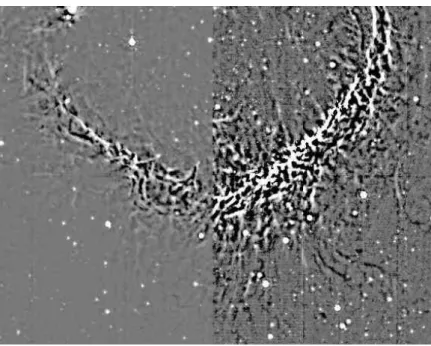
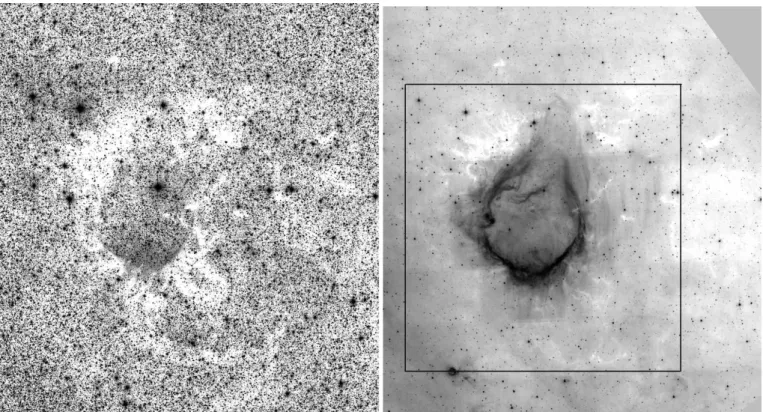
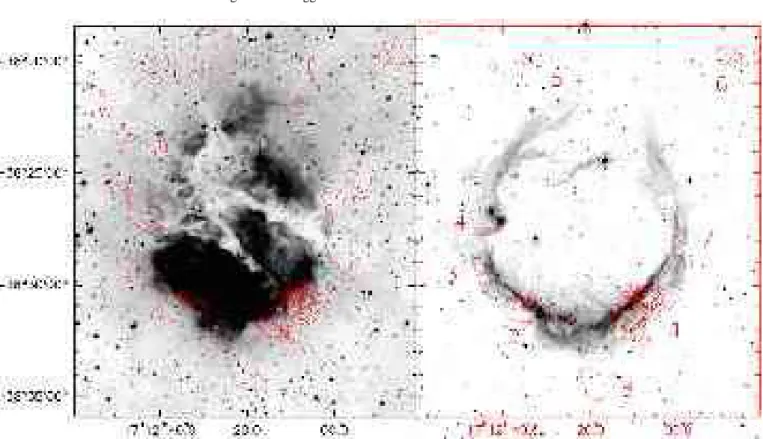
Triggered star formation on the borders of the Galactic HII region RCW 120
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
The six parameters describing the Kepler orbit (a, e, i, ω, Ω , and t 0 ), the distance, and the central mass, and the five coor- dinates describing the position on the sky and
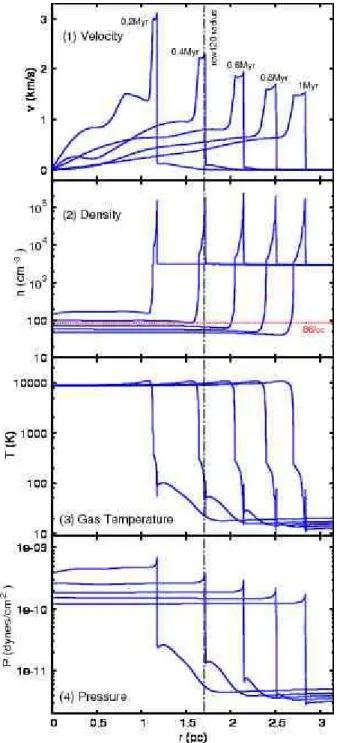
Here we present the results obtained for young compact sources observed towards the bubble H ii region RCW 120. Us- ing Herschel photometric PACS and SPIRE data, we re-examine
We demonstrated that it was possible to use the whole dataset (dead and living animals) to estimate the following: (i) the relative density – i.e., the density multiplied by an
3 Haplotype networks of MHC class II DR beta exon 2 alleles and of the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) control region (D-loop) at the nucleotide level for C.. Nodes are proportional to
There are only two classical class II B (β or light chain) genes for which the exon 2 sequence (which contains the polymorphic positions corresponding to the peptide-binding region)
We therefore down- sampled the NACO data into 100 bins with equal path lengths along the projected orbit (Fig. 4, middle) and gave these data in addition a lower weight of
sequence variation and evolution of MHC class I and class II DRB, DQA and DQB genes in the brown bear Ursus arctos to characterise the level of polymorphism, estimate the strength
HCN, H 13 CN, and N 2 H + lines split into a resolved set of hyperfine (hf) components, whose relative opacities are given by their Einstein coefficient for spontaneous decay and
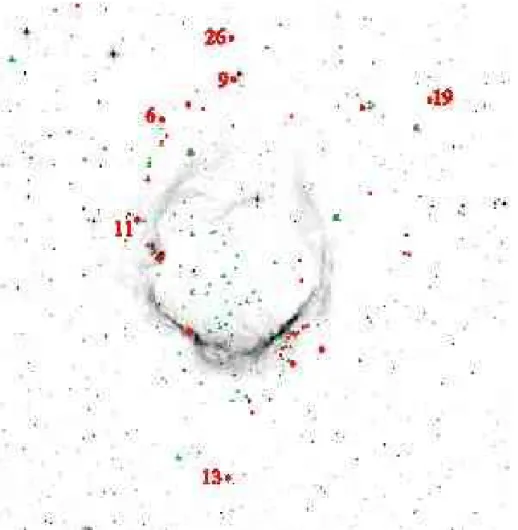
![Fig. 6. GLIMPSE colour-colour diagram, [3.6] − [4.5] versus [5.8] − [8.0], for the sources observed towards RCW 120](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14609549.545259/9.892.75.567.123.505/fig-glimpse-colour-colour-diagram-versus-sources-observed.webp)