Assessment of damage and residual load bearing capacity of a concrete slab after fire: Applied reliability-based methodology
Texte intégral
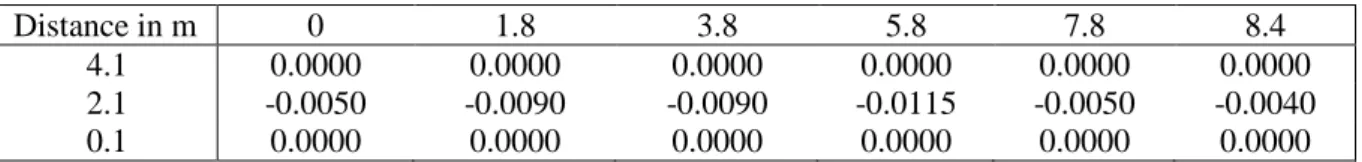
Figure



Documents relatifs
Hadge [22] has used a similar model to predict the pore pressure increase in cyclic triaxial tests of saturated sand; the proposed model in this thesis uses the
Here, we use momentum-resolved electron energy loss spectroscopy (k-EELS) to perform the first experimental demonstration of high-k modes and hyperbolic Cherenkov radiation in
92 Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge MA, United States of America 93 Group of Particle Physics, University of Montreal, Montreal QC, Canada.
The DES su- perluminous supernova hosts are similar in stellar mass to the PS+ and PTF samples, while the rapidly evolving tran- sient hosts are somewhat different to all of the
Relationship between the resting parasympathetic vagal tone and the evening salivary cortisol in controls, Crohn’s disease (CD) and Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients.. A
In this section, we characterize stationary equilibria of the English auction satisfying the NITS condition when advisors are biased toward overbidding. Equilibirum communication in
Then mice were subcutaneously injected with a first dose of anticonvulsants [carbamazepine (CBZ) 10 mg/kg, gabapentin (GBP) 30 mg/kg or pregabalin (PGB) 10 mg/kg] or saline and
lesterol FSR, caused by either high dietary choles- terol levels (as for breastfed infants) or low intake of dietary cholesterol (typical of formula-fed infants), could





