HAL Id: hal-00296262
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00296262
Submitted on 21 Jun 2007
HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access
archive for the deposit and dissemination of
sci-entific research documents, whether they are
pub-lished or not. The documents may come from
teaching and research institutions in France or
abroad, or from public or private research centers.
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est
destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents
scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non,
émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de
recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires
publics ou privés.
Distribution of lead in single atmospheric particles
D. M. Murphy, P. K. Hudson, D. J. Cziczo, S. Gallavardin, K. D. Froyd, M.
V. Johnston, A. M. Middlebrook, M. S. Reinard, D. S. Thomson, T.
Thornberry, et al.
To cite this version:
D. M. Murphy, P. K. Hudson, D. J. Cziczo, S. Gallavardin, K. D. Froyd, et al.. Distribution of lead
in single atmospheric particles. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, European Geosciences Union,
2007, 7 (12), pp.3195-3210. �hal-00296262�
www.atmos-chem-phys.net/7/3195/2007/ © Author(s) 2007. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.
Chemistry
and Physics
Distribution of lead in single atmospheric particles
D. M. Murphy1, P. K. Hudson1,2,*, D. J. Cziczo4, S. Gallavardin4, K. D. Froyd1,2, M. V. Johnston5, A. M. Middlebrook1, M. S. Reinard5, D. S. Thomson1,2, T. Thornberry1,2, and A. S. Wexler6
1Earth System Research Laboratory, NOAA, Boulder, CO 80305, USA
2Cooperative Institute for Research in the Environmental Sciences, Boulder, CO 80309, USA *now at Department of Chemistry, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA 52242, USA
4Institute for Atmosphere and Climate Science, ETH, Zurich 8092, Switzerland 5Department of Chemistry, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716, USA
6Departments of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering, Civil and Environmental Engineering, and Land, Air and Water Resources, University of California, Davis, CA 95616, USA
Received: 14 February 2007 – Published in Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss.: 13 March 2007 Revised: 23 May 2007 – Accepted: 23 May 2007 – Published: 21 June 2007
Abstract. Three independent single particle mass spectrom-eters measured Pb in individual aerosol particles. These data provide unprecedented sensitivity and statistical significance for the measurement of Pb in single particles. This paper ex-plores the reasons for the frequency of Pb in fine particles now that most gasoline is unleaded. Trace amounts of Pb were found in 5 to 25% of 250 to 3000 nm diameter parti-cles sampled by both aircraft and surface instruments in the eastern and western United States. Over 5% of particles at a mountain site in Switzerland contained Pb. Particles smaller than 100 nm with high Pb content were also observed by an instrument that was only operated in urban areas. Lead was found on all types of particles, including Pb present on biomass burning particles from remote fires. Less common particles with high Pb contents contributed a majority of the total amount of Pb. Single particles with high Pb content of-ten also contained alkali metals, Zn, Cu, Sn, As, and Sb. The association of Pb with Zn and other metals is also found in IMPROVE network filter data from surface sites. Sources of airborne Pb in the United States are reviewed for consistency with these data. The frequent appearance of trace Pb is con-sistent with widespread emissions of fine Pb particles from combustion sources followed by coagulation with larger par-ticles during long-range transport. Industrial sources that di-rectly emit Pb-rich particles also contribute to the observa-tions. Clean regions of the western United States show some transport of Pb from Asia but most Pb over the United States comes from North American sources. Resuspension of Pb from soil contaminated by the years of leaded gasoline was not directly apparent.
Correspondence to: D. M. Murphy
(daniel.m.murphy@noaa.gov)
1 Introduction
Lead (Pb) is a highly toxic metal with wide industrial uses. There was widespread lead pollution during the last cen-tury and even extending back to ancient civilizations. Lead pollution is so widespread that there is essentially no sur-face soil that is uncontaminated with Pb (Shotyk and Le Roux, 2005). There is extensive literature on lead pollu-tion and on airborne lead in particular. The nearly world-wide elimination of leaded gasoline has drastically changed the sources and fluxes of Pb. For example, airborne lead in the United States has decreased by a factor of 20 or more since 1980 (EPA, 2003). Airborne Pb in Shanghai dropped from about 500 to 200 ng m−3 after the phaseout of leaded gasoline there (Tan et al., 2006). The progression from the years of leaded gasoline can also be measured using isotopic signatures (e.g. Widory et al., 2004). Therefore, much of the older literature on airborne Pb is (fortunately) not very relevant to today’s atmosphere. Despite the large decreases in emissions, there are still substantial sources of Pb pol-lution. For example, the flux of Pb to the arctic is still dominated by anthropogenic inputs (Shotyk et al., 2005). Airborne Pb concentrations can still exceed 1 µg m−3 near point sources such as the smelter in Herculaneum, Missouri (http://www.dnr.mo.gov/env/esp/aqm/herculaneum.htm).
Lead and its common sulfur and oxygen compounds are solids at room temperature. Therefore, airborne Pb is pre-dominately particulate, with at most a few percent present as gas phase alkyl compounds (Wang et al., 1997; Shotyk and Le Roux, 2005). In most places most of the Pb is on parti-cles smaller than 1 µm diameter. This was the case in Ghent, Belgium (Maenhaut et al., 2002), Budapest, Hungary (Salma et al., 2002), Gosan, Korea (Han et al., 2005), and Seville,
Aviation gasoline (1999 NEI) Electric utility (mostly coal) Iron and steel smelting and industry Lead & nonferrous smelting and industry Lead, zinc, silver, gold ores Military and ammunition Refuse incineration and related Pulp mills and paper products Cement, lime, concrete products Other point sources Area emissions (1999 NEI)
600 500 400 300 200 100 0 US Pb air emissions (103 kg yr-1)
Figure 1. United States National Emission Inventory (NEI) for Pb by category. The
Fig. 1. United States National Emission Inventory (NEI) for Pb by
category. The point sources are from the preliminary 2002 inven-tory.
Spain (Alvarez et al., 2004), with somewhat larger sizes recorded in Mumbai (Gokhale and Patil, 2004). A multi-stage impactor in Atlanta recorded the highest Pb concentra-tions on stage 8, which samples below 100 nm (Solomon et al., 2003). An exception appears to be Zurich, where the ma-jority of Pb was in particles larger than 2.5 µm (Bukowiecki et al., 2005). An interesting progression was observed in the Los Angeles area. Lead was mostly in particles smaller than 350 nm in an industrial area in western Los Angeles but had a bimodal size distribution in Riverside, where there was a substantial amount in sizes larger than 1 µm for which crustal elements predominated (Singh et al., 2002). This may rep-resent resuspension of the lead deposited to the urban area over decades. The presence of Pb on sub-micrometer parti-cles means that it can be efficiently inhaled.
The above size distributions were generally obtained with multi-stage impactors that respond to the aerodynamic diam-eter of the particles. For particles much larger than the mean free path in air, the aerodynamic diameter is proportional to the square root of the density. For particles much smaller than the mean free path in air, the vacuum aerodynamic di-ameter is proportional to density. As will be shown below, Pb in sub-micrometer particles is present both as small amounts on a large number of particles and a few particles rich in Pb. Because of the high density of Pb and its compounds (usu-ally >6 g cm−3) as well as other metals usually associated
with Pb, those particles rich in Pb will usually have geomet-ric diameters considerably smaller than their aerodynamic di-ameters.
Figure 1 shows some broad categories combined from more specific point sources in a preliminary 2002 United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) National Emissions Inventory. Area and aviation (non-road) emissions were taken from the 1999 county summary inventory because they were not yet available in the preliminary 2002 inven-tory. About the top 50 point sources were manually checked against the EPA Toxic Release Inventory. In many cases the
Toxic Release Inventory was more plausible. For example, the largest source in the preliminary 2002 point source inven-tory is a small foundry (90 employees) with listed air emis-sions of 115 000 kg per year in the point source inventory and 5 kg per year in the Toxic Release Inventory. The largest point source in the United States, the Doe Run lead smelter, was listed as about 24 kg per year of airborne emissions in the point source inventory and over 45 000 kg per year in the Toxic Release Inventory. Making corrections such as this re-sulted in a net reduction of about one third in total emissions. Many errors probably remain. In particular, large emissions near Cleveland come from area sources that are difficult to explain. It is also not clear why the major cities in California have much larger area emissions than other cities. Figure 2 shows the geographical distribution of sources in the United States.
According to the EPA inventories, aviation gasoline is the largest single source of airborne Pb emissions in the United States. Leaded aviation gasoline (as opposed to jet fuel) is used in small piston aircraft. A wide variety of other sources, many also from fuels, make significant contributions to air-borne Pb. Smelters, foundries, and coal combustion all also emit significant amounts of Pb and other trace metals. Com-bustion often generates small particles with relatively volatile metals partitioning to the small particles whereas refractory elements such as silicon partition to larger particles (Flagan and Taylor, 1981).
