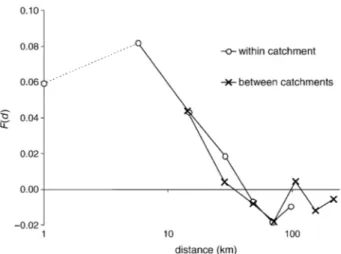
Documents relatifs
Usage of antimicrobials and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance among bacteria from mink.. Karl Pedersen, Anne Sofie Hammer, Charlotte Mark Sørensen,
lapin oiseau marmotte chien tortue souris L’ordre alphabétique h tt p :/ /ce n ici en ta .e kla b log.co m Sou rce image s: Réc it p ré
Consequently, the reported incidence of small ruminant scrapie increased, with significantly greater numbers of scrapie positive (based on PrP Sc detection), clinically
Social integration & economic resources mediate partnership effect on memory (3) Education. Partnership effects only for lower-educated
In this study we empirically analyze whether or not national identity values have the same resonance across ethnic minority and majority groups in 24 European
From this partial point of view on the stabilisation, we can strongly question the consistency displayed by the authors to link traditional earth constructions to the modern use
The virus has been detected in animals exposed to infected humans – domestic cats, dogs and ferrets, captive lions and tigers, farmed mink – as well as gorillas , indicating
Despite the fact that surface carbon stocks in the natural forest (4.0±0.6 kg m −2 ) are much higher than at the poplar plantation (1.7±0.4 kg m −2 ), no significant di fference