GetDDM: an open framework for testing optimized Schwarz methods for time-harmonic wave problems
Texte intégral
Figure
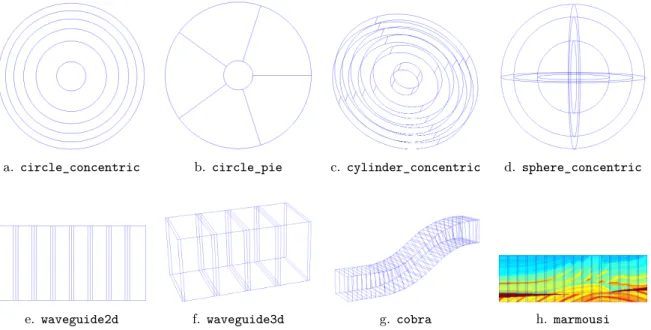
![Figure 3: Sample models solved with GetDDM. Top: acoustic waves around a submarine (image reproduced from [13])](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14596630.543339/31.892.237.658.123.330/figure-sample-models-solved-getddm-acoustic-submarine-reproduced.webp)
Documents relatifs
That is why, over and above his activity as a university professor and his engagement in preventive archaeology, Jean-Paul Demoule has undertaken numerous actions to further
We derive an implicit solution on each subdomain from the optimized Schwarz method for the mesh BVP, and then introduce an interface iteration from the Robin transmission
According to our clinic experience, wound closure after DSWI, either primary or delayed, will be performed most of the time based on the optical assessment performed by the surgeon
The excitation is at point (0, 0) and the analytical solution in infinite space is given by formula (84). Good agreements between the two types of absorbing boundary conditions and
It relies on the splitting of the time interval into time windows, in which a few iterations of an optimized Schwarz waveform relax- ation algorithm are performed by a
Thus the algorithm is dened as in the classical Schwarz case, but like in waveform relaxation, time dependent subproblems are solved, which explains the name of these methods..
inductors. In the multivariate problem, linear multidimensional interpolation is an attractive choice due to its computation speed and simplicity. Throughout this section, the
La classification présentée ici propose de discriminer deux composantes dans l’organisation de ces matériaux paracristallins : les défauts de structure du réseau graphiti- que,