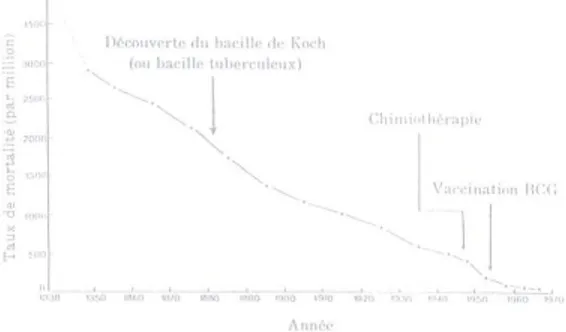
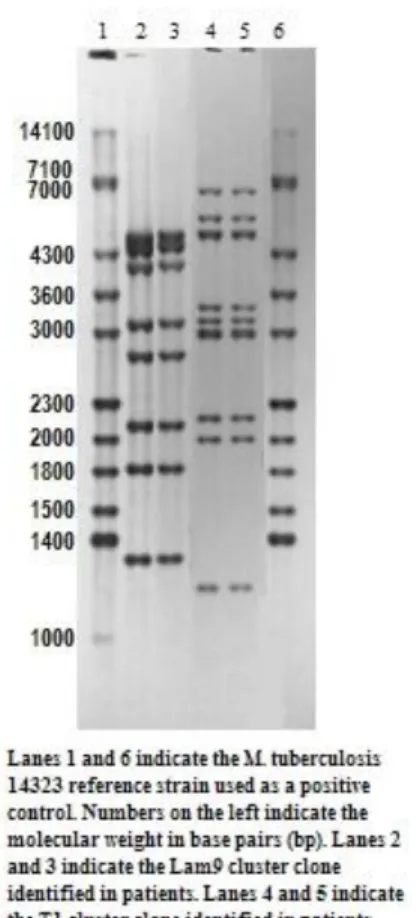
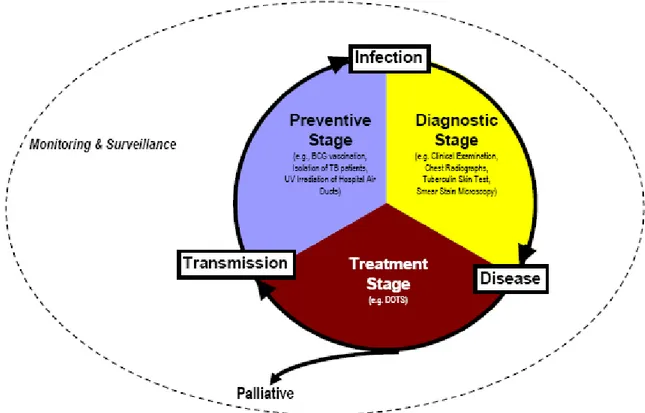
Transmission dynamics and tuberculosis control among HIV/AIDS patients
Texte intégral
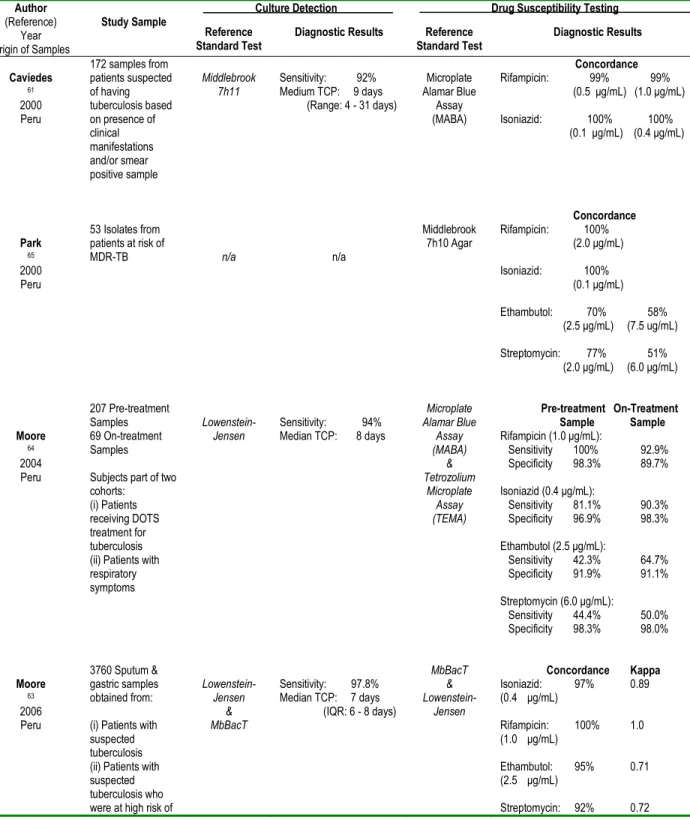
Figure


Documents relatifs
• Less effective than recommended regimen • Does not reduce in utero transmission • High risk of resistance to NVP • Probable sub-optimal viral response if NNRTI-ART is
These guidelines propose age-related clinical and immunological case definitions of advanced HIV/AIDS disease in infants and children for surveillance purposes.. Age-related
T he World Health Organization (WHO), the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) and the United Nations Offi ce on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) developed this
