Using Road IDs to Enhance Clustering in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
Il faudrait d'abord étudier comment la colonisation travaille à déciviliser le coloni s ateur, à l'abrutir au sens propre du mot, à le dégrader, à le réveiller aux instincts
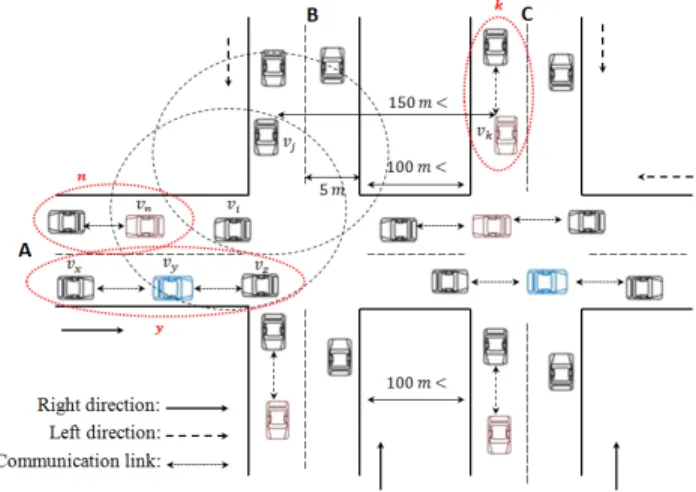
Pour mieux observer l’impacte de la densité du réseau comme illustré avec la Figure 3(b), nous fixons le nombre de nœuds et nous faisons varier le degré (nombre de voisins) des
In [7] an adaptive video communication system is proposed that allows a server with several video sequences of different qualities, i.e., multiple bitrates, to transmit the
persion and E R were obtained for PP-based CPNC, while these for PA 6 type CPNC form two distinct groups – all samples prepared in TSE compounding line show low relative modulus, E
Recent Institute for Ocean Technology (IOT) experience using a modern trials instrumentation capability during seakeeping, propulsion and manoevring trials on a small
In this section, we have evaluated and compared some routing protocols for video streaming in VANET, such as AODV, AOMDV, DSR, and DSDV in function of vehicle density
Results obtained here support the idea that different emission rates of study species growing in calcareous and siliceous soils is a consequence of the different nutrient
This paper presents an asymptotic analysis of the eigen value decomposition (EVD) of the sample covariance matrix as- sociated with independent identically distributed (IID)