A domain decomposition approach to finite-epsilon homogenization of scalar transport in porous media
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
The main aim of this study was to com- pare the proteomic profile of macrophages from CD patients with and without anti-TNFα treatment, to those from ulcerative colitis (UC)
This study has demonstrated that loading of pl-NP, specifically of amino-functional carbon dots, from dispersion state into the virtually fully interconnected void system of
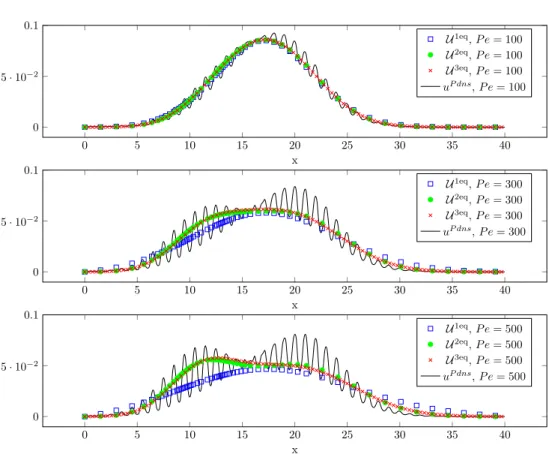
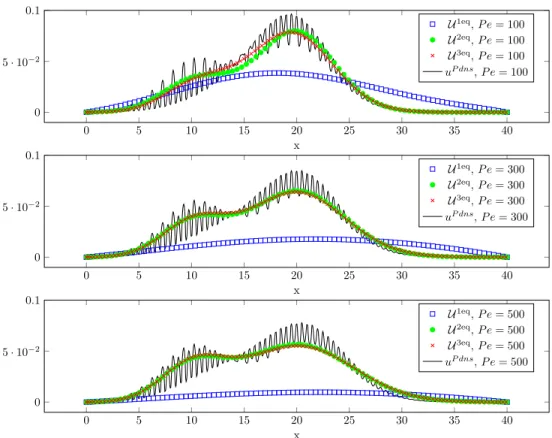
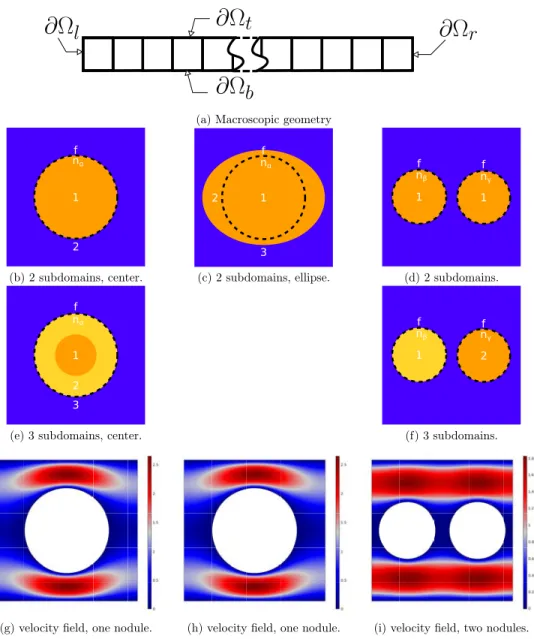
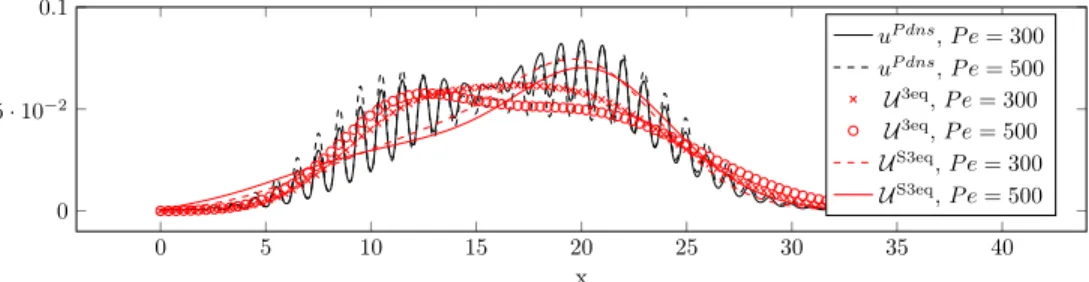
F ollowing [10℄, the hydrodynami dispersion is the averaged ma ros opi pi ture of the motion of the tra er parti les through the pore stru ture and of the hemi al rea tions of
Homogenization of the linearized ionic transport equations in rigid periodic porous media.. Grégoire Allaire, Andro Mikelic,
Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of
Of interest here is the date of the last HIV test performed among those individuals who reported having been tested at least once in their lifetime. To study
Our results suggest that learning within the semantic space is necessary, but not sufficient, for subjects to unlearn their Pavlovian bias, and that other task features, such
AAS, anabolic–androgenic steroid; ADT, androgenic deprivation therapy; AF, atrial fibrillation; Ais, aromatase inhibitors; APD, action potential duration; BrS, Brugada syndrome;