About 1×1012kg of coal were burned in the U.S. in 2004 (F. Freme, U.S. Energy Information Administration, U.S. Coal Supply and Demand: 2004 Review; http://tonto.eia.doe. gov/FTPROOT/features/feature04.pdf). Coal often contains 5 to 35 parts per million (ppm) of Pb (Raask, 1985; Linak and Wendt, 1993). Using 20 ppm, there is about 20 000 tons per year of Pb in the coal burned in the United States. The EPA emissions inventory estimates that about 1% of this is emitted to the air. The volatility of Pb and its compounds such as PbO lead to its concentration in the sub-micrometer fraction of particles emitted from coal combustion and in-cineration (Davison et al., 1974; Linak and Wendt, 1993). Sub-micrometer particles are less efficiently removed by par-ticulate emission control devices than larger particles. Hence a larger fraction could actually be emitted. Given the large amount of Pb in coal (Table 1), the airborne fraction of Pb from coal is crucial to the budget of atmospheric Pb.
Lead is also emitted by combustion of liquid fuels con-taining trace amounts of Pb. Such sources would be widely dispersed and produce fine particles. Table 1 shows an analy-sis of the Pb mass budget of several fuels in the United States. The Pb content of fuels varies widely and for some fuels there are only one or two samples in the open literature. Trace met-als are mostly in the asphaltenic fraction of crude oil (Drey-fus et al., 2005). The refining process concentrates metals into the heavy fractions such as heavy oil, asphalt, and coke, whereas gasoline and light fuels contain less Pb than crude oil. On a mass basis, therefore, the combustion of residual
55 50 45 40 35 30 25 120 110 100 90 80 70
Symbol size proportional to ln(emissions) EPA preliminary 2002 NEI point sources & EPA 1999 NEI aviation and area sources put on 1.5x1.5 grid
Environment Canada 2004 Inventory air emissions for 10 large point sources
0.1 to 5 metric tons yr-1
20 60
Figure 2. Lead emissions from the EPA 1999 and 2002 National Emissions inventories
Fig. 2. Lead emissions from the EPA 1999 and 2002 National Emissions inventories and the 2004 Environment Canada National Pollutant
Release Inventory on-line search. See text for modifications and error corrections to the inventories. To compensate for the different sizes of counties in the United States, county level data have been combined on a 1.5 by 1.5 degree grid. Each point is plotted at the weighted average position of the sources within the grid box. This helps properly position large point sources. Points less than 100 kg yr−1are not plotted. These Canadian data do not include all the sources that are in the EPA database. Blue asterisks are selected IMPROVE network sites shown in Fig. 3.
oils may be a significant source of airborne Pb, depending on the fraction that is emitted to the air. We were unable to lo-cate firm numbers on this fraction. Used motor oil has a high enough Pb content to contribute to the overall amount of fuel Pb (Boughton and Horvath, 2004). A significant amount is burned in small space heaters with no emission controls.
The importance of industrial and coal combustion sources to present-day emissions of Pb has been shown by the cor-relation with other elements. Several other metals, including Zn, are also present in trace amounts in coal and other fuels and have similar volatility and condensation processes in hot exhaust gases. Lead was correlated with Zn in the northern Pacific (Narita et al., 1999). In Detroit, Pb was correlated with As and Se, suggesting a fossil fuel combustion source (Utsunomiya et al., 2004).
Figure 3 shows selected data from the Interagency Mon-itoring of Protected Visual Environments (IMPROVE) net-work of sampling sites (Malm et al., 1994). Data through 2004 are available at http://vista.cira.colostate.edu/improve/ Data/data.htm. Absolute amounts of Pb are much higher in the eastern United States than the western United States. The geographic distribution, with elevated concentrations at sites in Illinois, Ohio, and Pennsylvania, is reasonably con-sistent with the emissions pattern (Fig. 2). As discussed later, IMPROVE sites in the western U.S. have a springtime maximum that is probably due to transport from Asia (see
also K. Rahn’s web site http://karws.gso.uri.edu/IMPROVE/ Pbpage.html). The eastern sites either have little seasonal pattern or a winter maximum. The origin of this winter max-imum is not clear, especially since there is less general avia-tion in winter than in summer.
The lower panel of Fig. 3 shows the ratio of Pb to Zn at the same sites. The ratios for the central and eastern United States are quite consistently between 0.3 and 0.4. For com-parison, the Pb/Zn ratio in aviation gasoline is very large, emissions from major smelters range between about 0.01 and 5, in bulk coal the ratio is 0.1 to 0.75 (Raask, 1985; Linak and Wendt, 1993), and in used motor oil it is about 0.04 (Boughton and Horvath, 2004). The sites in the west-ern United States show a range between the eastwest-ern U.S. and values near 0.7. These higher ratios are discussed later in the context of transport from Asia.
2 Methods
This paper examines the distribution of Pb in single particles. The use of on-line laser ionization mass spectrometers pro-vides high sensitivity along with data on hundreds of thou-sands of particles.
Most of the data shown here are from the Particle Analysis by Laser Mass Spectrometry (PALMS) instrument (Thom-son et al., 2000). Air containing particles is brought through
Table 1. Estimated United States mass budgets for Pb in selected fuels and crude oil.
Fuel 2005 U.S.
con-sumption (Tg) Pb content (ppm by mass) Total Pb (103kg yr−1) Airborne fraction Airborne Pb (103kg yr−1)
References and notes
Coal 1020 5–35 20000 ∼0.01 ∼200 Raask (1985); Linak and Wendt
(1993). Airborne fraction inferred from Table 1.1–18 in EPA docu-ment AP-42.
Aviation gasoline 0.8 ∼750 575 >0.75 490
Gasoline 390 0.005 2 0.75 1.5 Heathcote et al. (2000)
A few samples in Iowa
Jet fuel 72 0.005–0.011 0.6 1 ? 0.6 Shumway (2000)
Distillate oil 201 0.015–0.040 4 Miller et al. (1996); Rising et
al. (2004)
Residual oil 50 2–21 100–>500 Bratzel and Chakrabarti (1972);
Miller et al. (1996). 21 ppm may not be representative if crude oil numbers are correct
Used oil 3 30–50 100 Boughton and Horvath (2004);
Vermont (1994).
Coke 20 ≥residual oil? >80 Much coke combustion probably
has emission controls.
Crude oil 744 0.032–0.97 25–700 – – Bratzel and Chakrabarti (1972);
Ali et al. (1983); Magaw et al. (1999); Dreyfus et al. (2005). Limited number of samples.
Fuel consumption figures from U.S. Department of Energy Energy Information Agency http://www.eia.doe.gov/emeu/aer/txt/ptb0511.html with unit conversion by author.
a vacuum interface. Particles that cross a continuous laser beam scatter light to trigger a pulsed 193 nm laser. The light pulse hits a particle and a complete mass spectrum is recorded using a time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Only par-ticles larger than about 200 nm are detected. The most impor-tant consequence here is that fresh combustion particles are often not measured. Only positive ion spectra are considered in this paper since Pb produces only positive ions.
Data are shown from the PALMS instrument during four field campaigns. In 1999, the instrument was at the EPA Su-persite in Atlanta. In 2002 and 2004, the instrument was flown on the NOAA P-3 aircraft. In spring 2002 the air-craft was based in Monterey, California and the data include flights both over the ocean and over land. One flight was dedicated to sampling the greater Los Angeles urban area. In summer 2004 the aircraft was based in Portsmouth, New Hampshire and flights were made over the eastern United States and Canada and nearby ocean. These flights included passes through the plumes from urban areas and major power plants. Some data are also included from descents into Hous-ton made when the instrument was on the WB-57F aircraft in 2006. An overview of the overall particle chemistry observed during these missions is given in Murphy et al. (2006).
Between 1999 and 2004, a number of pertinent changes were made to the PALMS instrument. The instrument in At-lanta was a separate instrument from the aircraft version. It had a capillary inlet that was biased to sampling larger parti-cles. The aircraft instrument has an additional turn in the drift tube of the mass spectrometer to fit it in the airplane (Thom-son et al., 2000). Ion losses in this bend limit the sensitivity of the aircraft instrument to about a factor of two worse than the ground instrument. Furthermore, the instrument in the 2002 flights was tuned for minimum background instead of maximum sensitivity, with an additional ion loss of perhaps a factor of five. The 2004 and later data include the aerody-namic diameter of most of the particles. These aerodyaerody-namic diameters are measured at a pressure where the mean free path is larger than the particles, leading to a linear rather than square root dependence on particle density.
