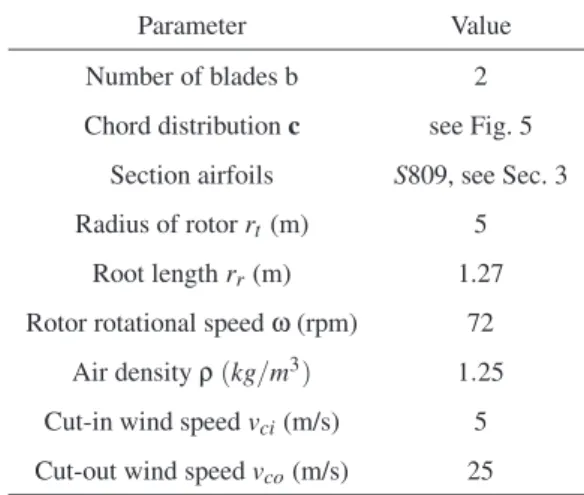
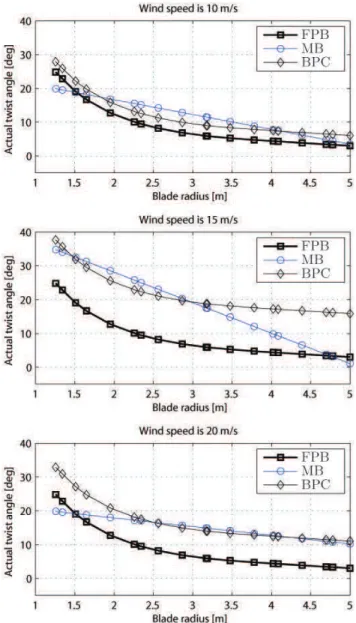
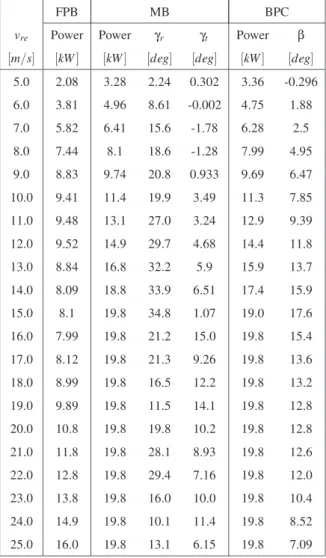
A Simplified Morphing Blade for Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines
Texte intégral
Figure
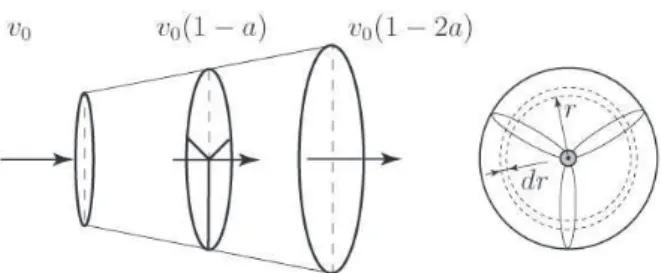

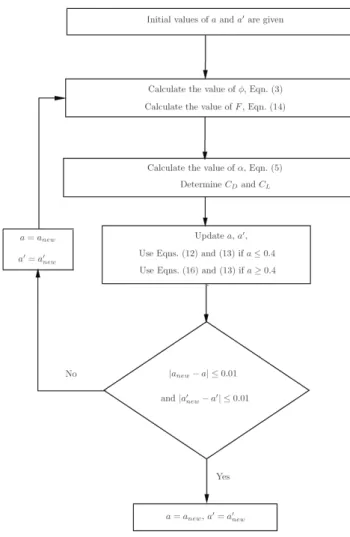
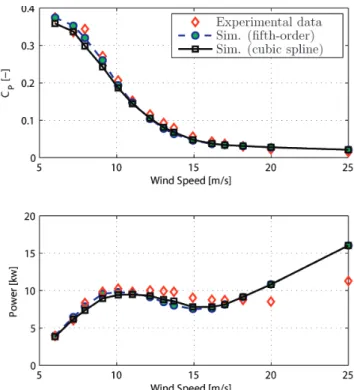
Documents relatifs
Indeed, the proposed solution to the problem of wind turbine maximum power point tracking (MPPT) control strat- egy relies on the estimation of the aerodynamic torque using a
The designed controller must be able to adjust the torque of the generator and as well the pitch angle of the blades in order to adapt the rotational speed of the turbine which
The degraded ROG based FTC modify the set-points and add an offset to the control inputs after fault occurrence in order to accommodate the fault with acceptable degraded
For the highly sensitive Leda clays and varved clays described by this paper, the field vane has yielded more consistent and somewliat higher undrained shear
For example, in a recent review of programs worldwide, Gentilini et al (2014) find that 119 developing countries have implemented at least one type of unconditional
This study shows that the geometrical thickness of clouds has a greater influence than the optical depth on the mean RHice determined over standard pressure layers from AIRS,
This paper presents the characteristics of a horizontal variable speed wind turbine, the state space model of the system and the design of a (sub) optimal H
In the above rated region, the pitch angle and the electromagnetic torque are the control variables that are used to reduce the structural loads and to maintain the