A posteriori error estimation based on potential and flux reconstruction for the heat equation
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
We present equilibrated flux a posteriori error estimates in a unified setting for conforming, noncon- forming, discontinuous Galerkin, and mixed finite element discretizations of
We consider the associated decision problem: given an execution graph, a deadline, and a bound on the energy consumption, can we find an execution speed for each task such that
The supplemental material provides the same comparison for all 100 materials in the MERL database: lobes from the measured data and lobes from the Cook-Torrance BRDF, us- ing
We derive an a posteriori error estimation for the discrete duality finite volume (DDFV) discretization of the stationary Stokes equations on very general twodimensional meshes, when
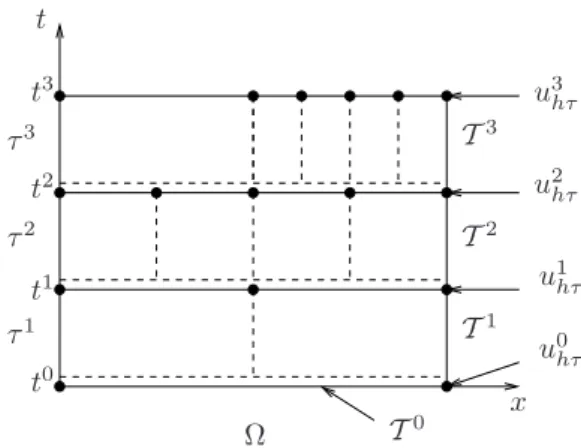
Key words: Mixed finite element method, global-in-time domain decomposition, nonconforming time grids, Robin interface conditions, a posteriori error estimate, stopping criteria..
Our estimates yield a guaranteed and fully computable upper bound on the error measured in the space-time energy norm of [19, 20], at each iteration of the space-time DD
We give an a posteriori error estimator for nonconforming finite element approximations of diffusion- reaction and Stokes problems, which relies on the solution of local problems
Polynomial robust stability analysis for H(div)-conforming finite elements for the Stokes equations. Elliptic reconstruction and a posteriori error estimates for parabolic