HAL Id: hal-01837386
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01837386
Submitted on 5 Jun 2020
HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access
archive for the deposit and dissemination of
sci-entific research documents, whether they are
pub-lished or not. The documents may come from
teaching and research institutions in France or
abroad, or from public or private research centers.
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est
destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents
scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non,
émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de
recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires
publics ou privés.
Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution - NonCommercial - NoDerivatives| 4.0
International License
A conceptual model describing plant roots - soil biota
interaction with tree ongoing experiments
Zhun Mao, Luis Merino Martin, Lorenzo Rossi, Alexia Stokes
To cite this version:
Zhun Mao, Luis Merino Martin, Lorenzo Rossi, Alexia Stokes. A conceptual model describing plant
roots - soil biota interaction with tree ongoing experiments. Global Soil Biodiversity Conference 2017
(GSBC2), Oct 2017, Nanjing, China. �hal-01837386�
A conceptual model describing
plant roots
-
soil biota
interaction
with three ongoing experiments
Core EASE - AMAP membersa: Zhun Mao, Luis Merino-Martín, Lorenzo MW Rossi, Alexia Stokes
1- The tangram schema
With: Mark Bakkerb,cand Martin Lukacd,e
bBordeaux Sciences Agro, UMR 1391 ISPA, 33170 Gradignan, France,cINRA, UMR 1391 ISPA, 33140 Villenave d’Ornon, France,dSAPD, University of Reading, RG6 6AR, UK,eFaculty of Forestry and Wood Sciences, Czech University of Life Sciences, 16521 Prague, Czech Republic.
The belowground community (roots, soil fauna and microorganism) plays a key role in maintaining an array of soil ecosystem functions and services. Such processes are complex and cover multiple disciplines. Here we design a conceptual schema that describes these links and can be applicable at multiple spatial scales for literature review and pedagogic activities.
2-
13C labelling experiment at Ecotron
•Experiment duration: 6 months
•3 chambers with controlled environmental conditions
CO2enriched
with 2%13C
•Two plant species: Medicago sativa versus Lolium perenne
•Two soils gathered from the same profile in Pisciotta (Italy): topsoil (0-30 cm depth) and subsoil (110-140 cm depth)
•Every pot is equipped with a plastic ring and dome to collect and sample soil respiration
Welcome to our lab in France ! 欢迎大家前来法国与我们交流、合作!
3- Experiment on eco-engineering plants
aAMAP, Inra, Ird, Cirad, Cnrs, University of Montpellier, 34398, Montpellier Cedex 5, France; Contact:alexia.stokes@cirad.fr(A. Stokes);maozhun04@126.com(Z. Mao).
20 cm
Cross section Plastic ring
Plastic dome Rubber cap for airsampling Water for air tight sealing Evidences: 1: Tilman et al. (1996) 2: Balvanera et al. (2006) 3: Balvanera et al. (2006) 4: Garnier et al. (2004) 5: Garnier et al. (2004) 6: Pratt et al. (2007) 7: Díaz et al. (2009) 8: Bardgett et al. (2014) 9: Stokes et al. (2009) 10 :Smith and Read (1997) 11: Kowalchuk et al. (2002) 12: Kunstler et al. (2012) 13: Balvanera et al. (2006) 14: Wagg et al. (2013)
Fig. The schema. (a) Real case and its (b) tangram form; (c) evidences (only one reference is selected for each link due to spacing limitation.
(a) (b)
(c)
With: Rémi Cardinaelf, Delphine Derrieng, Jacques Royh, Alexandrus Milcuh,i, Caroline Plainj,k, Giacomo Russol
fUPR Aida – CIRAD, Bâtiment 2 Avenue d’Agropolis 34398 Montpellier , France;gINRA, BEF, UR1138, Champenoux,
France;hEcotron Européen de Montpellier, Unité Propre de Service 3248, CNRS, Campus Baillarguet, F-34980
Montferrier-sur-Lez, France;iCNRS, Unité Mixte de Recherche 5175, Université de Montpellier, Université Paul
Valéry, École Pratique des Hautes Études, Montpellier Cedex 5, France;jUniversité de Lorraine, Ecologie et
Ecophysiologie Forestières, UMR1137, Vandoeuvre Les Nancy F-54500, France;kINRA, EEF, UMR1137, Champenoux
F-54280, France;lUniversity of Cassino, Via Di Biasio 43, 03043 Cassino (Fr), Italy.
