Bright nanoscale source of deterministic entangled photon pairs violating Bell’s inequality
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
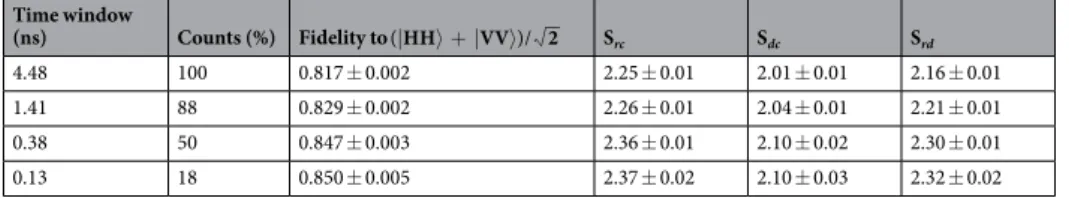
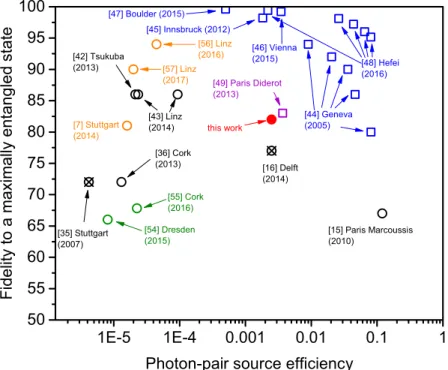
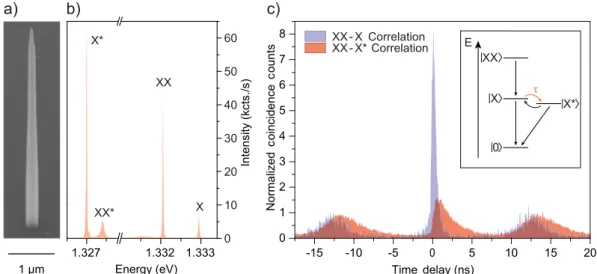
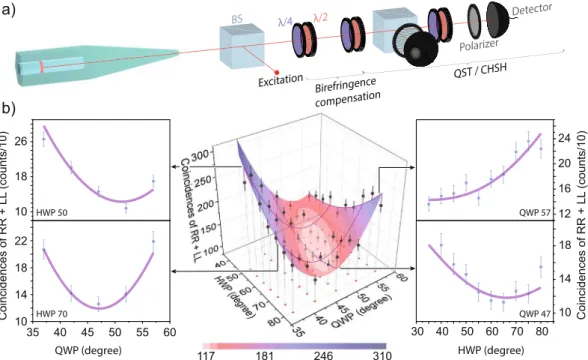
Finally, to evaluate the overall performance of a single- photon source based on an excitonic linear dipole under LA-phonon-assisted excitation, we measure the polarized
This source can be used as a heralded single photon source at telecom wavelength by using the signal photon at 770 nm to herald the idler.. The quality of the resulting source can be
This position is part of the project « A bright source of Indistinguishable Polarization-entangled On-Demand photon pairs » obtained together with the team of Julien
We present an original type of single photon source in solid state, based on the coherent laser light scattering by a single InAs quantum dot.. We demonstrate that the coherence of
We also note that given a well-known down- conversion process, the nonlocal phase of the daughter photon pair encodes the phase of the pump pulse and is invariant under local
Relative to the characteristic free-space excitation, we manage to measure with our set-up an addressing efficiency as large as 3% which proves the possibility to excite a
After the spin has been projected close to the down state, it almost stops to interact with r light, that is now reflected from the mirror. The l light continues to interact with
After studying in depth the conditions to obtain single and indistinguishable photons, we used two of these sources to demonstrate an elementary photonic network based on the