Toolpath planning optimization for end milling of free-form surfaces using a clustering algorithm
Texte intégral
Figure
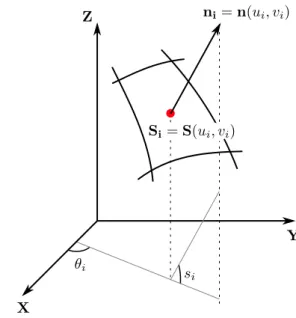
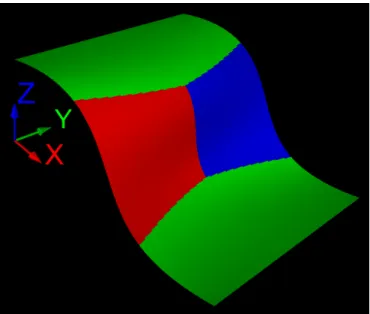
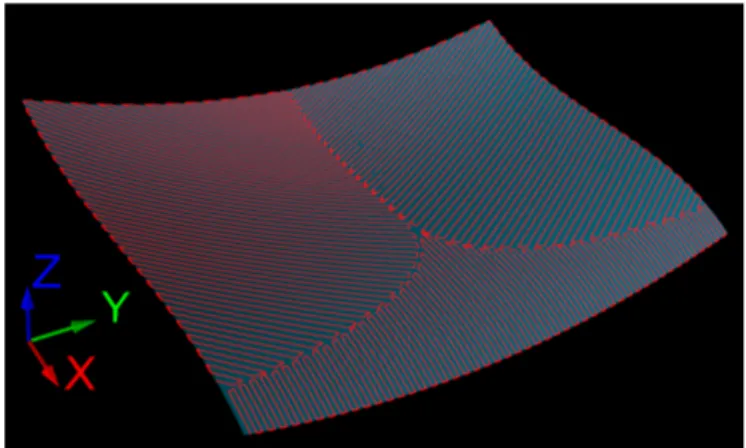
![Figure 3 shows an example of surface partitioning ob- ob-tained on the surface used in [3] with K = 3 and a 200 × 200 tessellation grid.](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/12425565.334137/4.892.456.829.453.670/figure-shows-example-surface-partitioning-tained-surface-tessellation.webp)
Documents relatifs
In fact, the best solution found by the GA, here called H-GA, uses only 31% of the dimensions from the canonical version of the descriptor and still achieves a similar performance.
Once a type of production is categorised by the two main factors (quantity and number of batches) its optimal dispersion can be obtained using the genetic algorithm with
Bartlett’s test for the equality of variances is used since long for determining the number of factors to retain in the context of a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [3]. We show
Although the decrease in the number of teeth can provide a greater range of stability, as all other parameters were considered constant, stress on the tool in this new scenario is
La mobilité et l’énergie interfaciale des joints de grains sont cruciaux pour décrire la croissance de grains, en effet on décrit généralement la vitesse (~ v) d’une interface
High sensitivity of 32 nA/ppb and low detec- tion limit of 0.4 ppb were achieved under short deposition time of 40 s, demonstrating favorable capabil- ity of proposed
The same DTBM-SEGPHOS-based CuH catalyst was also reported to effect the anti- Markovnikov hydroamination of terminal alkenes to generate linear aliphatic amines (Scheme 9).. [6b]
Because of no improvement after 2 weeks, malignancy was sus- pected, and 18-FDG-PET-CT was performed ( Fig. 1 a) showing intense FDG uptake affecting mediastinal and hilar lymph