The Aerosol Time of Flight Mass Spectrometer (ATOFMS) is a commercially available instrument (Model 3800, TSI, Shoreview, MN) described by Gard et al. (1997). The operating principles of this instrument are much the same as for PALMS. Particles and gas enter the instrument through an aerodynamic lens optimized for diameters between 300 and 1000 nm. Gas-phase molecules
are then removed via differential pumping stages. Particle transmission falls off to either side of these limits such that no particles were observed smaller than 250 nm or larger than 2500 nm during these studies. Particles are detected and optically sized using dual continuous lasers. Unlike the PALMS instrument, aerosol ablation and ionization is ac-complished with a pulsed 266 nm laser. Dual time-of-flight tubes allow for both positive and negative mass spectra being recorded for each particle. While Pb is only observed as a positive ion, associations with negative ions can thus be made.
An ATOFMS was deployed to the Jungfraujoch Research Station for the first two weeks of March 2006 as part of the Fifth Cloud and Aerosol Characterization Experiment in the Free Troposphere (CLACE 5). Located in the Swiss Alps at 3580 m above sea level, the Jungfraujoch allows access to mid-tropospheric air with minimal local aerosol sources (Baltensperger et al., 1997). As such, the data presented here are probably most comparable to the PALMS aircraft data. The focus of the deployment of the ATOFMS during CLACE 5 was the characterization of the chemical compo-sition of ice nuclei within mixed-phase clouds. The major-ity of observation time was therefore spent analyzing cloud ice residue. Every two hours from 08:00 through 18:00 local time several thousand unactivated particles were analyzed for comparison to the subset that nucleated ice. An “interstitial inlet” with a 2.5 µm cutpoint was used for sampling. When clouds were not present the background aerosol was sampled in the same manner and through the same inlet. The data described here are restricted to unactivated particles during cloud free periods.
The Rapid Single particle Mass Spectrometer (RSMS) performs size-selective single particle analysis between about 30 and 1200 nm diameter. Particles are drawn into the instrument through a size selective inlet (Mallina et al., 2000). The vacuum aerodynamic diameter of particles trans-mitted to the mass spectrometer source region is determined by the pressure at a critical orifice. The pressure is set by a flow-limiting orifice located upstream of the critical orifice. A valve switches between a bank of orifices to allow rapid changing of the selected particle size. Single particle mea-surements at the selected size are performed by free-firing a pulsed 193 nm laser beam through the source region.
Since the particle size is actively selected and the laser is free-fired, single particle mass spectra can be obtained for particle sizes below the minimum size that can be detected by light scattering. The disadvantage, though, is that the anal-ysis rate for particles large enough to be detected by light scattering is lower for RSMS than PALMS or the ATOFMS. To help compensate for the low analysis rate, the mass ana-lyzer in the RSMS instrument contains an elongated source region, linear flight tube and collinear geometry between the particle and laser beams to maximize the interaction region between the laser and particle beams. The linear flight tube yields lower mass resolution than a reflectron design. Further
4 3 2 1 0 F in e m o d e Pb (n g m -3) 12 10 8 6 4 2 12 10 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 Month of year Mauna Loa Mt Zirkel CO Denali AK Mammoth Cave KY Quaker City OH Everglades FL Bondville IL Isle Royale MI Great Smoky Mtn TN El Dorado MO Arendtsville PA Shenendoah VA Acadia ME Okefenokee GA Mt Rainier WA Breton LA Pt Reyes CA Dolly Sods WV San Gorgonio CA 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 F in e m o d e Pb /Z n 12 10 8 6 4 2 12 10 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 Month of year Mt Zirkel CO Denali AK Mammoth Cave KY Quaker City OH Everglades FL Bondville IL Isle Royale MI Great Smoky Mtn TN El Dorado MOArendtsville PA Shenendoah VA Acadia ME Okefenokee GA Mt Rainier WA Breton LA Pt Reyes CA Dolly Sods WV Mauna Loa San Gorgonio CA
Fig. 3. Seasonal patterns for fine mode Pb and Zn at several
IM-PROVE sampling sites, roughly grouped by western, central, and eastern United States. Dashed lines are only to distinguish between lines on the graph. These are averages for 1999 to 2004, although some of these stations have shorter records.
discussion of particle analysis by RSMS is given by Lake et al. (2003).
Data from five RSMS measurement campaigns are dis-cussed including August 1999 in Atlanta, Georgia (Rhoads et al., 2003), August–September 2000 in Houston, Texas (Phares et al., 2003), September 2002–August 2003 in Pitts-burgh, Pennsylvania (Bein et al., 2005), March–December 2003 in Baltimore, Maryland (Tolocka et al., 2005), and May 2005–February 2006 in Wilmington, Delaware. Single par-ticle measurements were supplemented at each of the mea-surement sites with concurrent meteorology data and various gas phase and particulate concentrations.
Although isotopic information on Pb would be useful in constraining sources, the time-of-flight mass spectrometers used in all three instruments are not designed for isotopic analysis. Space charge effects and the high energy imparted by laser ionization mean that the Pb peaks are often not suffi-ciently well resolved for the very accurate peak integrations required for isotopic analysis.
4 0.001 2 4 0.01 2 4 0.1 2 D e te c to r s ig n a l (m A ) 200 150 100 50 0 Ion mass/charge 208 Pb 56 Fe 7 Li 204 Pb Na 20020425 19:24 34.8 N; 119.2 W 4849 m;139 ppb CO 69 Ga NO 39 K 71 Ga 47 NH4 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 D e te c to r s ig n a l (m A ) 200 150 100 50 0 Ion mass/charge 208 Pb 39 K 118 Sn 12 C 204 Pb 24 Mg; C2 20040720 18:00 41.5 N; 74.7 W 1065 m; 173 ppb CO 0.68 µm 121 Sb 64 Zn 66 Zn 75 As SO 41 K AsO 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 D e te c to r s ig n a l (m A ) 200 150 100 50 0 Ion mass/charge 208 Pb 39 K SO 12 C 206 Pb C2 20040709 20:43 52.6 N; 64.4 W 4196 m; 329 ppb CO 0.69 µm CO 85 Rb 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 D e te c to r s ig n a l (m A ) 200 150 100 50 0 Ion mass/charge 208 Pb 39 K H3SO4 HSO2 SO 12 C 204 Pb NO 20040705 20:47 38.2 N; 69.6 W 2403 m; 97 ppb CO 0.92 µm HSO3 (a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 4. Examples of mass spectra of single particles containing Pb. (a) A common
Fig. 4. Examples of mass spectra of single particles containing Pb. (a) A common mixed sulfate-organic particle. (b) A particle in a
biomass burning plume over Canada. (c) A particle with other met-als. The association of Pb with one or more of K, Zn, Sn, and Sb was common. (d) A Pb-Ga particle from trans-Pacific flow west of California. Gallium is quite rare in atmospheric particles, but the isotopic pattern is definitive.
3 Results
3.1 PALMS
Lead was present both as a small signal in the mass spectra of many particles and as a large signal in a few mass spectra. Figure 4 shows some mass spectra of particles with Pb. Be-sides the Mg, K, Zn, As, Sn, and Sb shown (Fig. 4c), Cu and Fe were also common in Pb-rich particles, with occasional Li, Mn, and Ba. The gallium shown in Fig. 4d was found in 7 spectra, of which 6 were west of or near the California coast.
Figure 5 presents histograms of the frequency of different size peaks at a mass to charge ratio of 208, which is almost always208Pb. There are few other ions with the same masses as Pb. Because the Pb peaks at mass to charge ratios of 206 and 207 were not always well resolved, only mass 208 is used in Fig. 5 as a measure of Pb. Except for very small Pb signals for which the frequency depends on the varying detection limit, the histograms for Atlanta and aircraft flights over the eastern U.S. are very similar. This is consistent with
a regional source in Atlanta without any obvious dependence on wind direction (Lee et al., 2002). The data for the western U.S. show relatively higher concentrations for particles with moderate amounts of Pb.
The data sorted by portion of the western U.S. (Fig. 5b) provide some insight into the relatively higher concentra-tions. The Los Angeles area had slightly less frequent Pb signals when expressed as a fraction of the number of par-ticles. The aerosol number concentration in Los Angeles is much larger than offshore, so there was more Pb on an ab-solute basis. The relative concentrations were lower because of dilution by ammonium nitrate and other abundant species. Figure 5b also shows data from 2004 sorted by vacuum aero-dynamic diameter. The larger particles were more likely to have large Pb signals. Note that a particle large enough to be detected optically (larger than 200 or 300 nm) with a high lead content is likely to have a vacuum aerodynamic diame-ter greadiame-ter than 1 µm. There was almost no size dependence to the frequency of particles with smaller Pb content.
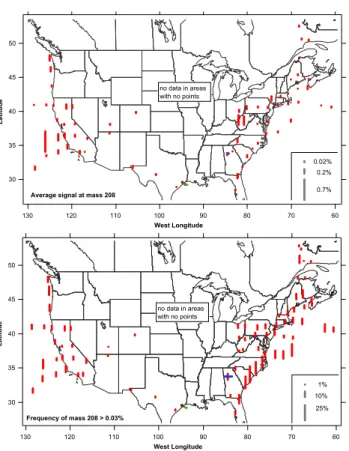
Figure 6 shows the geographic distribution of the average 208Pb signal and the frequency with which208Pb was more than 0.03% (the limit of consistent detection) of the ion cur-rent in each mass spectrum. The average signal is affected by those particles with high Pb content, such as 4c and 4d. In interpreting the average 208Pb signal it must be remem-bered that this is a relative measure. Considering the total amount of aerosol present, the absolute concentrations of Pb are higher in the northeastern United States than off the Cal-ifornia coast.
