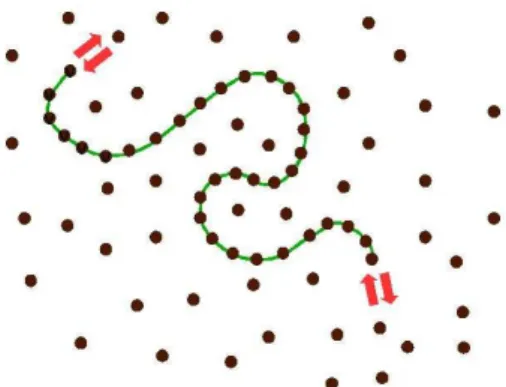
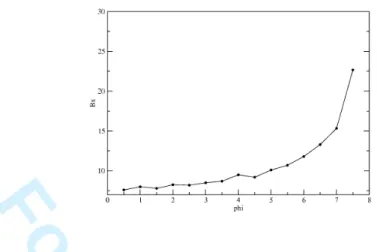
Mean Field and the Confined Single Homopolymer
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
Mean-field approximation of stochastic population processes in games 4 time intervals, gives the expected net increase in each population share during the time interval, per time
Unit´e de recherche INRIA Rennes, Irisa, Campus universitaire de Beaulieu, 35042 RENNES Cedex Unit´e de recherche INRIA Rh ˆone-Alpes, 655, avenue de l’Europe, 38330 MONTBONNOT
In this paper, we establish (1) the classical limit of the Hartree equation leading to the Vlasov equation, (2) the classical limit of the N-body linear Schr¨ odinger equation
The mean-field limit concerns systems of interacting (classical or quantum)
We deduced in [14] that sequences of approximate minimizers for (1.5) converge in the macroscopic limit to a ground state of the Pekar functional, thus showing that our model at
We prove the existence of the positronium, the bound state of an electron and a positron, represented by a critical point of the energy functional in the absence of external field..
The following theorem provides the link between the Liouville equation (73) satisfied by the velocity field v t (.) and the Cauchy problem (74) on a infinite dimensional
The Wigner measures method for the mean field problem is based on the analysis of a Liouville equation (or a continuity equation) which is derived naturally from the dynamics of