Initiation of immersed granular avalanches
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
L’étude anatomique et biomécanique du genou montre que le facteur anatomique le plus impliqué dans la rupture du ligament croisé antérieur est la pente
Dans le cas d’un stockage à haute température, c’est-à-dire dans la gamme de température mésophile optimale pour l’activité bactérienne de la digestion anaérobie des fibres
Un versant est voué à décrire les conditions de l’après- colonialisme (ce serait la postcolonialité) ; l’autre s’essaye à bâtir une épistémologie
When it is used adnominally, the proximal singular demonstrative pronoun da can also modify the locational demonstrative adverb hini ‘here’ for emphasizing the reference to
The present custom-made fluidic device was designed for the mechanical stimulation and characterization of cartilage micropellets and validated here using collagen- and alginate-based
Pour une séance d’improvisation libre, un musicien, ou plus souvent un groupe de musiciens, se réunissent pour jouer ensemble, a priori sans forme préétablie, ni durée fixée,
degrees as long as it continues to grow. It is frozen to its current value when it stops growing and a new root el- ement is created. We see that this model combines two aspects
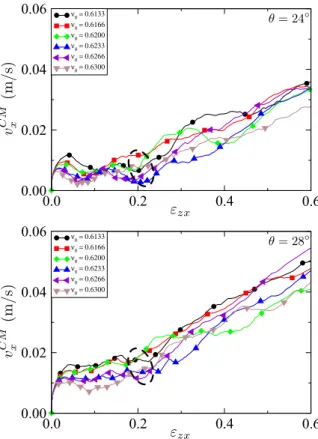
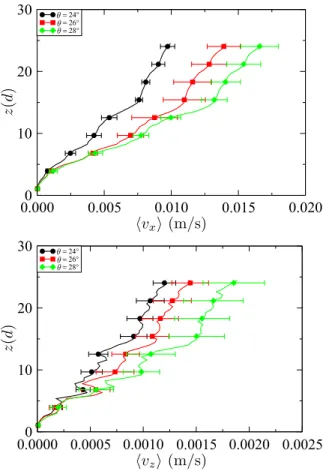
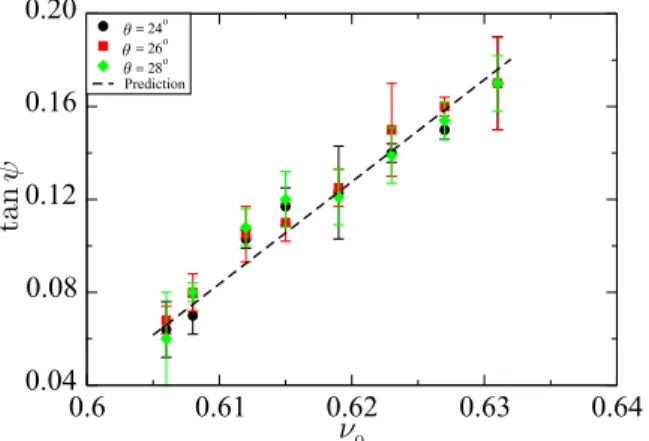
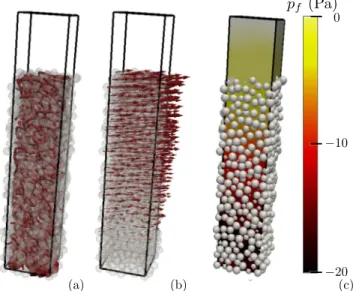
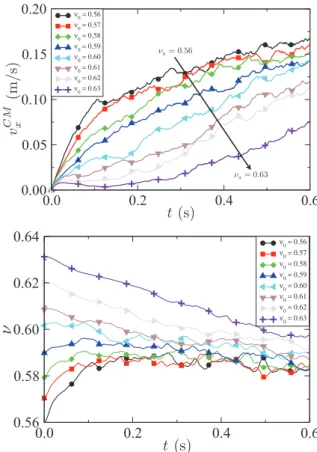
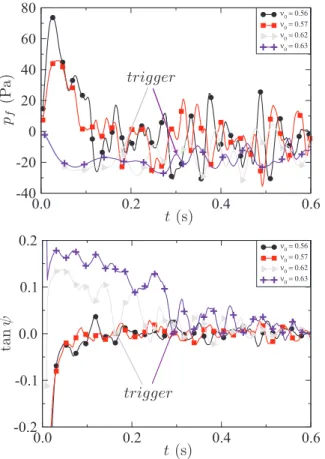
As a conclusion, at low shearing rate, the friction co- efficient µ of dense and immersed granular materials de- pends neither on the grain size nor on the viscosity of the