The maximum off California is discussed below under Asian transport. The other maximum in the average Pb sig-nal was in the Ohio River valley. The airplane spent some time there intentionally flying through power plant plumes. However, on a fine scale the average Pb in the mass spectra were only weakly positively correlated with gas phase mea-surements of SO2and the frequency of Pb was uncorrelated with SO2, so it is unclear if this maximum is due to power plant plumes or other emissions in this industrialized region. Many of the Pb-rich particles also contained Zn, as in Fig. 4c. The frequency of particles with measurable Pb was more uniform than the average signal. About 10% of all par-ticles sampled above North America contained measurable Pb. Since many mass spectra had Pb signals near the detection limit (Fig. 4a), it is likely that a better detec-tion limit would show an even higher frequency of Pb. The overall frequency for the aircraft data is consistent with that reported for PALMS data in Atlanta (Lee et al., 2002). The somewhat higher frequencies along the North and South Carolina coasts are from one flight. For that flight leg, the surface influence parameter calculated by the FLEXPART back trajectory model (Stohl et al., 2005) shows a significant contribution from large source regions in Arizona, Arkansas and southern Illinois and Missouri (Fig. 2 and http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/7/3195/2007/ acp-7-3195-2007-supplement.pdf).
10-6 2 4 10-5 2 4 10-4 2 4 10-3 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
Mass 208 (fraction of total ion current)
10-6 10-5 10-4 10-3 R e la ti v e c o n tr ib u ti o n to to ta l s ig n a l a t m a s s 2 0 8 2002 over land 2002 over Pacific Ocean 2002 Los Angeles region
2004 Eastern US < 1 µm 2004 Eastern US > 1 µm 1999 Atlanta all sizes
0.0001 2 4 6 8 0.001 2 4 6 8 0.01 2 4 6 8 0.1 F ra c ti o n o f m a s s s p e c tr a 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
Mass 208 (fraction of total ion current)
1999 Atlanta ground 2002 Western US airborne 2004 Eastern US airborne 2006 Jungfraujoch (ATOFMS)
(a) (b)
Fig. 5. Histograms of the size of208Pb peak in individual particles. In (a), the deviations below a mass 208 fraction of 0.001 are mostly
due to variations in signal-to-noise. Such small peaks often fell below the detection limit. The instrument in Atlanta had the largest absolute signals and that in 2002 the smallest. Panel (b) shows weighted histograms, or the histogram with the frequency multiplied by the midpoint of each bin. This shows the relative contribution to the average total signal. The data are also further broken into regions or sizes. The size cut for the 2004 data is by vacuum aerodynamic diameter. All data have been restricted to relative humidity less than 98% and the airborne data are restricted to altitudes above 150 m to exclude final approaches to airports and some flight segments in the marine boundary layer. See Fig. 6 for more detailed locations.
The vertical profiles of the average208Pb signal had little structure (Fig. 7). The decrease in the 2002 data near the surface is caused almost entirely by flight legs in the ma-rine boundary layer west of California. Sea salt particles in the marine boundary layer contained almost no Pb, reduc-ing its relative concentration. The peak in the 2002 data at just under 5 km is due to the influence of the flight leg that produced the large point on Fig. 6 off the coast of Califor-nia near 36◦N. Vertical profiles of the frequency of particles containing Pb also had little structure.
3.2 Results: ATOFMS
During the CLACE 5 campaign conducted at the Jungfrau-joch Research Station, about 5% of the analyzed aerosol par-ticles were identified as containing lead. Lead was identi-fied if the signal at the dominant isotope,208Pb, was larger than an arbitrary threshold set at twice the level of the spec-tra noise. This threshold value represented about 0.05% of the total signal in an average spectrum. At this level only the208Pb isotope was identifiable. Other isotopes (206Pb and 207Pb at 24.1% and 22.1%, respectively) became apparent when the relative208Pb signal was greater than about 0.25%. In no case was the204Pb isotope (1.4%) clearly identified. As is the case for the PALMS measurements, the 5% of spectra with Pb likely represents a lower limit of the fraction of par-ticles that contained lead since detection appears limited by signal.
Of the particles that had detectable lead, 25% had a rela-tive signal greater than 5% of the total spectrum. A typical
example of such a “high lead” particle is shown in Fig. 8a. Whereas spectra for typical ambient aerosols predominantly contained sulfate and organics fragments, Pb-rich particles always contained one or more of the following positive ions: Na+, Mg+, Al+, K+, Fe+, Zn+, Mo+, Ag+, Ba+. These ions were otherwise only observed in <5% of spectra with-out lead, with the exception of potassium which is commonly associated with biomass burning and was found in about 40% of the positive spectra (Hudson et al., 2004). Sulfate frag-ments were present in 99% of the negative spectra associ-ated with high Pb particles and 50% also contained NO−2 and NO−
3. Approximately 80% contained positive and/or nega-tive polarity organic fragments. The average aerodynamic diameter of the Pb-rich particles was larger than the back-ground aerosol, which had a peak at 350 nm. Instead, the size distribution for high lead particles peaked at 500 nm and none were observed with a diameter less than 300 nm. If the Pb-rich particles had high density then this means that most probable size was near or below the size limit of detection in ATOFMS.
The spectra of “low lead” particles, one of which is shown in Fig. 8b, were much more varied. About 40% contained the aforementioned metals as well as Ga+, Ge+ and Sn+. The remainder appeared in spectra that were otherwise in-distinguishable from those typically observed (i.e., sulfate and organics fragments commonly with K+ and nitrates). In addition, the aerodynamic diameters of the low lead par-ticles were indistinguishable from that of the background aerosol. Lead was found down to the smallest detected par-ticles, about 250 nm. It is worth mentioning that Pb was not
50 45 40 35 30 L a ti tu d e 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 West Longitude 1% 10% 25% Frequency of mass 208 > 0.03% no data in areas with no points 50 45 40 35 30 L a ti tu d e 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 West Longitude 0.02% 0.2% 0.7%
Average signal at mass 208
no data in areas with no points
Fig. 6. Geographical distribution of the average PALMS signal at
mass 208, which is almost always208Pb, along with the frequency of that peak in single particles. The data were binned into 2 to 2.5 degree boxes with the points plotted where taken – if the aircraft only flew through a corner of a grid box the point is plotted at the corner. There are a few more points plotted in the lower panel be-cause at least 150 mass spectra in a grid box were required to de-fine a frequency whereas at least 400 were required for the average, which can be affected by one particle with a large Pb signal. Mass spectra with a signal to noise less than about 1000 were not included in the frequency calculation. Aircraft data are from above 150 m al-titude and less than 98% relative humidity. The horizontal bars near Atlanta and Houston are from the 1999 Supersite and 2006 NASA WB-57F descents, respectively.
found on any of the elemental carbon particles, about 4% of the total number.
3.3 Results: RSMS
Single particle measurements made by the RSMS instrument in five eastern U.S. cities show that Pb is ubiquitous in the urban environment and provide insight into possible sources. These measurements were made across a size range of about 30 to 1200 nm in vacuum aerodynamic diameter. The size range differed slightly for the different measurement sites.
The fraction of particles analyzed by RSMS that contained measurable Pb ranged from about 0.5% in Atlanta (Rhoads et al., 2003) and Houston (Phares et al., 2003) to greater than
6000 4000 2000 0 A lti tu d e (m ) 0.005 0.004 0.003 0.002 0.001 0.000
Average mass 208 signal 2002 Western US 2004 Eastern US 2006 WB-57F Houston
Figure 7. Average vertical profiles of the fraction of total ions at m
Fig. 7. Average vertical profiles of the fraction of total ions at mass
208 for three missions. The only statistically significant variations are the decrease near the surface and the peak in the 2002 profile at 5 km.
3% in Pittsburgh (Bein et al., 2005) and Baltimore (Tolocka et al., 2005). Relative to the PALMS and ATOFMS measure-ments above, the number of particles analyzed with RSMS that contain a detectable amount of Pb is likely to be smaller because the dynamic range of signal intensity measurement is lower for RSMS than PALMS. Therefore, it is probable that trace levels of Pb in many particles were not detected with RSMS. In the RSMS measurements, particles contain-ing Pb were often detected in “bursts” that often correlated strongly with wind direction and the presence of other met-als, consistent with point source plumes that passed over the measurement site. Plots of dN/dlogdva vs. dvatypically reached a maximum around 200 nm with a peak value of 10– 100 cm−3Pb-containing particles averaged over an extended period of time (Tolocka et al., 2004).