We compare the carbon (C) sequestration potential of two types of soil used on the top of road embankments: organic soil and mineral soil. They differ in concentration of organic C and weathering level, and thus may have distinct microbial communities at rhizosphere and C sequestration capacity.
So il fu ng i So il Ba ct er ia
•Total of 36 pots with 6 replicates per treatment
With: Catherine Roumetm, Nathalie Frominm, Florian Fortm, Yves le Bissonnaisn, Olivier Taugourdeauo, Marie de Boisvilliersp, Michel Assenbaump,Claude Plassardq
mCNRS, Centre d’Ecologie Fonctionnelle et Evolutive (UMR 5175), 1919, route de Mende, 34293 Montpellier cedex;nUMR LISAH (Laboratoire d'Etude des Interactions entre Sol-Agrosystème-Hydrosystème), Montpellier;oVALORHIZ, Bat 6, Parc Scientifique Agropolis II ; 2196 Boulevard de la Lironde ; F34980 Montferrier sur Lez;pL’Avion Jaune, 1 Chemin de Fescau, 34980 Montferrier-sur-Lez;qUMR Eco&Sols (Ecologie fonctionnelle et Biogéochimie des sols et des agroécosystèmes), Montpellier.
Montpellier, Sept. 2016
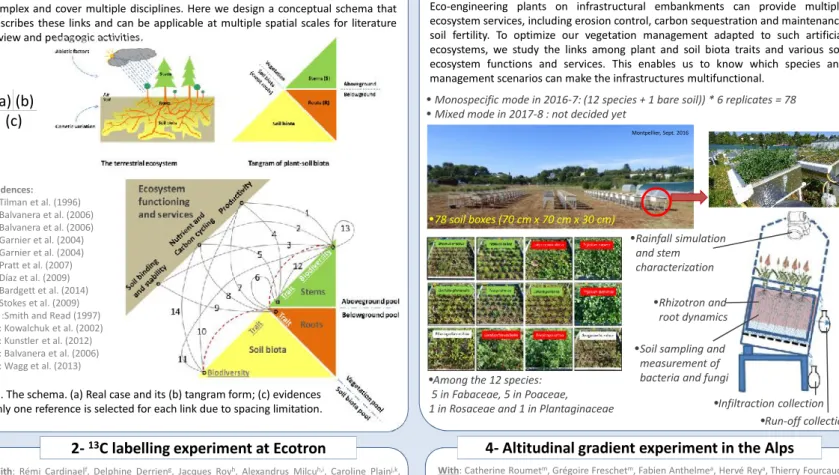
Eco-engineering plants on infrastructural embankments can provide multiple ecosystem services, including erosion control, carbon sequestration and maintenance soil fertility. To optimize our vegetation management adapted to such artificial ecosystems, we study the links among plant and soil biota traits and various soil ecosystem functions and services. This enables us to know which species and management scenarios can make the infrastructures multifunctional.
•Monospecific mode in 2016-7: (12 species + 1 bare soil)) * 6 replicates = 78 •Mixed mode in 2017-8 : not decided yet
•Run-off collection •Infiltraction collection •Rhizotron and root dynamics •Rainfall simulation and stem characterization
•Soil sampling and measurement of bacteria and fungi •78 soil boxes (70 cm x 70 cm x 30 cm)
•Among the 12 species: 5 in Fabaceae, 5 in Poaceae, 1 in Rosaceae and 1 in Plantaginaceae
4- Altitudinal gradient experiment in the Alps
Soil carbon sequestration is heavily influenced by input rates and decomposability of organic matter, transport to deeper soil horizons and physical protection in aggregate complexes. We investigate how elevation acts as an environmental filter on belowground plant traits and soil microbial and faunal communities. Simultaneously, we also examine soil functioning and services under land-use gradients due to forest management and tourism impacts.
With: Catherine Roumetm, Grégoire Freschetm, Fabien Anthelmea, Hervé Reya, Thierry Fourcauda
•A sampling transect from 1200 m to above treeline •Each of the 3 forest plots (25 x 25 m²) per altitude contains two model species: Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) H. Karst.) and bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) •Floristic inventory for understorey
species
•Soil, roots and earthworm sampling •Analyses of fungi and bacteria
•Forest logging is controlled by the state. •Soil quality is good in
undisturbed areas. •Mycorrhization is intense.
•Site description •Forest inventory