Local Q-Linear Convergence and Finite-time Active Set Identification of ADMM on a Class of Penalized Regression Problems
Texte intégral
Figure
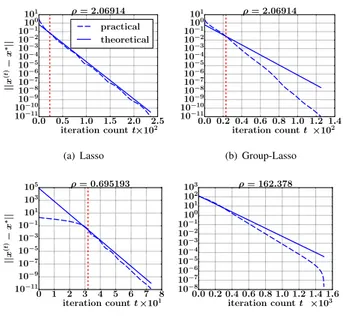
Documents relatifs
In a previous work, the geometric degree of nonconservativity of such systems, defined as the minimal number of kinematic constraints necessary to convert the initial system into
After giving some expla- nations about the capillarity (physical justification and purpose, motivations related to the theory of non-classical shocks (see [28])), we prove
Thus, (2.13) depends on the particular law µ of the entries of the Wigner matrix W N which implies the non-universality of the fluctuations of the largest eigenvalue of rank
T HEOREM. Let f be an automorphism of the finite extension G of a soluble FAR group. For i) it suffices to assume only that G is a group with finite Hirsch number (even in a
Keywords: Douglas–Rachford splitting, ADMM, Partial Smoothness, Finite Activity Identification, Local Linear Convergence..
Rates for time- discretization seem to be unknown except in some special cases (see below), and a fortiori no rates are known when the basic process is
In this section we obtain some homogenization results for minima and minimizers of some classes of variational problems for energies of integral type both in BV and Sobolev spaces..
Nonlinear Schr¨ odinger equation, two-step time discretization, linearly implicit method, finite element method, L 2 and H 1 error estimates, optimal order of convergence.. ∗