ADJUVANT TREATMENT OF VULVAR CANCER WITH IMRT
Mota, A.1, Leite, R.1, Pimenta, A1, Ribeiro, F.1, Sousa, M1, Fortunato, M.1, Santos, F.1, Roldão, M.1
1Radiotherapy Department of Instituto Português de Oncologia de Lisboa Francisco Gentil , E.P.E. - Portugal
There are very few studies regarding IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) and the treatment of vulvar cancer. Therefore, we will present our experience on IMRT treatment in adjuvant vulvar cancer, at our Department.
RESULTS
This work is based on a retrospective analysis of vulvar cancer treated with surgery and adjuvant IMRT between January 2009 and February 2012.
All patients were treated with IMRT (sliding window), in a Clinac 2100CD (linear accelarator), with photon energy 6MV. For dosimetry, the inversed planning system was used. It was evaluated the Planning Target Volume (PTV) coverage, the dose's homogeneity distribution and the dose tolerance of the organs at risk – rectum (V40), bladder (V40), small bowel (V35) and bone marrow (V20).
The acute toxicity (intestinal, genitourinary and skin) was evaluated according to the Radiation Therapy Organization Group criteria.
CONCLUSIONS: IMRT seems to be a promising treatment in vulvar cancer. IMRT planning has a proper PTV coverage with considerable sparing of organs at risk and is well tolerated by patients.
We also achieve with IMRT a low loco-regional relapse, as mentioned in literature.Treatment Response 50% patients alive at the present analysis
30% patients had loco-regional relapse 1 patient had distant metastasis 30 patients
AGE: 32 to 88 years (median: 75) HISTOLOGY: Squamous cells carcinoma
ALL COMPLETED TREATMENT MEAN DOSE: 62.32Gy (50-66Gy)
FOLLOW-UP: 13 to 50 months
Graphics 1 and 2: Overall Survival and Progression Free Survival (Kaplan Meier)
OAR AVERAGE DOSE
Rectum 33.04 Gy
Bladder 31.51 Gy
Small bowel 23.85 Gy
Bone marrow 22.27 Gy
OAR AVERAGE DOSE
V40 Rectum 28.40 Gy
V40 Bladder 26.09 Gy
V35 Small bowel 26.40 Gy
V20 Bone marrow 48.59 Gy
Table 1 and 2: OAR average doses
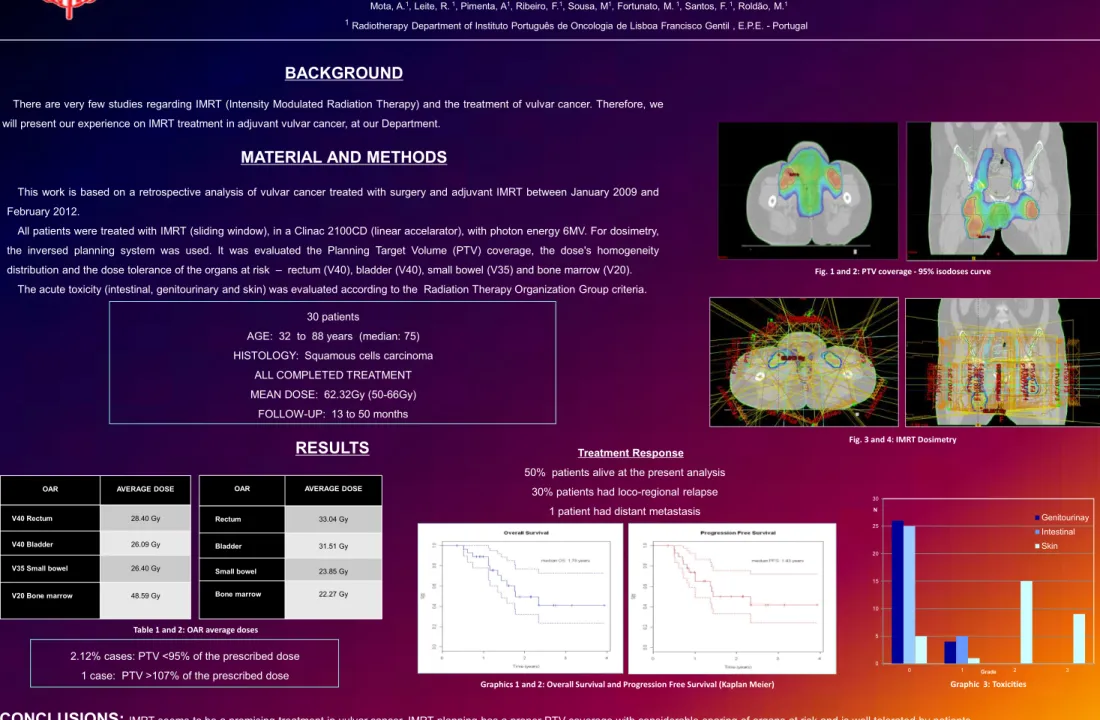
Fig. 3 and 4: IMRT Dosimetry Fig. 1 and 2: PTV coverage - 95% isodoses curve
Bibliography:1. D'Souza DP, Rumble RB, Fyles A, Yaremko B, Warde P, IMRT Indications Expert Panel. The role of IMRT in gynecologic cancers. Toronto (ON): Cancer Care Ontario (CCO); 2010 Oct 29. Various p. (Evidence-based series; no. 21-3-7 2. Beriwal et al, IMRT for the treatment of vulvar carcinoma: a comparative dosimetric study with early clinical outcome, Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys . 2006 April 1;64(5):1395-400. Epub 2006 Jan 25 3. King et al, Current Practice of IMRT to Treat Carcinoma of the Vulva - Results of an International Survey, ASTRO Presentation 2011
MATERIAL AND METHODS
BACKGROUND
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 0 1 2 3 N Grade Genitourinay Intestinal Skin Graphic 3: Toxicities2.12% cases: PTV <95% of the prescribed dose 1 case: PTV >107% of the prescribed dose