Calculation of Generalized Polynomial-Chaos Basis Functions and Gauss Quadrature Rules in Hierarchical Uncertainty Quantification
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
Another unique advantage of the proposed gPC method is that Sobol’s sensitivity indices to identify the influential inputs in the propagation of process uncertainty can be
Five of these models (intradermal or topical capsaicin, low- or high-frequency electrical stimulation, thermode-induced heat-injury) were found to reliably induce
Generally, CDF can be estimated in three ways: (a) analytical calculation (b) standard MC sim- ulation (c) meta-model MC simulation –i.e., genera- tion of an experimental design of
In this paper, we have compared the surrogate-assisted S- CMA-ES, which uses GP and RF continuous regression models, with s ∗ ACM-ES-k algorithm based on ordinal re- gression by
A two-stage surrogate modelling approach for the approximation of models with non-smooth outputs.. Maliki Moustapha,
Surrogate modelling for stochastic dynamical systems by combining NARX models and polynomial chaos expansions... S URROGATE MODELLING FOR STOCHASTIC DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS BY COMBINING
Si l'on pose la liberté comme la valeur de principe, telle que la religion vaut dans la mesure où elle la favorise, soit parce que la première est objet de la seconde, soit
As shown in Figure 2 , the accelerating field provided by the cathode penetrates into the drift region, providing the focusing of the ions into the holes of the PCB.. Operating at
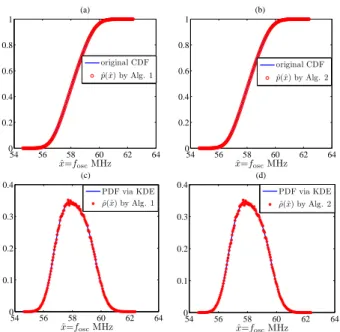
![Fig. 11. Probability density functions extracted by asymptotic probability extraction (APEX) [29], [30], compared with the results from kernel density estimation (KDE)](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14194540.478798/12.918.143.776.74.643/probability-functions-extracted-asymptotic-probability-extraction-compared-estimation.webp)