Differential language network functional connectivity alterations in Alzheimer's disease and the semantic variant of primary progressive aphasia
Texte intégral
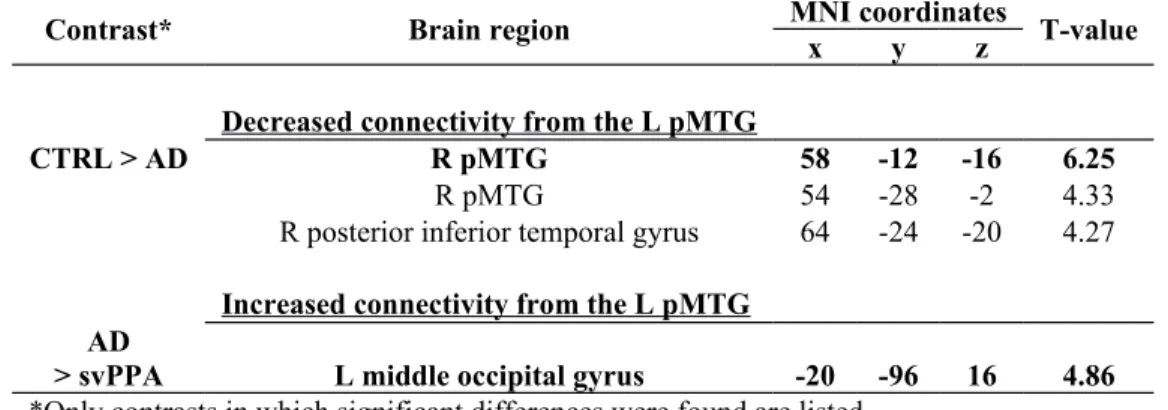
Figure


Documents relatifs
This work aimed to fabricate the bionano hybrid material by loading algae cells (Chlorella vulgaris) on the ultrafine TiO2/Ag chitosan hybrid nanofiber mats (TiO2/Ag NF) and
LoginitialEner.U se/cap is the log of the energy use per capita at the beginning of period; Log(GDP/cap) is the log of the per capita GDP of country i; Log(GDP/cap) 2 is the log of
On remarque des allures générales proches des mesures effectuées, présentées sur la Figure 2 et la Figure 3, les différences seront plus explicitées dans la version finale
case the edge states are gapped out in zero flux, leading to a vanishing dissipative diagonal susceptibility.. The response will depend on the nondiagonal damping rates γ mn ,
Notre nouvelle architecture présente tous les avantages d’une architecture de référence telle que A-DTLS auquel nous aurions ajouté un cache de données, et plus encore :
In this paper we proposed a maximum likelihood approach for Hawkes processes that can handle both self-exciting and self-regulating scenarii, the first case be- ing already covered
Les solides obtenus, nommés D600, D800, D900 et D1000, ont été analysés par différentes techniques, telles que l’analyse de la distribution granulométrique par granulomètre
Related species tend to cooccur within the same regions (23). This cooccurrence may generate the observed pattern of module phylogenetic structure regardless of evolutionary