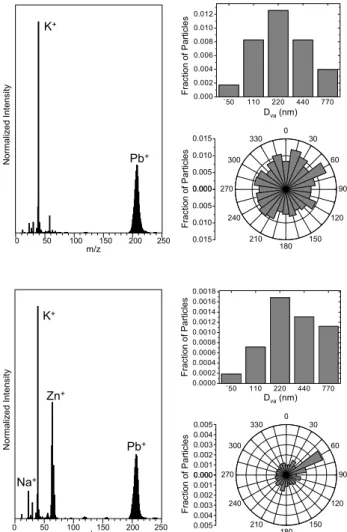
An example of Pb in urban aerosol is shown in Fig. 9 for RSMS measurements in 2005 at Wilmington, Delaware. Two main classes of particles containing Pb were found in the dataset. The first, shown in Fig. 9a, shows K and Pb as dominant features in the mass spectrum. Other ions sug-gest the presence of Na, elemental carbon, organic carbon and possibly amines. This particle class encompassed about 1% of the particles analyzed. The number concentration reached a maximum around 200 nm although many parti-cles were observed at the smallest size analyzed in this ex-periment (50 nm). It should be noted that these are vacuum
Fig. 8. Examples of ATOFMS mass spectra of single particles
con-taining lead at the Jungfraujoch Research Station. (a) A particle with >5% of the relative signal from lead and containing several commonly associated metals. The negative spectrum contains frag-ments from sulfates and nitrates as well as Cl−. The inset shows the
clear isotopic distribution of lead. (b) A particle with K+and
sul-fate and organic fragments. Other than a lead peak with <1% of the relative signal, this particle is indistinguishable from background aerosols of probable biomass origin with added sulfate.
aerodynamic diameters and the physical diameters are likely to be a factor of 4 or more smaller depending on composi-tion and density. This means that most of the Pb-rich par-ticles measured by RSMS would be too small for detection by PALMS or ATOFMS. The wind rose plot for this particle class is diffuse, which suggests multiple sources. In general, industrial sites (steel processing, manufacturing, power gen-eration, refining) are located from the northeast to the south-west of the site, while residential and traffic (Interstate 95) sources are prevalent in the north and west.
A second, minor class is shown in Fig. 9b, which en-compassed about 0.1% of the particles analyzed. Domi-nant features in the mass spectrum include Na, K, Zn, and Pb with smaller signals from Fe, elemental carbon and or-ganic carbon. As above, the number concentration reached a maximum around 200 nm, although the size distribution was skewed toward larger particles suggesting that the tail of a coarse mode was also observed. The wind rose plot
`50 110 220 440 770 0.000 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.010 0.012 K+ Pb+ 0.000 0.005 0.010 0.015 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 0.000 0.005 0.010 0.015 m/z 0 50 100 150 200 250 N o rm a liz e d I n te n s it y F ra ct io n o f P a rt ic le s F ra c ti o n o f P a rt ic le s Dva(nm) `50 110 220 440 770 0.0000 0.0002 0.0004 0.0006 0.0008 0.0010 0.0012 0.0014 0.0016 0.0018 K+ Zn+ Pb+ 0.000 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.004 0.005 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 0.000 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.004 0.005 Na+ m/z 0 50 100 150 200 250 N o rma liz e d I n te n s it y Fra c ti o n o f P a rt ic le s F ra c ti o n o f Pa rt icl e s Dva(nm)
Fig. 9. Major particle classes in Wilmington, Delaware that contain
Pb: a K and Pb class and a Na, K, Zn, and Pb class. The class the lower panel appears to be emitted from a steel processing facility. Stack sampling at the facility confirms the source of these particles.
shows a clear feature at 60◦, which is the direction of a steel manufacturing and processing facility located about 10 km from the measurement site. In a separate experiment, aerosol was sampled directly from the emission stack of this facil-ity and analyzed by RSMS. About 4% of the particles in the stack sample gave the same mass spectrum as that in Fig. 9b. (The remaining particle spectra, perhaps formed by hot vapor condensation during the sampling process, were organic/elemental carbon in character and contained no sig-nificant metals.) The stack measurements confirm the inter-pretation of the ambient data in Fig. 9b that these particles were emitted from the steel facility.
The data in Fig. 9 are also characteristic of measurements in the other four cities. Particles containing Pb almost always contained K and often Zn as well. Many of these particles were internally mixed, showing mass spectral signatures for organic carbon, nitrate, and/or sulfate. The size distribution
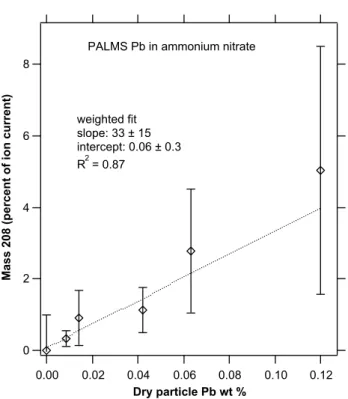
8 6 4 2 0 Ma s s 2 0 8 (p e rc e n t o f io n c u rr e n t) 0.12 0.10 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0.00 Dry particle Pb wt % weighted fit slope: 33 ± 15 intercept: 0.06 ± 0.3 R2 = 0.87
PALMS Pb in ammonium nitrate
Figure 10. Laboratory calibration of Pb in ammonium nitrate particles generated by
)
Fig. 10. Laboratory calibration of Pb in ammonium nitrate particles
generated by nebulizing a solution.
usually peaked around 200 nm, although the number con-centration remained large at smaller sizes (Tolocka et al., 2004). A significant wind directionality was also commonly observed for Pb particles containing a large combination of metals. In Pittsburgh, a particle class containing Na, K, Zn and Pb, though in different proportions from those in Fig. 9b, was attributed to a zinc processing facility (Bein et al., 2005). A transient plume of particles containing Na, Si, K, Ca, Fe, Ga and Pb was attributed to coal combustion (Bein et al., 2006). Mass concentrations of Pb obtained from MOUDI samples at the Pittsburgh site showed a maximum around 200 nm along with evidence for the tail of a coarse mode near 1000 nm. The coarse mode appeared to be dominated by multi-metal classes, while the fine mode contained mostly particles having K, Pb and secondary aerosol components as the dominant species. Reconciliation of RSMS data with mass concentrations from MOUDI samples suggest density and shape factors of 3.0 g cm−3and 1.4 for Na-K-Zn-Pb par-ticles, and 3.9 g cm−3and 1.5 for Na-Si-K-Ca-Fe-Ga-Pb par-ticles. During plume events, the 24 h average Pb concentra-tion (PM1.2) could reach 0.5 µg m−3(Bein et al., 2006).
4 Discussion
4.1 Calibration
It is difficult to convert the ion fractions shown in the pre-ceding figures into absolute concentrations of Pb. The con-version depends on both the ionization efficiency of Pb and the size range and sampling biases of the mass spectrometer. Figure 10 shows a PALMS calibration for Pb in ammonium nitrate particles that also contained trace amounts of added Fe. The linearity is good for laser ionization. The slope of about 33 shows that PALMS is much more sensitive to Pb than ammonium nitrate. The high sensitivity to Pb is similar to results for other metals such as Fe in sulfuric acid (Cziczo et al., 2001). Mixed solutions with both Pb and Fe in ammo-nium nitrate showed similar sensitivities for Pb and Fe.
Separate calibrations for Pb were performed for ATOFMS. The ATOFMS mass scale was calibrated on a daily basis dur-ing CLACE 5 usdur-ing a standard solution of 900 micrograms per milliliter of six components (Li, Na, K, V, Ba, and Pb) in a 5% solution of HNO3balanced by distilled, deionized wa-ter (i.e., ∼0.02 wt% lead with respect to HNO3). Aerosols atomized from this solution were passed through a diffusion dryer at 30% relative humidity and size selected with a dif-ferential mobility analyzer at 0.5 µm. The dominant positive ions were K, V, and VO, each of which had relative peak areas of 10–20%. Li and Na ions had relative areas on the or-der of 5–10% followed by Ba and BaO with approximately 1%. Lead ions were observed in about half of spectra with an average relative area of 0.5%, giving a relative sensitivity of Pb to nitric acid of about 12. This is a factor of 3 lower than found for lead in ammonium nitrate for PALMS, proba-bly because the easily ionized alkali metals in the ATOFMS calibration mixture reduce the relative contribution from Pb as well as the different ionization laser wavelength.
It should not be assumed that the average Pb signals shown, for example, in Fig. 6a should be divided by the PALMS calibration slope of about 33 to obtain Pb mass frac-tions. First, the relative sensitivity to ammonium nitrate is a measure not only of how easily Pb is ionized but how dif-ficult it is to ionize ammonium nitrate. A Pb calibration in a more easily ionized matrix such as sea salt would have a much smaller slope. Many particles with Pb also contained K, which could considerably change the relative sensitivity. A relative sensitivity for realistic atmospheric particles could be much lower, perhaps 5 to 10.
