Resistive Non-Volatile Memories Characteri-zation by Conductive Atomic Force Micros-copy (C-AFM) in Ultra-High Vacuum Environment
Texte intégral
Figure
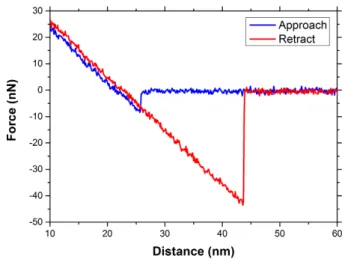
Documents relatifs
Consequently, in order to compare our results in LiCl-LiF with pure fluoride salt, instead of listing ap- parent redox potentials, the difference between reduction peak po- tentials
3 Quelques Objets de Access (en bref) Structure de Access Base de Donn´ee Ensemble d’enregistrements Champ 4 Devoir maison Composition
Widgets & layout Utiliser l’XML pour le layout Labels, boutons & champs
It is evident that in our NB-IoT NTN scenarios with LEO orbit, due to the high-speed movement of the satellite, the relation of users inside a cell (either Earth-fixed or
When the sweeping frequency increases the oxide capacitance begins to be d and the applied voltage will rapidly increase across the polymer layer. The increase
With on/off ratio as high as 10 3 , a large retention time and good cycle endurance, the nanoparticles based device is a serious candidate to replace currently available
The distribution of albedo neutrons was previously computed [1] using the FLUKA code associated to a simple atmospheric model and the GCR spectra modulated by
More precisely, the conditional Gibbs measure, the Coulomb gas on a Riemannian manifold, a new way to obtain already known results in the Euclidean space about Coulomb gases and