Hierarchical representation of complex systems for supporting human decision making
Texte intégral
Figure
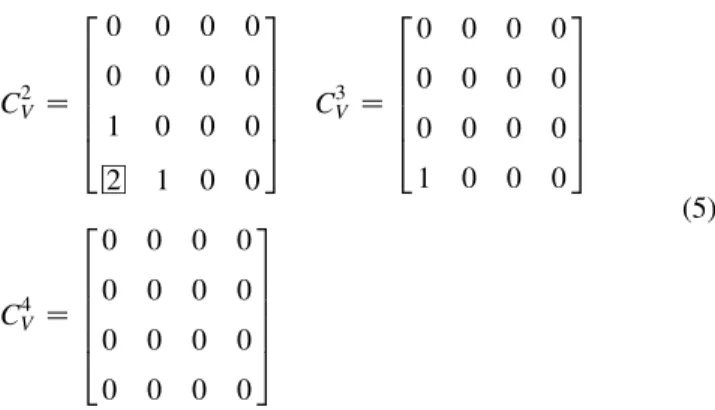

Documents relatifs
We present the framework and its hierarchical model by way of assessing the susceptibility of a safety-critical system to intentional hazards, con- sidering criteria of diverse
Unit´e de recherche INRIA Rennes, Irisa, Campus universitaire de Beaulieu, 35042 RENNES Cedex Unit´e de recherche INRIA Rhˆone-Alpes, 655, avenue de l’Europe, 38330 MONTBONNOT ST
Concerning the extraction of complex urban structures such as urban blocks and urban districts, we have compared the obtained results to those presented in [6], where a
In this paper we present a new transformation of any general basic belief assignment (bba) into a Bayesian belief assignment (or subjective probability measure) based on
Several difficulties arise as soon as these two non-conforming grids have to interact in the same physical problem, and accurate methods are presented for each
ISI team works in the context of design of complex systems by improving development life-cycle processes, particularly requirement en- gineering & management, modeling
X 1 Reliability Measures the capability of the method to yield the same RUL prediction quality, when different analysts apply it on similar sets of data related to