Hyperelasticity with volumetric damage
Texte intégral
Figure
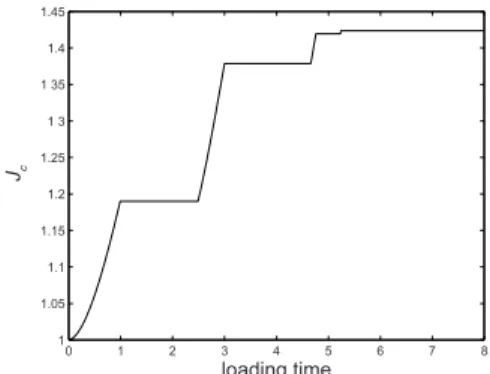
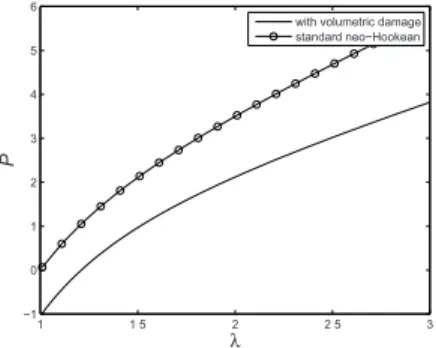
Documents relatifs
- We find that at low temperatures the optical absorption coefficient a of (Si4+, Fez+) doped YIG is changed substantially in an irreversible fashion by
The corresponding CL intensity profiles integrated along the growth direction shown in Figure 2(c), reveals the reduction in CL intensity after performing the line profile scan
Une dépendance simple et linéaire de A et J(q) en fonction du volume explique les effets de la pression et de la dilution par le La. Ces deux paramètres augmentent fortement
Si 5 lanternes identiques coˆ utent 216,25 $, combien coˆute chaque
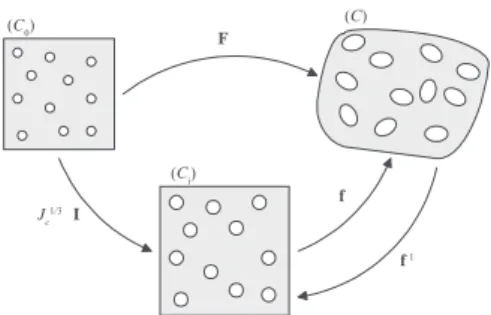
Continuum damage mechanics concepts are coupled to this hyperelastic formulation by following two different hypotheses, the principle of strain equivalence, introduced by Lemaitre
(i) to contribute to a more accurate assessment of glacier retreat, snow cover and climate change in Koshi Basin, Nepal; (ii) to have a better understanding of the contribution
The few studies that exist indicate that schools who adopt a comprehensive and integrated approach to meeting the whole-person needs of students, enjoy a high degree of
Fig. 4b corresponds to Fig. 4a but is based on merged data covering about three years. Corresponding results based on CLAES temperatures for 1992 are shown in Fig. 4c and com- pare