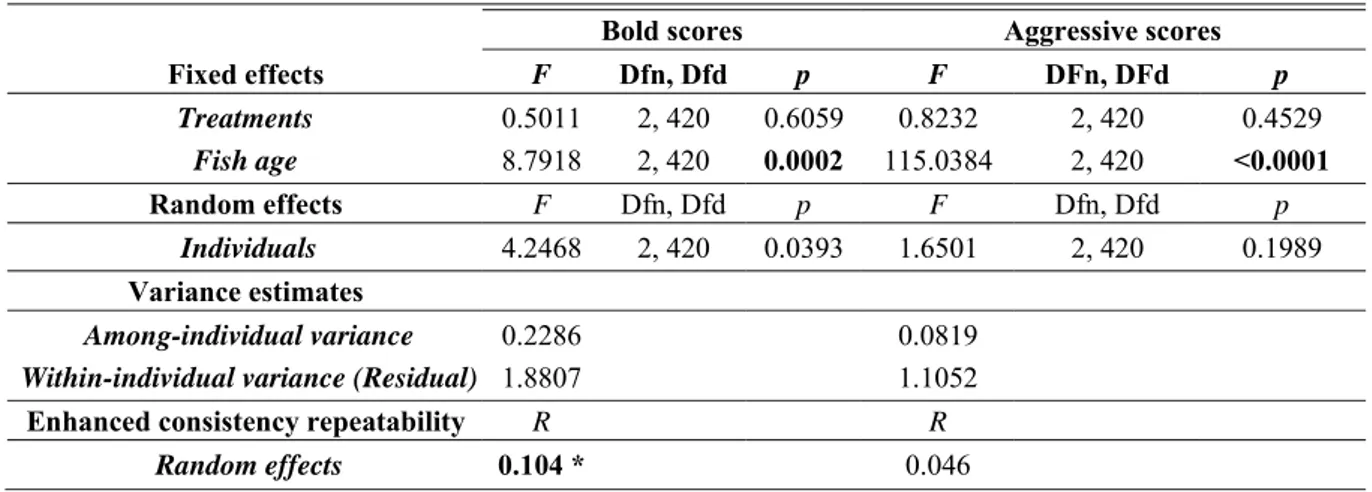
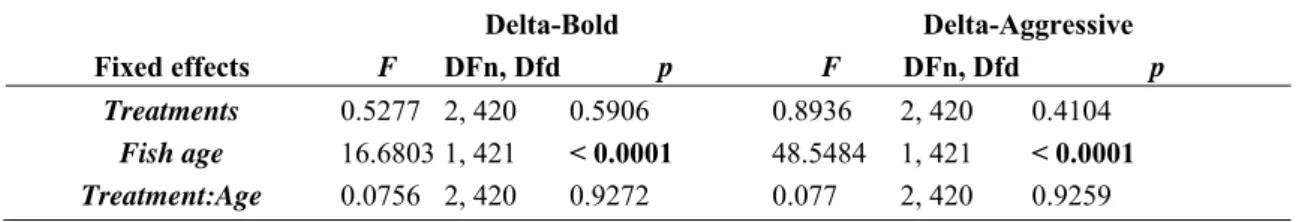
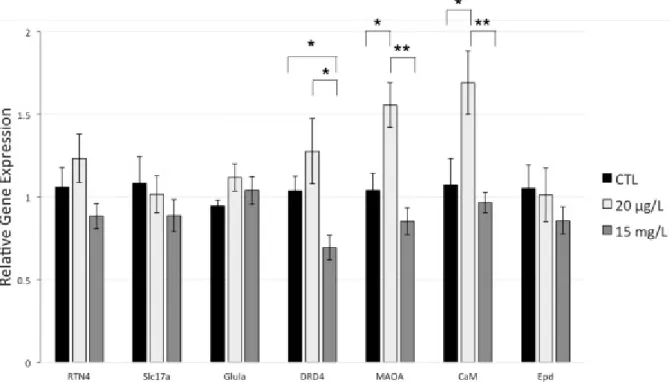
Behavior and gene expression in the brain of adult self-fertilizing mangrove rivulus fish (Kryptolebias marmoratus) after early life exposure to the neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA)
Texte intégral
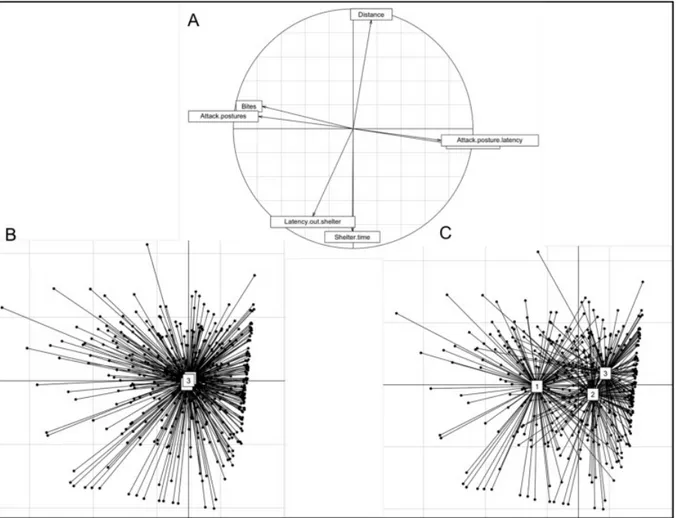
Figure


Documents relatifs
tagal mangrove zone, the density of denitrifying bacteria followed the same pattern than the density of total bacteria: the PW discharges induced an increase in the number of nosZ
Notamment, des échantillons provenant de diverses sources d’approvisionnement en eau au Canada, telles que les eaux de surface et les eaux souterraines, ainsi que l’eau
Western blot analyses of protease re- sistant prion protein in both distal sciatic nerves and the immunohistochemical de- tection of PrP Sc in the corresponding brain areas
The main assumptions about the mode of action of BMAA have emerged from in vitro toxicological studies carried out on different cellular models, notably rodent, leech and human
In conclusion, the results of this project should help to (1) give a clear picture of ALS distribution over 10 French counties; (2) identify clusters where environmen- tal factors
Prenatal stress and early-life exposure to fluoxetine have enduring effects on anxiety and hippocampal BDNF gene expression in adult male offspring... Running head: Developmental
Table 1 shows that having witnessed interparental violence in childhood was significantly associated with numerous family- level stressors, with much higher frequencies (at least
Exposure to interparental violence during childhood was significantly associated with all five adulthood mental health outcomes that were studied, with higher odds ratios for