Second, a pure Pb particle cannot produce more than 100% Pb ions. A simple algebraic expression with the de-sired asymptotes of a relative sensitivity of S at low concen-tration and 100% ion yield for a pure substance is
C = x/(x + S(1 − x))
where x is an ion fraction, C is the fractional concentration, and S is the relative sensitivity. For S greater than 1, this
has the effect of stretching the x-axis on a histogram such as Fig. 5.
4.2 Contamination
Contamination is always a concern when measuring trace metals. For example, sample contamination caused early work to overestimate Pb in water samples (Nriagu et al., 1993). There are several reasons why the data here should be representative of the actual distribution of Pb on particles. Laser ionization done in vacuum inherently has essentially zero background for Pb. The only concern is if Pb parti-cles are being generated in the inlet or if ambient partiparti-cles are acquiring Pb by bouncing off an inlet wall. However, laboratory particles without added Pb do not give any Pb sig-nal, showing that the vacuum inlet is not contributing any Pb signal. The intercept on Fig. 11 also shows that fresh biomass burning particles are measured with essentially zero Pb. There are no Pb-containing materials such as solder in any of inlets for the data in this paper. There are four com-pletely independent inlets: two for PALMS, since the inlet in Atlanta shared no common components with the aircraft in-let, the inlet for the ATOFMS, and the inlet for RSMS. Data within clouds were excluded because cloud droplets and ice at aircraft velocities can abrade inlet walls. Finally, the fact that the Pb signal drops both in the marine boundary layer (Fig. 7) and the stratosphere (not shown) indicates that the Pb measured at intermediate altitudes is real.
4.3 Biomass burning plumes
Besides the wide geographic and altitude distribution of Pb, it was also present on many types of particles. One type of particular interest is biomass burning particles. On 9 July and 27 July 2004, the P-3 aircraft sampled forest fire plumes from fires in northwestern Canada and eastern Alaska (de Gouw et al., 2006). The plumes, especially those encountered north of Maine, passed over lightly populated areas before they were sampled. None of the biomass particles observed in the plumes had a large Pb signal. Yet they contained small amounts of Pb nearly as often as particles from urban plumes. Figure 11 shows the fraction of biomass-burning particles over eastern Canada that contained Pb as a function of the amount of sulfate on those particles. For this plume analysis, biomass burning particles were defined by cluster analysis of the mass spectra with the additional constraints of gas phase acetonitrile greater than 250 ppbv and latitude north of 48◦. Few particles contained much sulfate, but those that did of-ten contained Pb. In contrast, none of the particles sampled from a fresh biomass burning plume over Utah in 2002 con-tained measurable Pb or sulfate (Hudson et al., 2004). The flight with a higher frequency of Pb (9 July) also encountered more gas phase SO2. The correlation between Pb and sulfate is a strong indication that the Pb was added to the particles during transport rather than coming from Pb in the burning
0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 F re q u e n c y o f m a s s 2 0 8 > 0 .0 3 % 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.00
Positive ion sulfate peaks (fraction)
5629 1653
127 20
2002 fresh Utah fire plume 2004 fire plume eastern Canada 1999 Atlanta carbon-potassium particles
202
Figure 11. Frequency of
208Pb in particles in biomass burning plum
Fig. 11. Frequency of208Pb in particles in biomass burning plumes
as a function of the sulfate content of those particles. Fire plume points are marked with the number of spectra with sulfate peaks in that range. There were many more particles in the Atlanta dataset.
vegetation or soil. This correlation between sulfate and Pb in single biomass burning particles was not present for many other types of particles during these flights. The correlation is probably present in these biomass burning plumes because the major airborne Pb sources between Alaska and eastern Canada are smelters that are also major sources of SO2. In Atlanta, a similar correlation between Pb and sulfate was also found for carbon-potassium particles but not the entire data set.
4.4 Asian sources
Off the coast of California, the high average Pb signal near 36 N and 125 W (Fig. 6) included 59 particles with mass 208 greater than 10% of the total ion current in a relatively small region. All of these particles were en-countered above 2 km, with the majority on a flight leg at 4.9 km. Compared to other Pb-rich particles during the 2002 flights, these had more K and much less As and Sn. According to a FLEXPART simulation, the time pe-riod when they were sampled corresponded with transport from Asia (see http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/7/3195/ 2007/acp-7-3195-2007-supplement.pdf). Carbon monoxide was moderately elevated to about 120 ppbv. This flight pe-riod had total aerosol volumes of 1 to 3 µm3cm−3 below 1 µm diameter and 1 to 10 µm3cm−3 in the coarse mode. These are unusually large for this altitude and probably mean that there was little scavenging of Asian emissions during this particular transport event.
The IMPROVE data shown in Fig. 3 also suggest trans-port of Pb to the western United States in springtime. The
5 6 7 0.01 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 F re q u e n c y o f p e a k 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1
Mass 208 (fraction of ions)
39 K 64, 66, 68 Zn 23 Na 121,123 Sb 118,120 Sn 63, 65 Cu 75 As 2004 Eastern US 5 6 7 0.01 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 F re q u e n c y o f p e a k 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1
Mass 208 (fraction of ions)
39 K 64, 66, 68 Zn 23 Na 121,123 Sb 118,120 Sn 63, 65 Cu 75 As 2002 over Pacific Ocean
Fig. 12. Frequency of peaks observed by PALMS in particles with
various amounts of208Pb. There may be some small overestimates of other metals due to fragmentation of other species at the same masses. In each case either an isotopic pattern was required, such as the presence of all three Zn isotopes, or the peak was required to be much larger than neighboring peaks. For arsenic, mass 75 was required to be at least 5 times both 73 and 77 to differentiate As from CaCl+and organic spectra with peaks at every odd mass.
maxima at several western sites in April coincide with the timing of transport from Asia. Particulate matter at three Asian sites and the North Pacific had Pb/Zn ratios of 0.6 to 0.8 (Cohen et al., 2004; Narita et al., 1999). Mauna Loa stays
near the Asian Pb/Zn ratio throughout the year, even when absolute concentrations of both are very low. The Mount Zirkel site at 3243 m in Colorado is an especially clear exam-ple of a site reaching the Asian Pb/Zn ratio in the springtime and going to the North American ratio of 0.3 to 0.4 the rest of the year.
Although the signature of transport from Asia is clear, it contributes less than 1 ng m−3even in springtime in the west-ern United States. Most of the airborne Pb over the United States cannot be from Asia.
4.5 Other metals in Pb-rich particles
The particles that produced large Pb signals also usually con-tained other metals. Figure 12 shows the fraction of particles that contained selected other metals as a function of the ion signal from Pb. Particles over the Pacific Ocean west of Cal-ifornia and those over the eastern United States had fairly similar frequencies of other metals. The biggest difference is that particles over the ocean were more likely to contain Na. Figure 13 shows the average mass spectra of all particles for which the208Pb signal was least 10% of the total ion signal. In these instruments metals are commonly found as the ele-mental ion, so there is little information on the chemical form of the metal in the particles. The PbO+ion was occasionally observed.
4.6 Mechanisms for distributing Pb among particles It seems unlikely that about 10% of the accumulation mode aerosol particles over the United States originated from sources that emit Pb. The special case of the biomass burn-ing plumes shows that particles can acquire Pb durburn-ing atmo-spheric transport. In addition, particles over a wide range of sizes contained Pb. Two ways that so many particles could contain Pb are condensation of gas phase Pb compounds and coagulation with small Pb-rich particles. Of these, it is likely that coagulation is much more important. Gas phase Pb com-pounds are present only at very low concentrations (Wang et al., 1997; Shotyk and Le Roux, 2005). Another argument in favor of coagulation is that even in the areas with the most Pb many mass spectra with excellent signal to noise showed no Pb. This distribution is more easily explained by coagulation than by deposition from the gas phase, which should lead to some Pb on almost every particle. Finally, Pb-rich particles smaller than 50 nm aerodynamic diameter were directly ob-served in urban areas. The coagulation of such particles with larger organic-sulfate particles could explain why some but not all of those particles have Pb. Coagulation of Pb-rich particles onto other particles has been observed with detailed electron microscopy (Utsunomiya et al., 2004; Cho¨el et al., 2006).
Coagulation calculations show that reasonable times are required for 5 or 10% of accumulation mode particles to acquire Pb by coagulation with smaller, Pb-rich particles.
