Stochastic Runge-Kutta methods and adaptive SGD-G2 stochastic gradient descent
Texte intégral
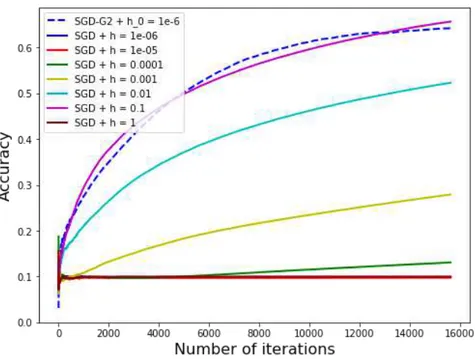
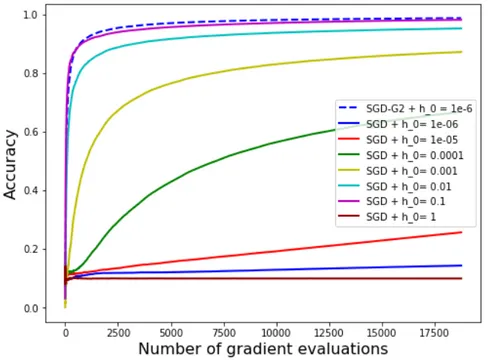
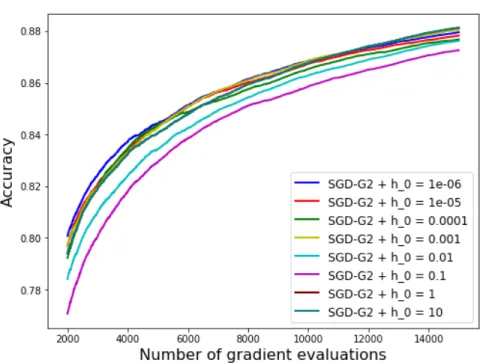
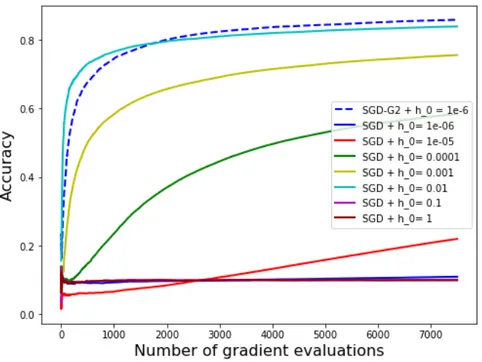
Figure

Documents relatifs
It is used in many countries, notably in swimming to determine if the rate and by result the distance per stroke, also called stroke length, used by a swimmer at a given moment in
Finally, we apply our analysis beyond the supervised learning setting to obtain convergence rates for the averaging process (a.k.a. gossip algorithm) on a graph depending on
In particular, second order stochastic gradient and averaged stochastic gradient are asymptotically efficient after a single pass on the training set.. Keywords: Stochastic
Bottou and Bousquet (2008) characterize the asymptotic learning properties of stochastic gradient algorithms in the large scale regime, that is, when the bottleneck is the
In this paper, we propose two techniques, lock-free schedul- ing and partial random method, to respectively solve the locking problem mentioned in Section 3.1 and the
SQL has the sample and computational complexity of a same order since it performs only one Q-value update per sample, the same argument also applies to the standard Q-learning,
GWAS analysis on AS and WTCCC datasets To eval- uate the ability of our procedure to discover new asso- ciations between SNPs and ankylosing spondylitis, we compare our procedure
The HAPGEN2 software allows to generate a controls-only matrix of SNPs (no disease allele). We filtered this matrix according to the minor allele frequency to only keep SNPs with a