Euclidean addition chains scalar multiplication on curves with efficient endomorphism
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
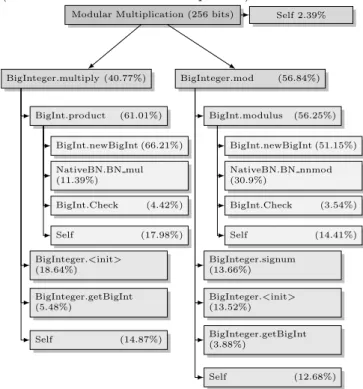
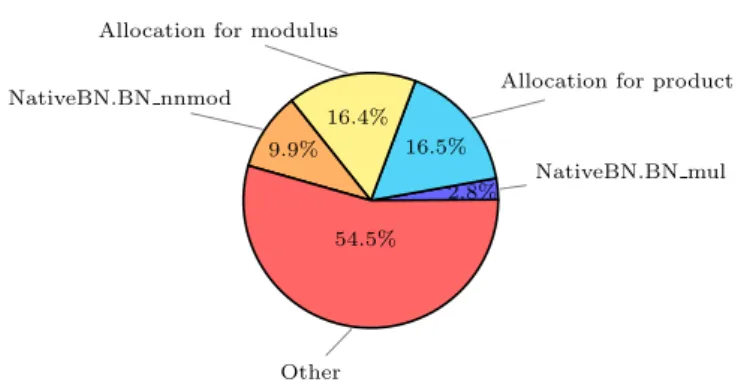
Therefore, we note that so far, practical implementations of multiplication algorithms of type Chudnovsky over finite fields have failed to simultaneously optimize the number of
Like GLV, our method involves reducing curves defined over number fields to obtain curves over finite fields with explicit CM.. However, we emphasise a profound difference: in
Galbraith, Lin, and Scott [9] and the author [26] have already con- structed families of endomorphisms equipped with a convenient ready-made basis; in this work, we generalize
The problem is the lack of an effective information technology for processing and analyzing data that would enable the medical analyst to identify hidden patterns
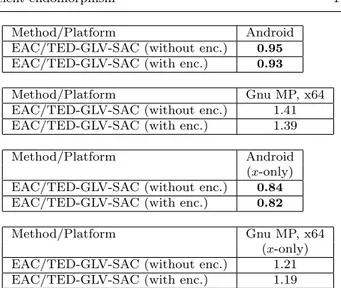
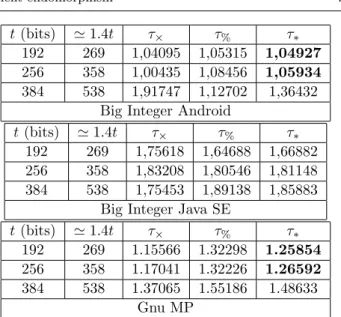
Keywords: ECC, scalar multiplication, Lim-Lee method, comb method, Koblitz curves, Frobenius endomorphism, τ-adic representation..
For Huff curves, the authors of [5] give differential addition formulas for use with the Montgomery ladder. Furthermore, we contrast its performance with a reference implementation
We propose a new GCD algorithm called Accelerated Euclidean Algorithm, or AEA for short, which matches the O(n log 2 n log log n) time complexity of Sch¨ onhage algo- rithm for
Our main contribution is a multiscale approach for solving the unconstrained convex minimization problem introduced in [AHA98], and thus to solve L 2 optimal transport.. Let us