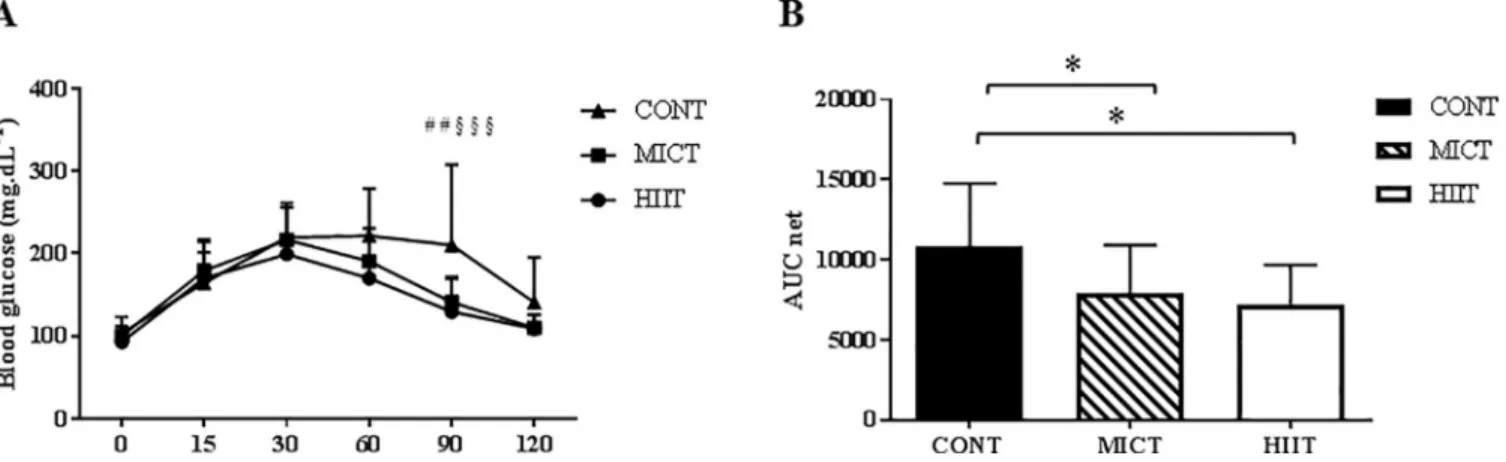
High intensity interval training promotes total and visceral fat mass loss in obese Zucker rats without modulating gut microbiota
Texte intégral
Figure




Documents relatifs
[r]
The diarrhoea ratio (Table 1 ) of the recipient piglets was significantly decreased compared with that of the control piglets (P < 0.05), and the daily number of
Carbohydrate analysis using specific chemical degradations, mass spectrometry, 1 H and 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance showed that this polysaccharide is a linear
ACHM, Animals Containing Human Material; ESC, embryonic stem cells; ICM, inner cell mass; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem
A reason for these open questions in the network in- formation theoretic framework, is that Gaussian ensembles are roughly the only ensembles that can be analyzed over
Experiments showed that the ratio of the 5/2 ultraharmonic to the 1/2 subharmonic for binary localization cavitation activity achieves 100% sensitivity and specificity for
To our knowledge ActivCollector is the first system of clinical data centralization and modelling of metabolic process available for the researchers in nutrition. His
The present study proposes the combined use of DGDR- and UKF-based methodologies to extract information from AP signals at baseline and under β-AS. Initial DGDR parameter estimates