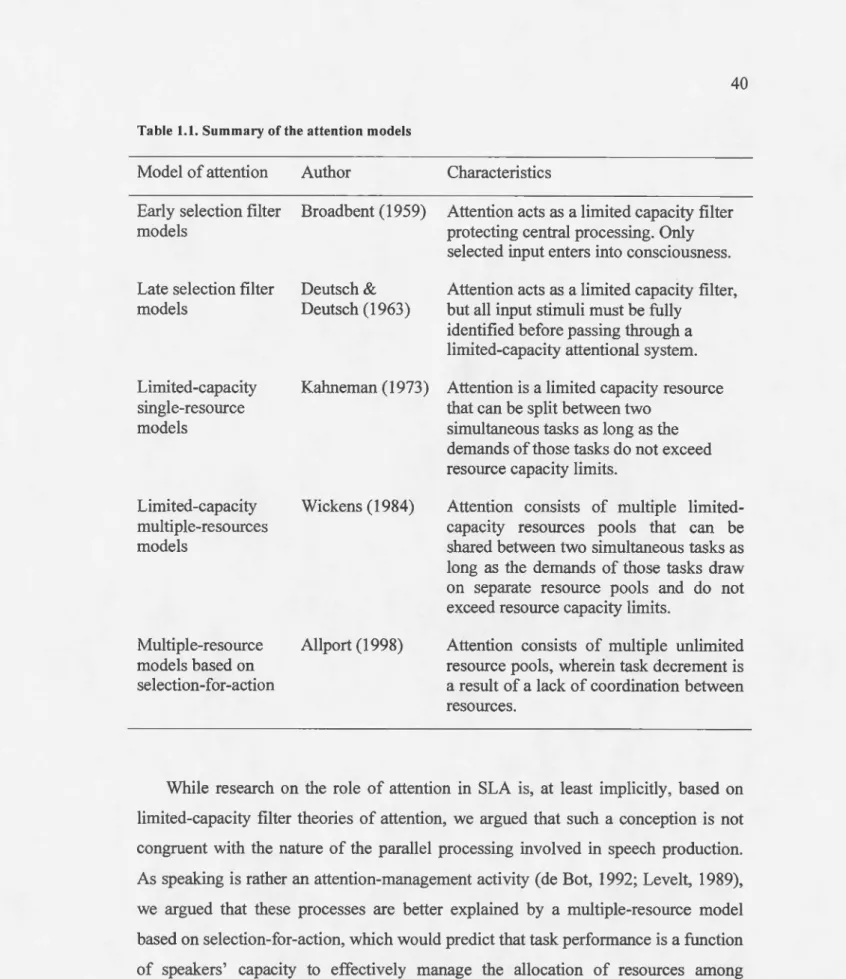
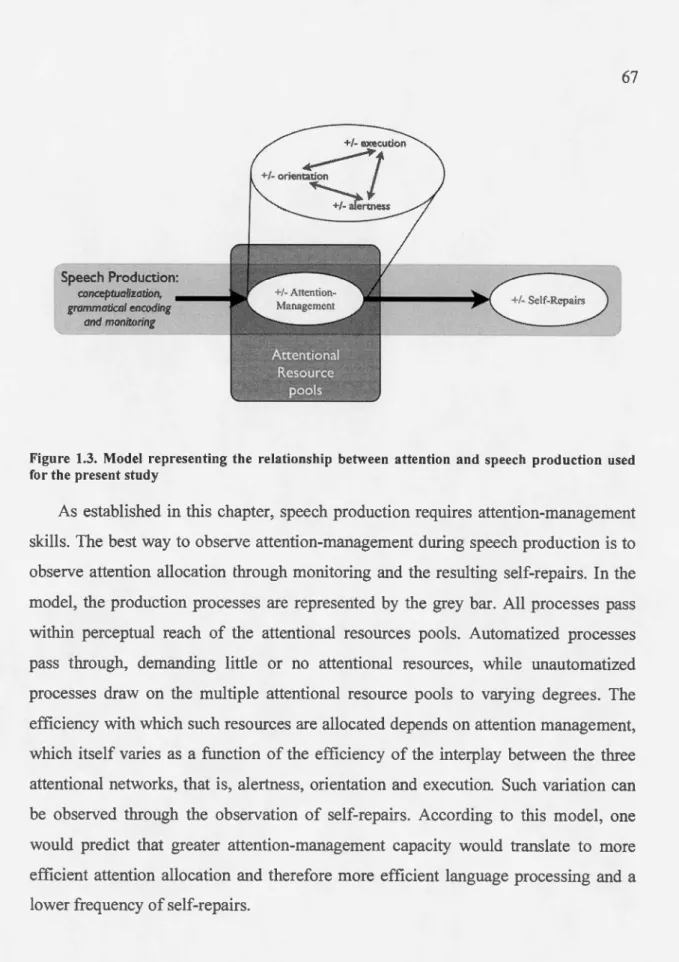
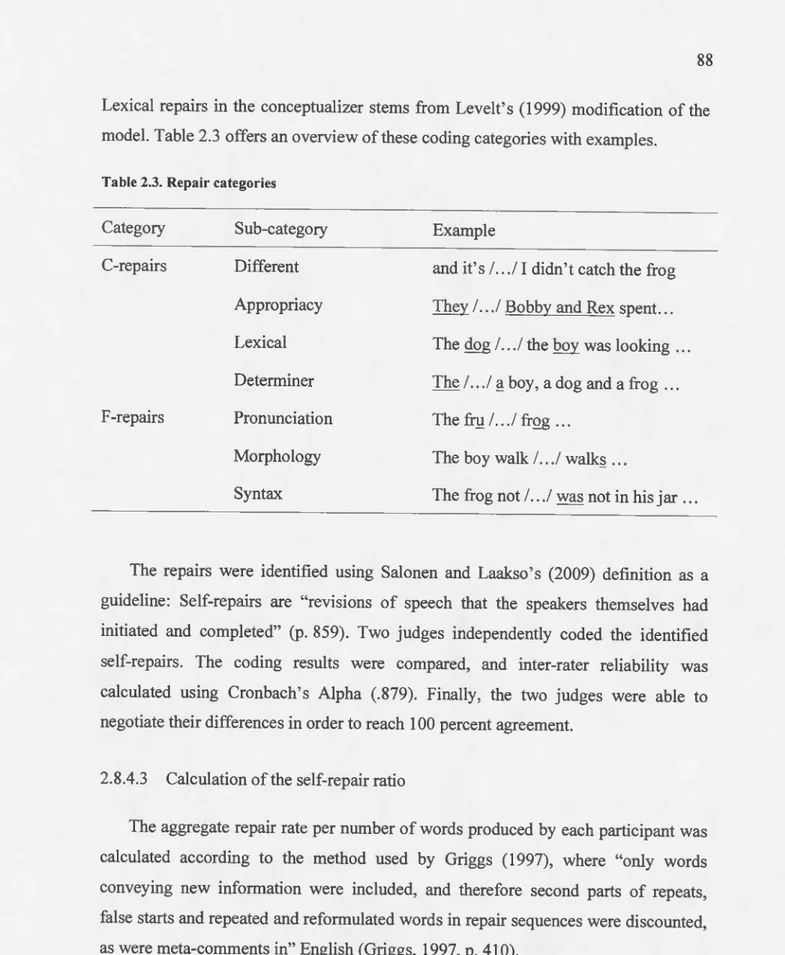
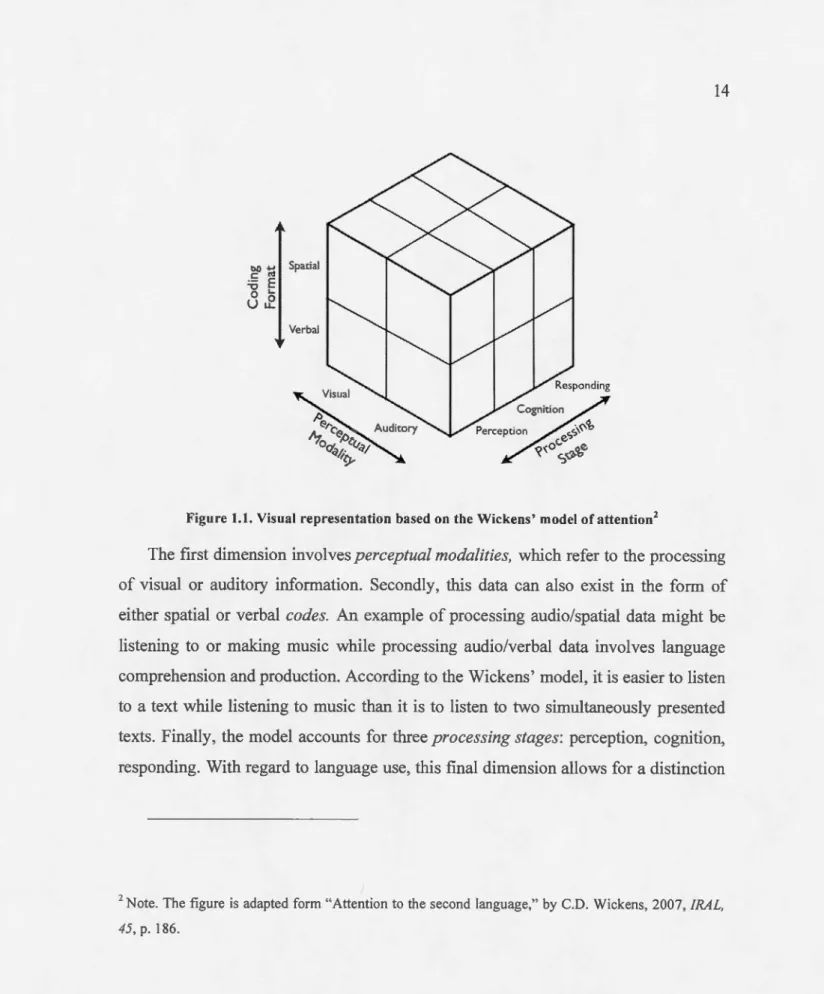
Attention and second language speech production : the relationship between attention and the production of self-initiated self-repairs
Texte intégral
Figure


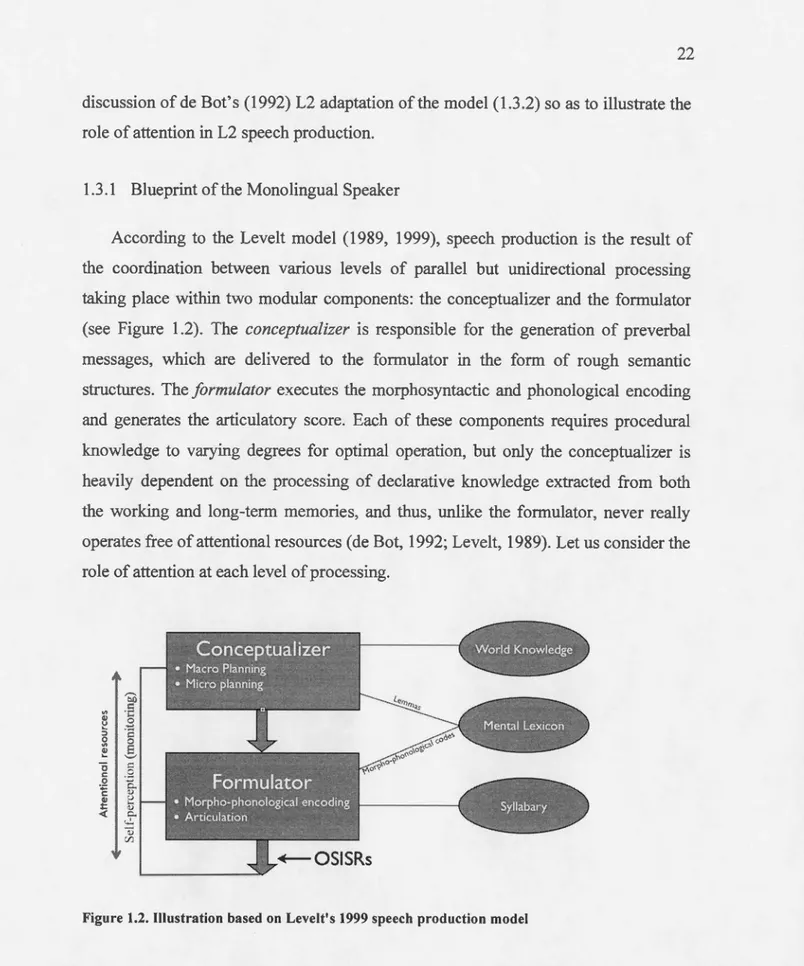
Documents relatifs
For FG (and also other cognitively-oriented approaches like the “Givenness Hierarchy” of Gundel, Hedberg & Zacharski, 1993), the context-bound Topic functions are predicated
In this work we presented a model to describe the interdependent relationship between farming ac- tivity and biodiversity on farmed land where, besides considering the negative
These different approaches to language contact lead us to distinguish two different stages of the description of linguistic dynamics: Firstly, the elaboration of social
Concerning the first factor, results are shown in table 6 (where S8 indicates the percentage of referring expressions of a given syntactic type in the eighth session of Mr. S., S9
The aim w as to study how statements about strategy w ere structured and how , in turn, they w ere contributing to the on-going structuring process of the field (M ounoud 1997;
The model designed (see Figure 1) and tested for the DDI-2013 Relation Extraction task in- cludes the following layers: three parallel em- bedding layers: one with pre-trained word
Manon Cassier, Julien Longhi, Damien Nouvel, Agata Jackiewicz, Jean-Yves Antoine, Anaïs Lefeuvre-Halftermeyer1. To cite
This paper reports a novel method for robot localization based on visual attention. This method takes advantage of the saliency-based model of visual attention at two different