Monotone and Consistent discretization of the Monge-Ampere operator
Texte intégral
Figure


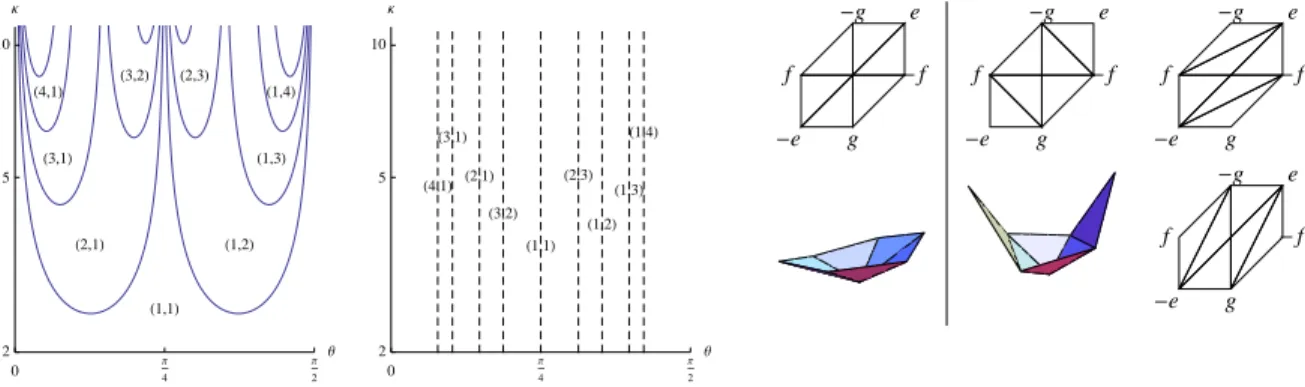
Documents relatifs
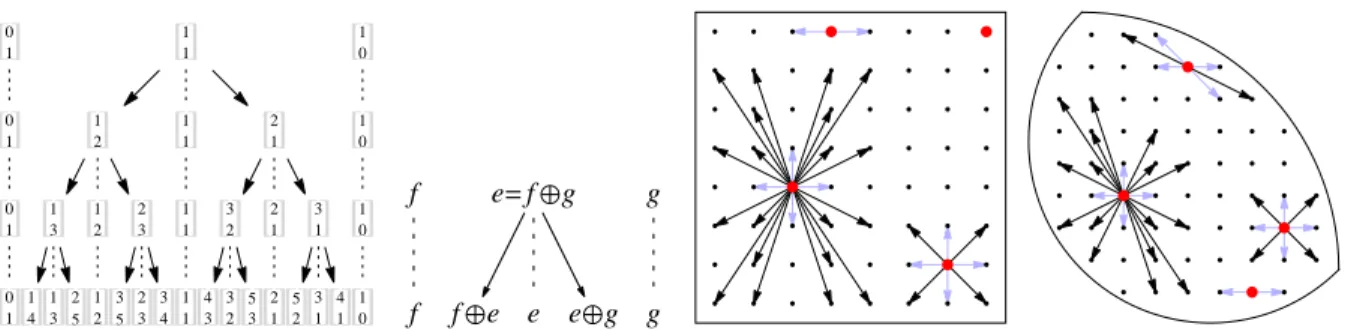
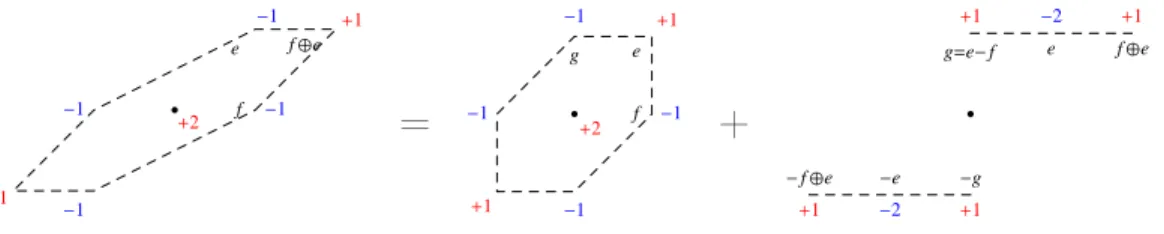
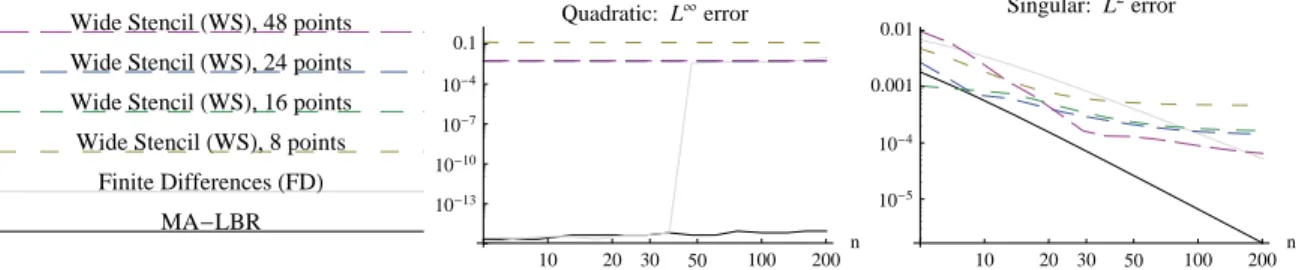
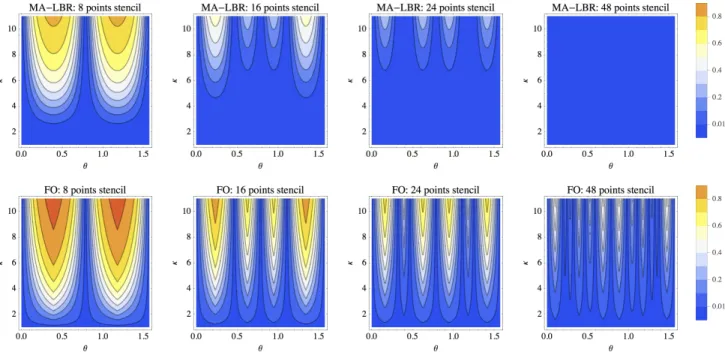
Instead of monotonicity and consistency of the scheme, the proof re- lies on three ingredients : specific properties of the LBR discretization of the Monge-Ampère operator
Key words: Variational formulation, non-symmetric mixed problem, mixed finite elements, gen- eralized saddle point theory, organic pollution.. 1 L.M.A.C., EA 2222, Universit´ e
In fact, for a given method defined in 1D, several parameters can vary in 2D and 3D, for example: • The mesh topology, which is a main point for the numerical
For the analogous discretization of the two-dimensional Stokes problem in the Cartesian case, Bercovier and Pironneau in [ 2 ] prove an inf–sup condition and Verfürth in [ 15 ]
Ainsi, l'analyse du gradient granulométrique sert à comprendre l'évolution longitudinale de la dynamique d'un cours d'eau et ses interactions avec les
Objective: To determine the optimal venous tubing diameter for adult cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) to improve gravity drainage and to reduce priming volume.. Methods: (A) Maximum
Keeping only the flux in (1.4) yields the primal formulation of the second order (or standard) method, while keeping only the current yields its dual formulation.. Various
We design adaptive finite differences discretizations, which are degenerate elliptic and second order consistent, of linear and quasi-linear partial differential operators