Muscle contraction: a mechanical perspective
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
Abstract—In this paper, we propose a successive convex approximation framework for sparse optimization where the nonsmooth regularization function in the objective function is
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
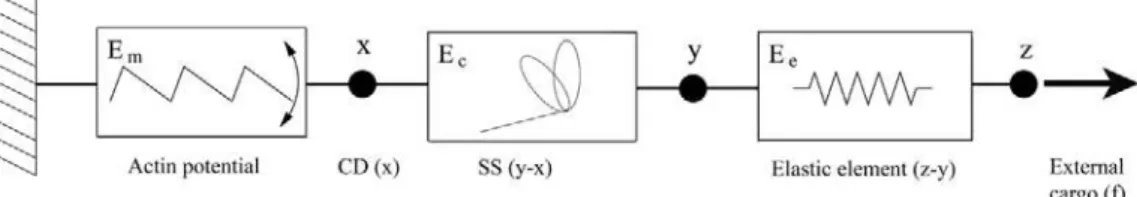
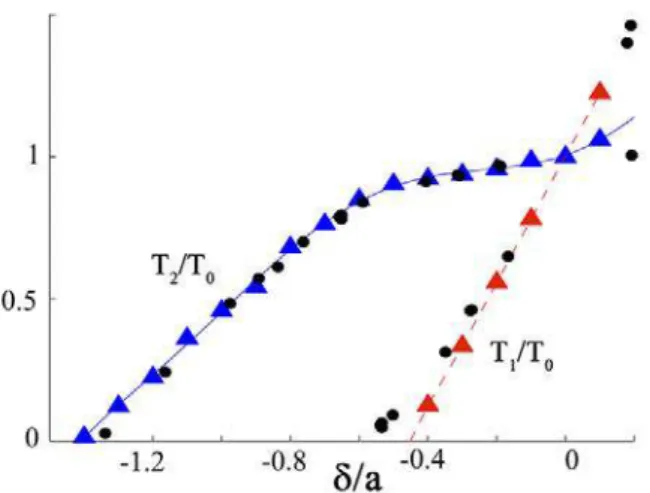
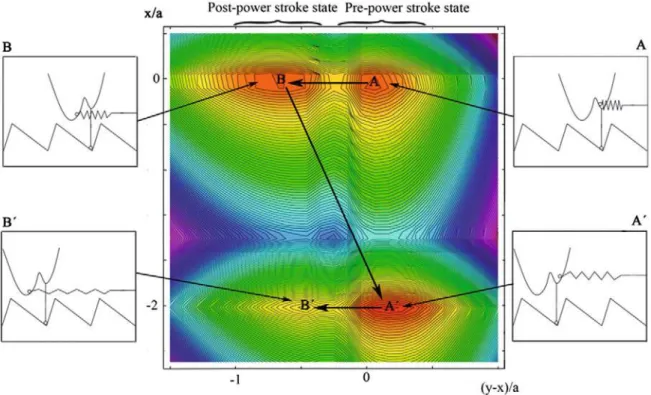
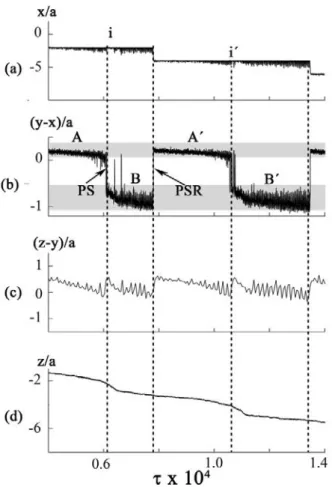
In our model a cross-bridge in itself is seen as a special chemical entity having inter- nal mechanical variables – or degrees of freedom – pertaining to the actual
Our goal is, on one hand, to write down explicit first and second order optimality conditions for general 2-dimensional shape optimization problems with convexity con- straint and,
In this paper, we adopt a global (in space) point of view, and aim at obtaining uniform estimates, with respect to initial data and to the blow-up points, which improve the results
Conversely, it is easy to check that the latter condition implies that T a is bounded.. Moreover Λ is composed of eigenvalues λ associated with finite dimensional vector
Recycling programs in St. John’s are inefficient, and are having a negative impact upon the
Let X be an algebraic curve defined over a finite field F q and let G be a smooth affine group scheme over X with connected fibers whose generic fiber is semisimple and