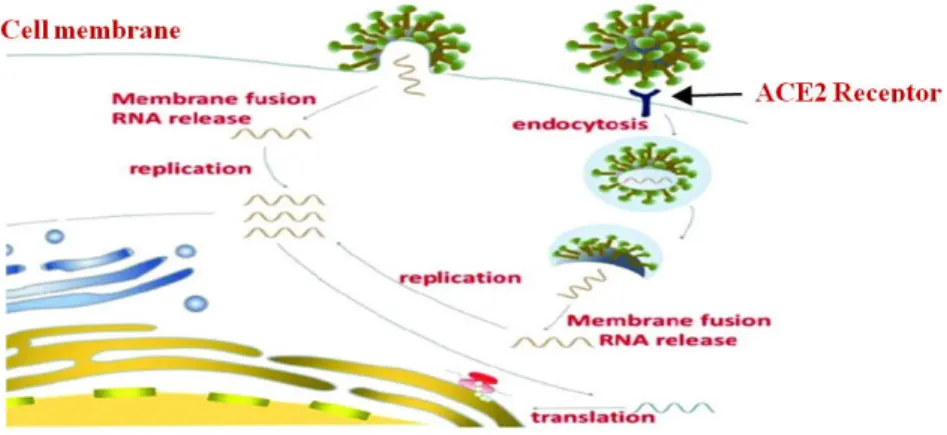
Covid-19: Predicting inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 in Caco-2 cells: viral cellular entry
Texte intégral
Figure
![Table 1. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 in human Caco-2 cells [8] and calculated molecular specifiers of repurposed drugs](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/12377758.330113/10.892.103.798.461.1090/table-inhibition-sars-human-calculated-molecular-specifiers-repurposed.webp)
![Table 2. Cell entry inhibitor binding energies to ACE2 and TMPRRS2 receptors [7] and calculated molecular specifiers of repurposed drugs](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/12377758.330113/11.892.100.795.161.793/inhibitor-binding-energies-receptors-calculated-molecular-specifiers-repurposed.webp)
Documents relatifs
The present experiments were designed to evaluate genotoxic effects of DA and to discriminate between clastogenic and/or aneugenic effect of both Okadaic acid and Domoic acid
In the present study, two polyphenols (quercetin, and hesperidin) chosen according to their structural characteristics, were used to evaluate the localization from their
Caco-2 cells were grown and differentiated in 75 cm² cell culture flasks incubated for 24 h with different species and concentrations of Al by adding 1 mL of Al-containing
However, additional biological functions (DNA damage response of cells, repair of DNA, and modification of DNA), which include genes coding for proteins implied in the regulation
In this study, we assessed whether β -cyclodextrin ( β -CD), which is used to extract and protect alpejuro phenolic compounds (hydroxytyrosol-O-glucoside, tyrosol, caffeic,
In this report, a continuation of our previous retinoid- related metabolic studies, 15,16) we have begun investigat- ing of the role of retinoids in the regulation of UGT2B7
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
Our results provide evidence for an important role of the 5- domain trans-membrane molecule CD133 in the regulation of cellular cross-talk with the extracellular