An Inertial Newton Algorithm for Deep Learning
Texte intégral
Figure

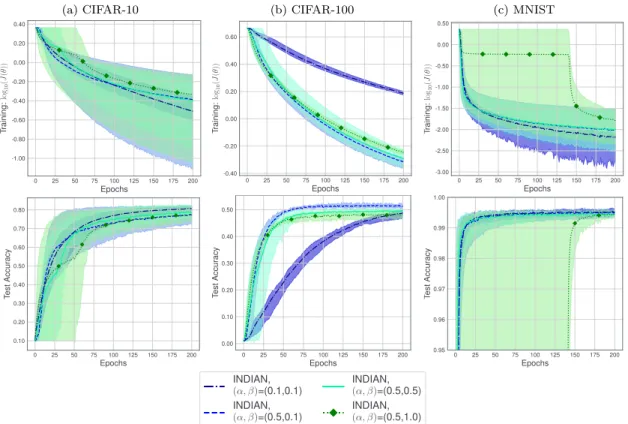

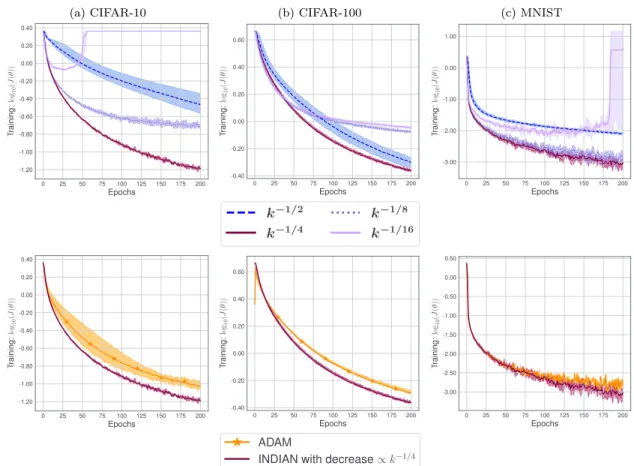
Documents relatifs
These results are in perfect agreement with the Landauer principle: in a quasi-static process, the mean work or heat required to erase 1 bit of information is ln 2 = 0.693.
Generally worse than unsupervised pre-training but better than ordinary training of a deep neural network (Bengio et al... Supervised Fine-Tuning
“Extracting gamma-ray information from images with convolutional neural network methods on simulated cherenkov telescope array data,” in IAPR Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks
Our results confirmed with a long-term follow-up that ex- clusive partial breast using IORT is feasible for early- breast cancer with an absolute risk of carcinologic events
Our method provides a supervised learning solution to classify an unknown column in such tables into predefined column classes which can also come from a knowledge graph..
In the paper, the authors took an attempt to briefly describe their experience in organizing work with data analysis using neural networks and machine
Magnetization versus magnetic field for mixed cobalt-iron oxalate at room temperature (full diamonds) and for the oxides resulting from the selective laser decomposition at
Training loss evolution for PerSyn and GoSGD for different frequency/probability of exchange p .... Convergence speed comparison between GoSGD and EASGD for