10-4 10-3 10-2 10-1 200 150 100 50 0
Mass to charge ratio
10-4 10-3 10-2 10-1 A v e ra g e s ig n a l 10-4 10-3 10-2 10-1 2004 Eastern US n=313 2002 Western US n=219 1999 Atlanta n=330 Sn Zn As Sb H3SO4+ 39 K 23 Na 12 C Ag HK2SO4+ 56 Fe 7 Li 63 Cu 63 Cu 64 Zn 187 Re H3SO4 68 Zn 56 Fe 56 Fe Sn 116,118,120 Sn Sb Sb 7 Li H3SO4 75 As 39 K 39 K 12 C 12 C 23 Na 23 Na 206 Pb 206 Pb 206 Pb 7 Li NO HSO3
Fig. 13. Averages of PALMS mass spectra with mass 208 greater
than 10% of the ion current. The Pb isotope pattern is not accurate since it is dominated by whether or not the peak-finding routines found 206 and 207.
Figure 14 shows the time required for accumulation mode particles to acquire Pb by coagulation with a constant 100 cm−3concentration of smaller, Pb-rich particles. When expressed as a fraction of particles, this time constant is in-dependent of the concentration of accumulation mode parti-cles. The times will be shorter or longer depending on the concentration of small particles. These calculations are from expressions in Table 10.1 of Seinfeld (1986) for 2 km altitude and small and larger particle densities of 2.5 and 1.5 g cm−3, respectively, although the calculation is not very sensitive to these parameters. A factor of 1.25 was used as an estimate for the effect of van der Waals forces.
Figure 14 also indicates that coagulation with the assumed ultrafine particles is faster for larger particles. For the case discussed earlier of the biomass burning plume of Canada, particles with vacuum aerodynamic diameters larger than 700 nm were about twice as likely to contain Pb than par-ticles smaller than 400 nm. This is consistent with the coag-ulation calccoag-ulation, although it is difficult to compare in de-tail because the size of the original Pb-containing particles is not known and the accumulation mode particles change size during transport due to condensation of sulfates and other species. 4 3 2 1 0 T im e fo r 5 % to c o a g u la te w ith A itk e n p a rti c le (d a y s ) 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0
Geometric diameter of scavenging particle (µm)
100 cm-3 of 100 nm diam.
100 cm-3 of 50 nm
Fig. 14. The time required for 5% of accumulation mode
parti-cles of a given diameter to coagulate with a constant background of smaller particles.
5 Conclusions
Lead has been observed in particles over a wide size range from less than 50 nm to more than 2 µm. Expressed as a fraction of the total aerosol, there was little gradient in Pb with altitude from the top of the boundary layer to the tropopause. Across a wide range of locations, altitudes, and particle chemistry, more than 5% of particles contain small amounts of Pb. There was a wide range of the amount of Pb in individual particles. A significant fraction of the to-tal Pb signal comes from a few particles that contain large amounts of Pb. These particles often contain other metals, especially Zn. Many of the Pb-containing particles by num-ber have very small Pb signals and are otherwise similar to particles without Pb. In Atlanta, Wilmington, and other ur-ban areas the Pb-rich particles had a strong dependence on wind direction but the particles with small Pb signals were almost independent of wind direction.
These particles with small amounts of Pb may be the re-sult of coagulation of smaller particles with accumulation mode aerosol. For the United States, the largest sources of airborne Pb are aviation gasoline, coal combustion, and smelters. All of these are combustion sources that can pro-duce very small particle. The fraction of Pb in coal that be-comes airborne and the Pb content of residual fuel oil are two parameters that could significantly affect the budget of airborne Pb. One special example of Pb interacting with aerosols was that some particles in a biomass burning plume acquired both Pb and sulfate as the plume traversed Canada, probably from smelters along the way.
The percentage of particles containing Pb was as high or higher over the Pacific Ocean west of California than it was over the continental United States. Some of this Pb is clearly due to long-range transport from Asia. On an absolute basis, however, North American sources were more important to Pb in the eastern United States. The overall fraction of particles with detectable Pb was also similar at a high altitude site in Switzerland to measurements in the United States. In both continents there was little size dependence and there was a wide range of Pb contents in individual particles. In both continents most of the particles with the highest Pb contents contained other metals whereas particles with very small Pb contents were similar to those without any Pb.
The special capabilities of single particle mass spectrom-etry were essential to obtaining these results. Only the mea-surement of large numbers of particles could obtain statis-tically significant samples of Pb-rich particles. High sensi-tivity was required to measure the small amounts of Pb in many other particles. The results show a very geographically broad distribution of Pb in particles, consistent with multiple sources. These are some of the first data showing that Pb is present in particles in the free troposphere. The way Pb is distributed among different types of particles will affect how airborne Pb enters both the human lung and ecosystems. Acknowledgements. Funding by the Collaborative Research Center
641 “The Tropospheric Ice Phase” of the German Research Foundation is gratefully acknowledged for the Jungfraujoch measurements. Funding by the United States Environmental Protection Agency under grant number XA-97309801 is gratefully acknowledged for the Wilmington RSMS measurements. We thank B. Linak and M. Murphy for pointing out some references on Pb in fuels.
Edited by: M. Ammann
References
Ali, M. F., Cukhari, A., and Saleem, M.: Trace metals in crude oils from Saudi Arabia, Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev., 22, 691– 694, 1983.
Alvarez, F. F., Rodr´ıguez, M. T., Espinosa, A. J. F., and Dab´an, A. G.: Physical speciation of arsenic, mercury, lead, cadmium and nickel in inhalable atmospheric particles, Anal. Chimica Acta, 524, 33–40, 2004.
Baltensperger, U., Gaggeler, H. W., Jost, D.T., Lugauer, M., Schwikowski, M., Weingartner, E., and Seibert, P.: Aerosol cli-matology at the high-alpine site Jungfraujoch, Switzerland, J. Geophys. Res., 102(D16), 19 707–19 715, 1997.
Bein, K. J., Zhao, Y., Wexler, A. S., and Johnston, M. V.: Speciation of size-resolved individual ultrafine particles in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, J. Geophys. Res., 110, D07S05, doi:10.1029/2004JD004708, 2005.
Bein, K. J., Zhao, Y., Pekney, N. J., Davidson, C. I., Johnston, M. V., and Wexler, A. S.: Identification of sources of atmospheric PM at the Pittsburgh Supersite. Part II: Quantitative comparisons
of single particle, particle number, and particle mass measure-ments”, Atmos. Environ., 40, S424–S444, 2006.
Boughton, B. and Horvath, A.: Environmental assessment of used oil management methods, Environ. Sci. Technol., 38, 353–358, 2004.
Bratzel Jr., M. P. and Chakrabarti, C. L.: Determination of lead in petroleum and petroleum products by atomic absorption spec-trometry using a carbon rod analyzer, Anal. Chim. Acta, 61, 25– 32, 1972.
Bukowiecki, N., Hill, M., Gehrig, R., Zwicky, C. N., Lienemann, P., Heged¨us, F., Falkenberg, G., Wingartner, E., and Baltensperger, U.: Trace metals in ambient air: Hourly size-segregated mass concentrations determined by synchrotron-XRF, Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 5754–5762, 2005.
Cho¨el, M., Deboudt, K., Flament, P., Lecornet, G., Perdrix, E., and Sobanska, S.: Fast evolution of tropospheric Pb- and Zn-rich particles in the vicinity of a lead smelter, Atmos. Environ., 40, 4439–4449, 2006.
Cohen, D. D., Garton, D., Stelcer, E., Hawa, O., Wang, T., Poon, S., Kim, J., Choi, B. C., Oh, S. N., Shin, H.-J., Ko, M. Y., and Uematsu, M.: Multielemental analysis and characterization of fine aerosols at several key ACE-Asia sites, J. Geophys. Res., 109, D19S12, doi:10.1029/2003JD003569, 2004.
Cziczo, D. J., Thomson, D. S., and Murphy, D. M.: Ablation, flux, and atmospheric implications of meteors inferred from strato-spheric aerosol, Science, 291, 1772–1775, 2001.
Davison, R. L., Natusch, D. F. S., Wallace, J. R., and Evans Jr., C. A.: Trace elements in fly ash: Dependence of concentration on particle size, Environ. Sci. Technol., 8, 1107–1113, 1974. De Gouw, J. A., Warneke, C., Stohl, A., Wollny, A. G., Brock, C.
A., Cooper, O. R., Holloway, J. S., Trainer, M., Fehsenfeld, F. C., Atlas, E. L., Donnelly, S. G., Stroud, V., and Lueb, A.: Volatile organic compounds composition of merged and aged forest fire plumes from Alaska and western Canada, J. Geophys. Res., 111, D10303, doi:10.1029/2005JD0006175, 2006.
Dreyfus, S., P´echeyran, C., Magnier, C., Prinzhofer, A., Lienemann, C. P., and Donard, O. F. X.: Direct trace and ultra-trace metals determination in crude oil and fractions by inductively coupled mass spectrometry, J. ASTM International, 2, 1–8, 2005. Environmental Protection Agency: Latest findings on National
Air Quality, 2002 Status and Trends, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, http://www.epa.gov/air/airtrends/aqtrnd02/ 2002 airtrends final.pdf, 2003.
