Protective Effect of Resveratrol against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Enhanced High Energy Compounds and eNOS-SIRT1 Expression in Type 2 Diabetic Female Rat Heart
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
Greater impairment of energy metabolism and coronary flow in type 2 diabetic female rats than in male during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.. Desrois Aix Marseille Univ,
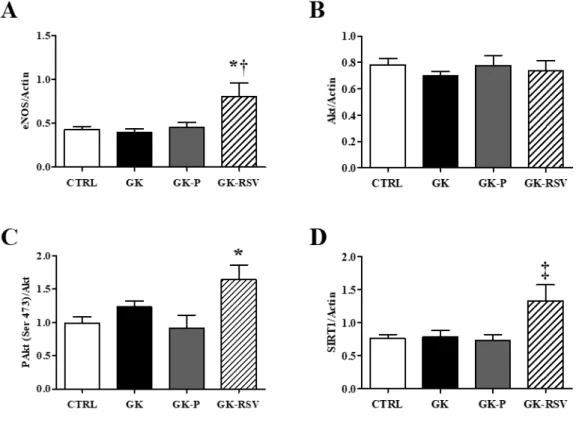
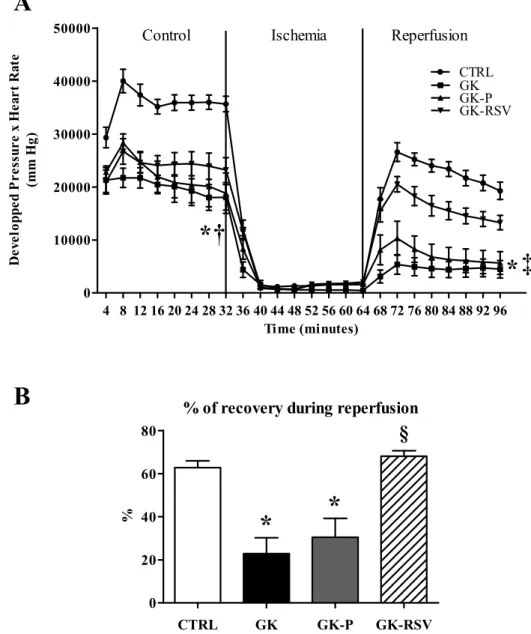
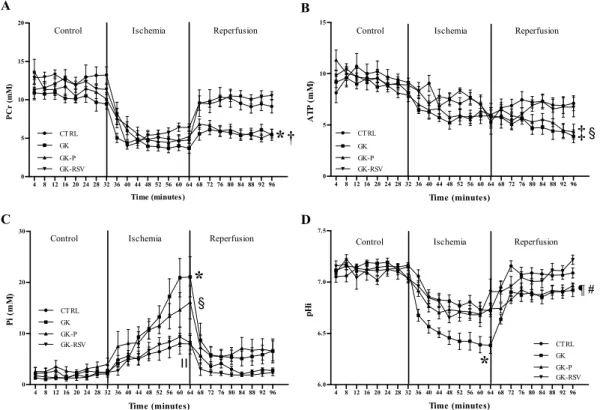
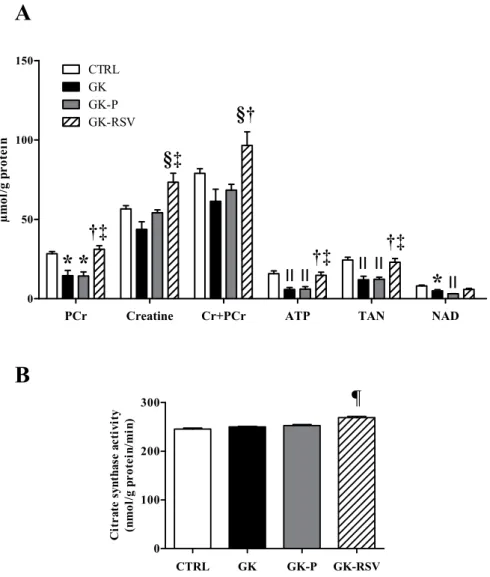
Resveratrol improves mitochondrial energetic pathway and endothelial function in type 2 diabetic female rat heart submitted to ischemia-reperfusion injuryN.
Modification of cardiac morphology was associated with impaired myocardial sensitivity to ischemia-reperfusion injury in a diet-induced metabolic syndrome model.. 53rd Annual Meeting
Today, among numerous cardioprotective strategies used to prevent deleterious myocardial remodeling associated with several pathological states and/or to reduce the vulnerability of
To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to investigate the effects of prolonged exposure to simulated urban environmental CO pollution on myocardial sensitivity to I/R.
From here, several injury cascades are activated, including activation of cell death programs like apoptosis and (regulated) necrosis, endothelial dysfunction implicating
We have demonstrated, both in vitro and in vivo models of ischemic stress as it occurs during cold ischemia, that kidney epithelial cells subjected to glucose deprivation
Infarct size (expressed as percentage of the area at risk) measured in wild-type (WT) and ob/ob mice subjected to 30 min of coronary artery occlusion and 24 h of reperfusion in