Genome-wide association study identifies novel restless legs syndrome susceptibility loci on 2p14 and 16q12.1.
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
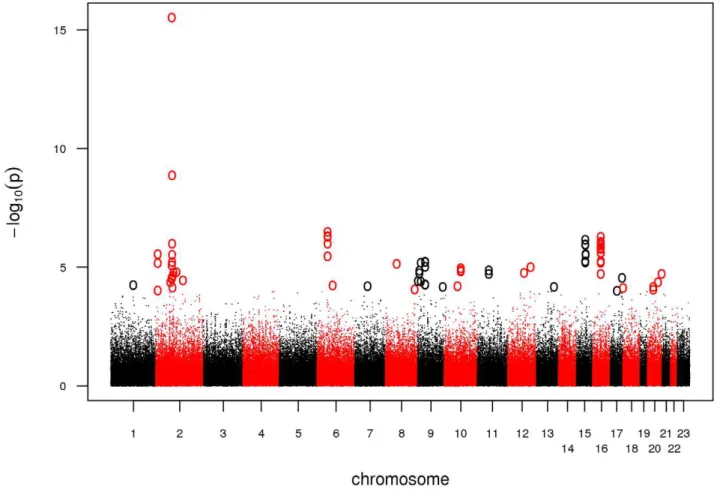
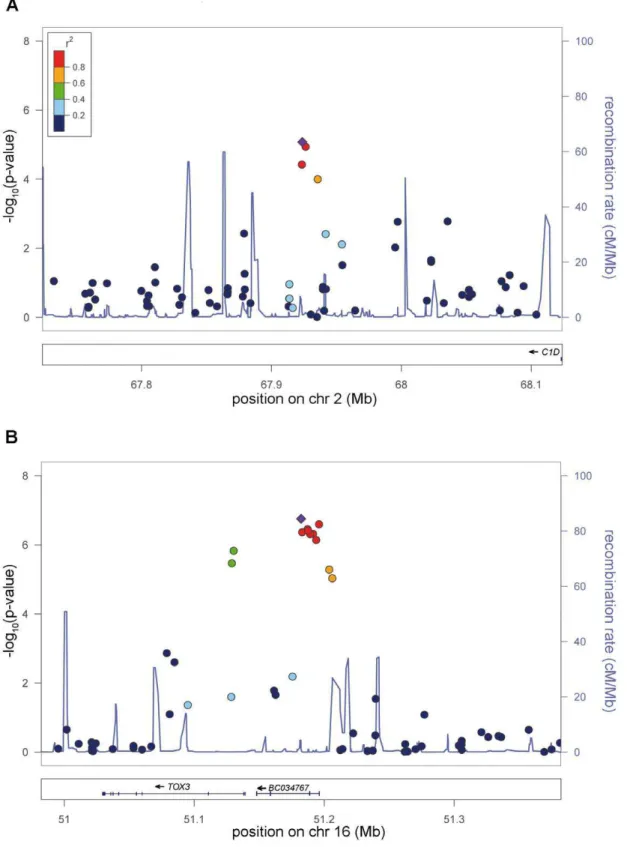
SNPs at five distinct new loci showed consistent evidence of replication, and meta-analysis of all 13,838 cases and 110,275 controls from the GWAS and replication series
Almost all genes so far identified in all forms of hearing loss are those directly related to hearing as qualitative traits (i.e. disease genes mainly involved in monogenic
70 Department of Adult Psychiatry, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland 71 Zorg op Orde, Leidschendam, The Netherlands 72 Department of General Internal
Expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) analysis using RNA- seq data suggests that index SNPs in nearly half of the identified loci (20/44) are associated with cis gene expression
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
Joint genome-wide association study of progressive supranuclear palsy identifies novel susceptibility loci and genetic cor- relation to neurodegenerative diseases... Geschwind 1,3
Combined analyses showed independent association at the known HLA-DQB1 region and revealed associations at PSORS1C1 , TNIP1 , and RHOB loci, in agreement with a strong immune
In conclusion, GWAS breast cancer FGFR2, TNRC9, MAP3K1, and 8q24 loci are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and genetic variation in FGFR2 gene may predict