Arrival Time Statistics in Global Disease Spread
Texte intégral
Figure
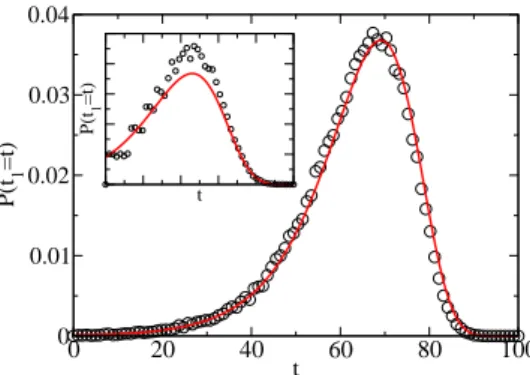


Documents relatifs
Videotaped lessons of a model on energy chain, from two French 5 th grade classes with the same teacher, were analysed in order to assess the percentage of stability as
Bounded cohomology, classifying spaces, flat bundles, Lie groups, subgroup distortion, stable commutator length, word metrics.. The authors are grateful to the ETH Z¨ urich, the MSRI
But for finite depth foliations (which have two sided branching), there are many examples where it is impossible to make the pseudo-Anosov flow transverse to the foliation [Mo5] and
Delano¨e [4] proved that the second boundary value problem for the Monge-Amp`ere equation has a unique smooth solution, provided that both domains are uniformly convex.. This result
In Section 7, by using H¨ ormander’s L 2 estimates, we establish the local L 2 closed range property for (0) b with respect to Q (0) for some weakly pseudoconvex tube domains in C n
The phasing of precession and obliquity appears to influence the persistence of interglacial conditions over one or two in- solation peaks: the longest interglacials are
We prove that there exists an equivalence of categories of coherent D-modules when you consider the arithmetic D-modules introduced by Berthelot on a projective smooth formal scheme X
In these applications, the probability measures that are involved are replaced by uniform probability measures on discrete point sets, and we use our algorithm to solve the