Flagan, R. C. and Taylor, D. D.: Laboratory studies of submicron particles from coal combustion, Eighteenth Symposium on Com-bustion, 1227–1237, The Combustion Institute, 1981.
Gard, E., Mayer, J. E., Morrical, B. D., Dienes, T., Fergenson, D. P., and Prather, K. A.: Real-time analysis of individual atmo-spheric aerosol particles: Design and performance of a portable ATOFMS, Anal. Chem. 69, 4083–4091, 1997.
Gokhale, S. B. and Patil, R. S.: Size distribution of aerosols (PM10) and lead (Pb) near traffic intersections in Mumbai (India), Envi-ron. Mon. Assessment, 95, 311–324, 2004.
Han, J. S., Moon, K. J., Ryu, S. Y., Kim, Y. J., and Perry, K. D.: Source estimation of anthropogenic aerosols collected by a DRUM sampler during spring of 2002 at Gosan, Korea, Atmos. Environ., 39, 3113–3125, 2005.
Heathcote, R., Simmons, D., and Bernholtz, S.: Analysis of motor-vehicle fuels for metals by inductively coupled plasma-mass
spectrometry, Iowa Ground Water Quarterly, 39, 1–4, 2000. Hudson, P. K., Murphy, D. M., Cziczo, D. J., Thomson, D. S.,
de Gouw, J. A., Warneke, C., Holloway, J., Jost, H.-J., and H¨ubler, G.: Biomass burning particle measurements: Charac-teristic composition and chemical processing, J. Geophys. Res., 109, D23S27, doi:10.1029/2003JD004398, 2004.
Kaufmann, R. L.: Laser-microprobe mass spectroscopy (LAMMA) of particulate matter, Physical and Chemical Characterization of Individual Airborne Particles, edited by: Spurny, K. R., Ellis & Horwood Ltd., Chichester, 1986.
Lake, D. A., Tolocka, M. P., Johnston, M. V., and Wexler, A. S.: Mass spectrometry of individual particles between 50 and 750 nm in diameter at the Baltimore Supersite, Environ. Sci. Technol., 37, 3268–3274, 2003.
Lee, S.-H., Murphy, D. M., Thomson, D. S., and Middlebrook, A. M.: Chemical components of single particles measured with Particle Analysis by laser Mass Spectrometry (PALMS) during the Atlanta SuperSite Project: Focus on organic/sulfate, lead, soot, and mineral particles, J. Geophys. Res., 107, AAC 1, doi:10.1029/2000JD000011, 2002.
Linak, W. P. and Wendt, J. O. L.: Toxic metal emissions from incin-eration: Mechanisms and control, Prog. Energy Comb. Sci., 19, 145–185, 1993.
Magaw, R. I., McMillen, S. J., Gala, W. R., Trefry, J. H., and Trocine, R. P.: Risk evaluation of metals in crude oils, Proc. 6th Int. Petrol. Environ. Conf., 16–18 November, Houston, TX, 460– 473, 1999.
Malm, W. C., Sisler, J. F., Huffman, D., Eldred, R. A., and Cahill, T. A.: Spatial and Seasonal Trends in Particle Concentration and Optical Extinction in the United-States, J. Geophys. Res., 99, 1347–1370, 1994.
Maenhaut, W., Cafmeyer, J., Dubtsov, S., and Chi, X.: Detailed mass size distributions of elements and species, and aerosol chemical mass closure during fall 1999 at Gent, Belgium, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B., 189, 238–242, 2002.
Mallina, R. V., Wexler, A. S., Rhoads, K. P., and Johnston, M. V.: High speed particle beam generation: A dynamic focusing mech-anism for selecting ultrafine particles, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 33, 87–104, 2000.
Miller, C. A., Ryan, J. V., and Lombardo, T.: Characterization of air toxics from an oil-fired firetube boiler, J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc., 46, 742–748, 1996.
Murphy, D. M., Cziczo, D. J., Froyd, K. D., Hudson, P. K., Matthew, B. M., Middlebrook, A. M., Peltier, R. E., Sullivan, A., Thomson, D. S., and Weber, R. L.: Single-particle mass spectrometry of tropospheric aerosol particles, J. Geophys. Res., 111, D23S32, doi:10.1029/2006JD007340, 2006.
Narita, U., Tanaka, S., and Santosa, S. J.: A study on the concen-tration, distribution, and behavior of metals in atmospheric par-ticulate matter over the North Pacific Ocean by using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry equipped with laser ablation, J. Geophys. Res., 104, 26 859–26 866, 1999.
Nriagu, J. O., Lawson, G., Wong, H. K., and Azcue, J. M.: A proto-col for minimizing contamination in the analysis of trace metals in Great Lakes waters, J. Great Lakes Res., 19, 175–182, 1993. Phares, D. J., Rhoads, K. P., Johnston, M. V., and Wexler,
A. S.: Size-resolved ultrafine particle composition analy-sis, Part 2: Houston, J. Geophys. Res., 108(D7) 8420, doi:10.1029/2001JD001212, 2003.
Raask, E.: The mode of occurrence and concentration of trace ele-ments in coal, Prog. Energy. Combust. Sci., 11, 97–118, 1985. Rhoads, K. P., Phares, D. J., Wexler, A. S., and Johnston,
M. V.: Size-resolved ultrafine particle composition anal-ysis, Part 1: Atlanta, J. Geophys. Res., 108(D7) 8418, doi:10.1029/2001JD001211, 2003.
Rising, B., Wu, J., and Sorurbakhsh, P.: Survey of ultra-trace metals in gas turbine fuels, 11th Annual International Petroleum Envi-ronmental Conference, 12–15 October 2004.
Salma, I., Maenhaut, W., and Z´aray, G.: Comparative study of el-emental mass size distributions in urban atmospheric aerosol, J. Aerosol Sci., 22, 339–356, 2002.
Seinfeld, J. H.: Air Pollution, Wiley and Sons, New York, 738 pp., 1986.
Shotyk, W. and Le Roux, G.: Biogeochemistry and Cycling of Lead, in: Biogeochemical Cycles of the Elements, vol. 43 of Metal Ions in Biological Systems, edited by: Sigel, A., Sigel, H., and Sigel, R. K. O., M. Dekker, New York, pp. 240–275, 2005. Shotyk, W., Zheng, J., Krachler, M., Zdanowicz, C.,
Koe-mer, R., and Fisher, D.: Predominance of industrial Pb in recent snow (1994–2004) and ice (1842–1996) from De-von Island, Arctic Canada, Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L21814, doi:10.1029/2005GL023860, 2005.
Shumway, L. A.: Trace element and polycyclic aromatic hydrocar-bon analyses of jet engine fuels: Jet A, JP5, and JP8, Technical Report 1845, SPAWAR Systems Center, San Diego, 2000. Singh, M., Jaques, P. A., and Sioutas, C.: Size distribution and
diur-nal characteristics of particle-bound metals in source and recep-tor sites of the Los Angeles Basin, Atmos. Environ., 36, 1675– 1689, 2002.
Solomon, P. A., Chameides, W., Weber, R., Middlebrook, A., Kiang, C. S., Russell, A. G., Butler, A., Turpin, B., Mikel, D., Scheffe, R., Cowling, E., Edgerton, E., St. John, J., Jansen, J., McMurry, P., Hering, S., and Bahadori, T.: Overview of the 1999 Atlanta Supersite Project, J. Geophys. Res., 108(7), 8413, doi:10.1029/1002JD001458, 2003.
Stohl, A., Forster, C., Frank, A., Seibert, P., and Wotawa, G.: Tech-nical note: The Lagrangian particle dispersion model FLEX-PART version 6.2, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 2461–2474, 2005, http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/5/2461/2005/.
Tan, M. G., Zhang, G. L., Li, X. L., Zhang, Y. X., Yue, W. S., Chen, J. M., Wang, Y. S., Li, A. G., Li Y., Zhang, Y. M., and Shan, Z. C.: Comprehensive study of lead pollution in Shanghai by multiple techniques, Anal. Chem., 78, 8044–8050, 2006. Thomson, D. S., Schein, M. E., and Murphy D. M.: Particle
anal-ysis by laser mass spectrometry WB-57F instrument overview, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 33, 153–169, 2000.
Tolocka, M. P., Lake, D. A., Johnston, M. V., and Wexler, A. S.: Number concentrations of fine and ultrafine particles containing metals, Atmos. Environ., 38, 3263–3273, 2004.
Tolocka, M. P., Lake, D. A., Johnston, M. V., and Wexler, A. S.: Size-resolved fine and ultrafine particle composition in Baltimore, Maryland, J. Geophys. Res., 110, D07S04, doi:10.1029/2004JD004573, 2005.
Utsunomiya, S., Jensen, K. A., Keeler, G. J., and Ewing, R. C.: Di-rect identification of trace metals in fine and ultrafine particles in the Detroit urban atmosphere, Environ. Sci. Technol., 38, 2289– 2297, 2004.