In this study, we aimed to: define the spectrum of HIV-related causes of hospitalization; assess the profile of hospitalized HIV-positive adults; and examine the clinical
The aims of the present exploratory study were to measure the prevalence of self-reported recreational and medicinal cannabis use, perceived benefits and adverse
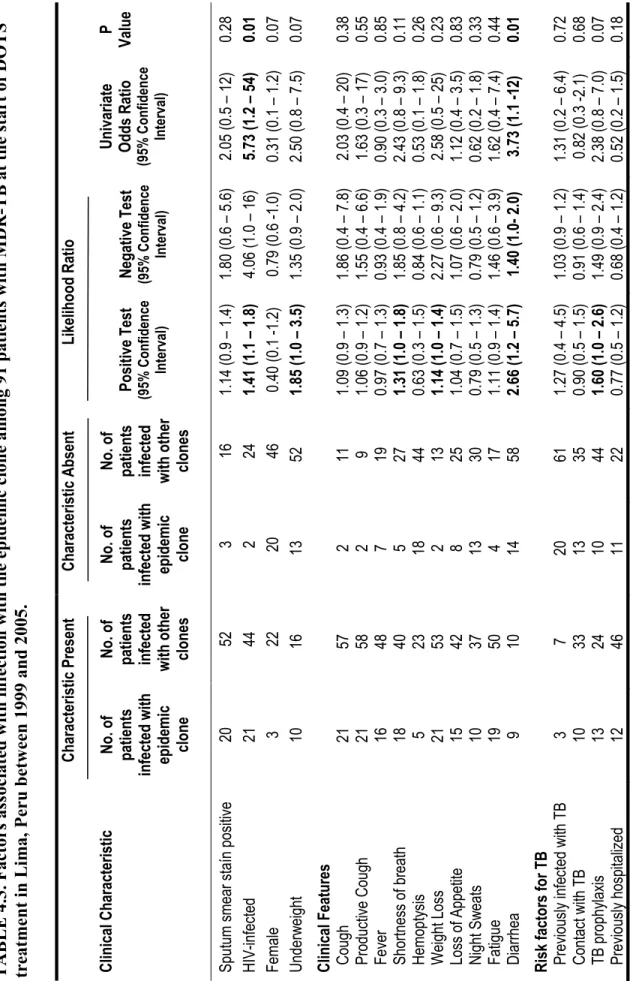
To appreciate the evolution of the Haarlem3 MDR-TB outbreak at the long-term, we assessed the clinical outcomes of patients for several years (2 to 8 years) beyond the 24-month
Overall, our study shows that lower CD4 cell counts led to a higher incidence rate of both AIDS-related and non-AIDS-related events. Several studies have also noted the
In short, to understand the transmission and contraction of HIV/AIDS in Africa, it is important to consider other contextual factors like political economy, poverty, gender,