Feature-based map merging with dynamic consensus on information increments
Texte intégral
Figure

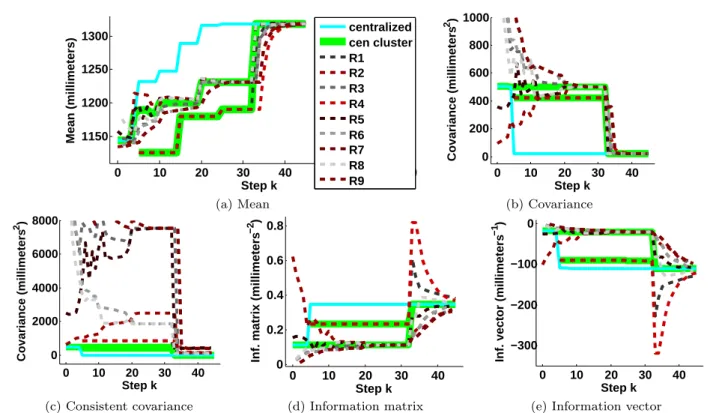
Documents relatifs
The idea of a map of a Web region is essentially that of representing in a concise way information in the region in terms of connectivity among a set of distinguished
Thus this operation has time complexity O(D selected + D included ) and in the worst case, when all regions are newly included in the resulting region, we cover the darts of the
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
In the definition phase, we have chosen to analyze researchers’ sci- entific productions and to position these productions in relation to themes from our state of the art, and to
We made this choice because “two scientific contributions that are at the core of NEMO’s research program are the foundational theory UFO (Unified Foundational
Clearly the pentagram map is invariant under the action of the projective group (linear on lifts), and therefore one is able to write it as a map on the moduli space of
Sushama Prasad, Yun Peng, and Timothy Finin Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department. University of Maryland Baltimore County email: !"$#
If a metric σ lies in GF (M ) but has some rank one cusps, its bending measured geodesic lamination λ has some compact leaves with a weight equal to π.. Thus we get that b GF is