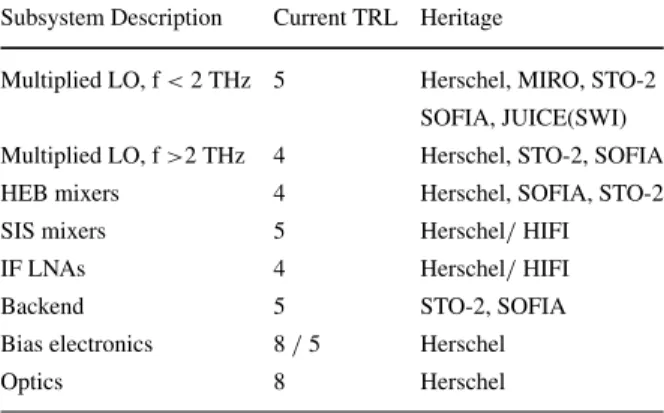
The far-infrared spectroscopic surveyor (FIRSS)
Texte intégral
Figure

![Fig. 2 Observations of different gas phases towards G132.5 [111]. Multiple components of warm neutral gas create very broad lines of HI emission](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14432555.515434/7.659.79.584.86.476/observations-different-phases-multiple-components-neutral-create-emission.webp)
![Fig. 4 [CII]/FIR luminosity ratio variation as a function of position in Orion [32]. This behavior is reminiscent of the “[CII] /FIR deficit” seen in local ULIRGs](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14432555.515434/11.659.77.577.509.868/luminosity-variation-function-position-behavior-reminiscent-deficit-ulirgs.webp)
![Fig. 6 SPIRE 250 μm image of M33 and PACS spectroscopy of HII regions in M33 in [CII], HI, CO, and](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14432555.515434/16.659.81.578.89.370/fig-spire-image-pacs-spectroscopy-hii-regions-cii.webp)
Documents relatifs
Ratio of the EW of He i 7065 to He ii 5412 as a function of spectral type for the low-metallicity models calculated in the present study, the solar metallicity models of Martins
Hence, for a given initial mass, we can expect modifications in the spectral appearance of evolutionary tracks, both in terms of spectral type and luminosity class ( Markova et
Regarding our modelling results, early crustal growth models predict ridgecrests significantly less shallow than progressive crustal growth models because a larger continental
The substantial data set of new surface wave group-velocity mea- surements combined with existing data from CU-Boulder has pro- vided the opportunity for constructing a new 3-D
These results indicate that Ca 2+ binding to the Syt 1 C2A domain is required for suppression of the asynchronous component of release, whereas Ca 2+ binding to C2B triggers
![Fig. 7 Number counts expected from FIRSS ‘blind surveys’ in [NII] 205 μm and [CI] 370 μm channels](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14432555.515434/18.659.79.583.83.575/fig-number-counts-expected-firss-blind-surveys-channels.webp)
![Fig. 8 Intensity of IR fine-structure lines as a function of wavelength. FIRSS would allow observations at 370 μm and 205 μm probing primarily [CII] 158 μm at z=0.3 and 1.3, [OIII] 88 μm at z=1.3, and [OI]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14432555.515434/19.659.78.580.88.431/intensity-structure-function-wavelength-firss-observations-probing-primarily.webp)