Nonlocal Mumford-Shah Regularizers for Color Image Restoration
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
We define here our proposition that combines a fundamental gener- alization of the monogenic signal to color with the monogenic wave- lets described above. The challenge is to avoid
Spatial-Frequency Domain Nonlocal Total Variation Model In order to better recover oscillating patterns in images such as microtextures, and to get a truly nonlocal denoising scheme,
Contributions and outline – In this paper, we propose a new variational model and a proximal algorithm with con- vergence guarantees for joint image denoising and contour
The first one, which we already encountered in the binary model in [15], is that, due to the presence of the fidelity term, we no longer have the conservation of mass, i.e., of
’variation ratio gain’, which is aimed to prove theoretically the significance of color effect on low-resolution faces within well- known subspace face recognition frameworks.
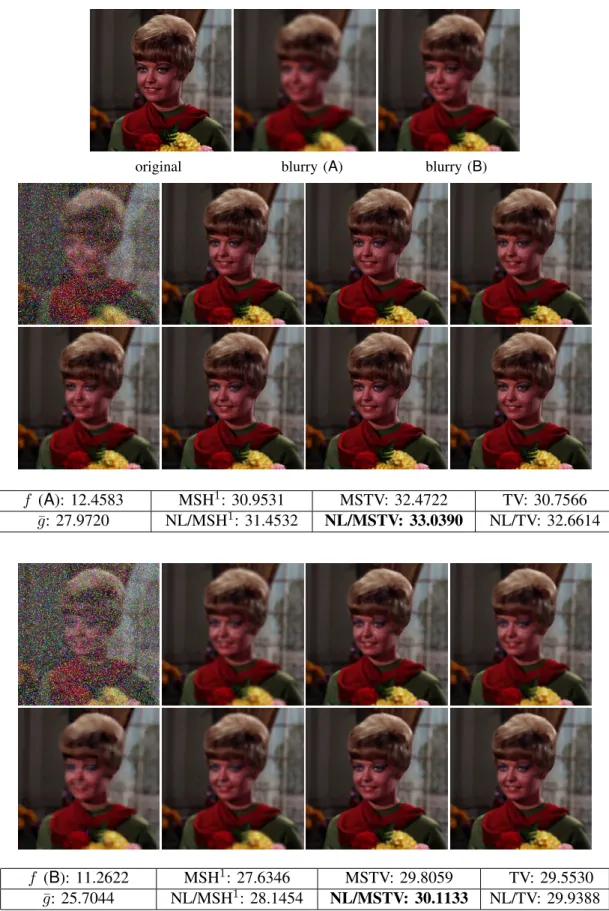
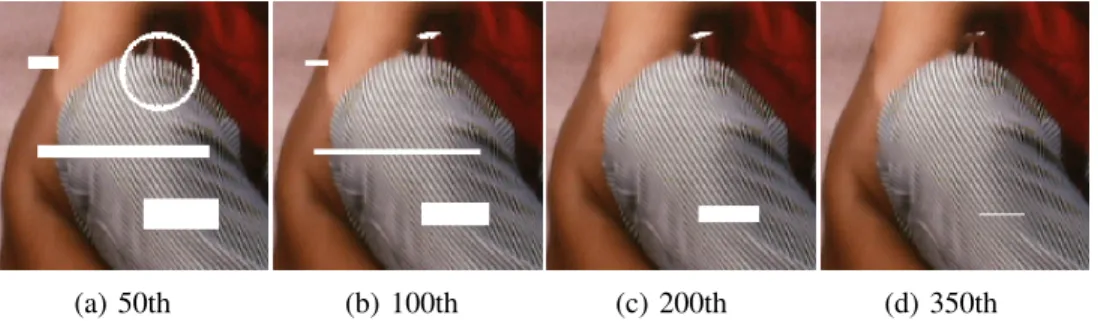
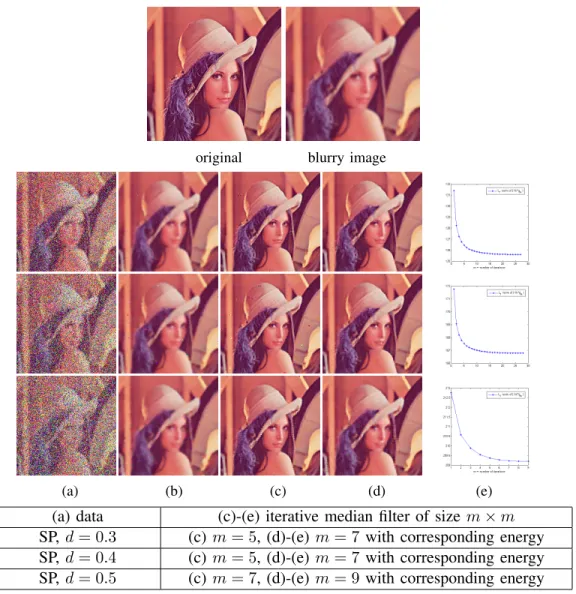
In this paper, we are interested in addressing the vectorial (color) image restoration problem through the minimization of a unique criterion that takes benefit of a vectorial
Table 5: Signal to noise ratio of the Y color information con- tained in G and G n channels, θ y/g denotes the geometric angle between the y color axis and the raw G axes of the
Table 5: Signal to noise ratio of the Y color information con- tained in G and G n channels, θ y/g denotes the geometric angle between the y color axis and the raw G axes of the