Enhancing power grid synchronization through time delayed feedback control of solitary states
Texte intégral
Figure
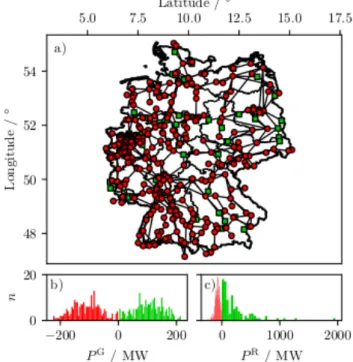
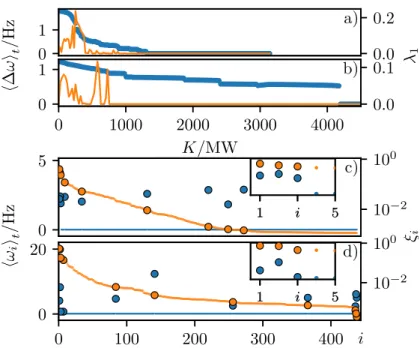

Documents relatifs
We conduct a geographical concordance analysis between the power grid and both the road network and built-up areas of the city of Grenoble.. We analyze the fractal behavior
In order to ensure secure and reliable services, initially, we have to understand the objectives and the security requirements to cope with before providing a comprehensive
Zombi is a multilevel simulator, where a species tree is first simulated, then genomes evolve along the branches of this species tree, and finally, sequences are generated
Since this data can be used to infer information about the daily activities of energy consumers, it is important that utility companies and their consumers employ privacy-
Simulation results show that, although a fuzzy-logic-controlled braking resistor can im- prove transient stability, the communication delay associated with the online calculation of
In recent years, many authors have revisited the design of linear and nonlinear observers by adding nonlinear dynamic filters on the output injection term to reduce the effect
The array efficiency PV represents the mean energy conversion efficiency of the PV array, which is the ratio of daily array energy output (DC) to the product of
We give lower and upper bounds on the chromatic number of the d th power of the face-centered cubic grid.. Note that a coloring of the d th power of graph is also called a