Effects of radionuclide contamination on leaf litter decomposition in the Chernobyl exclusion zone
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
• 1) Assess the effect of functional identity of litters (through functional group of litters and trait-based approaches) on litter decomposition by soil invertebrates.. • 2) Assess
We hypothesised a negative effect of increased drought period on soil biota (i.e. decrease of abundance and diversity) and on litter decomposition (i.e. decrease of leaf mass
Rates of leaf litter decomposition in streams are strongly influenced both by inorganic nutrients dissolved in stream water and by litter traits such as lignin, nitrogen (N)
Litter incubated in the experimental half decom- posed 15%–49% faster than litter incubated in the control half (RM ANOVA, P < 0.001 for stream half; Table 2), but
Specifically, we test if study type (laboratory versus correlative field studies versus manipulative field studies), identity of the nutrient added in stream manip- ulative studies
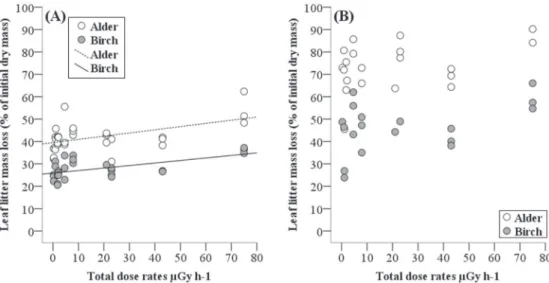
Summary of ANCOVA results of the effects of average total dose rates (ATDRs) absorbed by decomposers and soil physico-chemical characteristics (SoilPc; covariate) on
A. DALALYAN AND A.B. We study the problem of aggregation under the squared loss in the model of regression with deterministic design. We obtain sharp PAC-Bayesian risk bounds
National policy makers need to prioritize immunization serv- ices so that they compete successfully with other health services, donors need to provide support in ways that