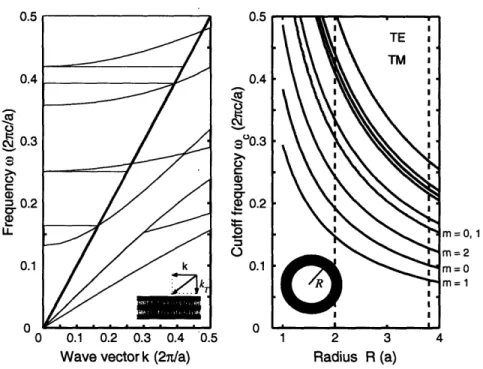
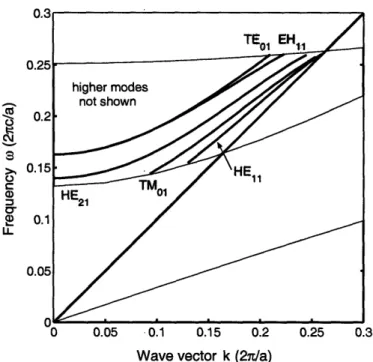
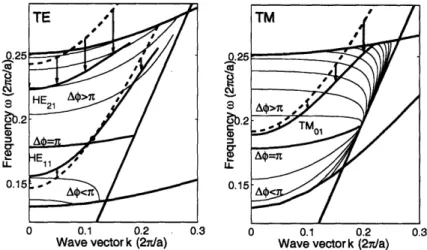
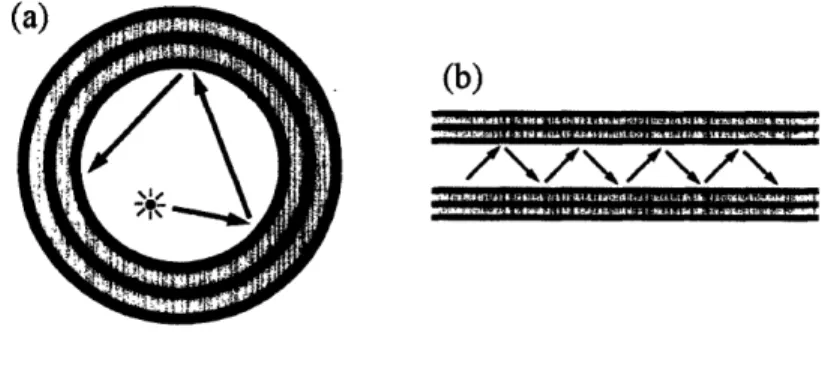
Cylindrical photonic crystals
Texte intégral
Figure


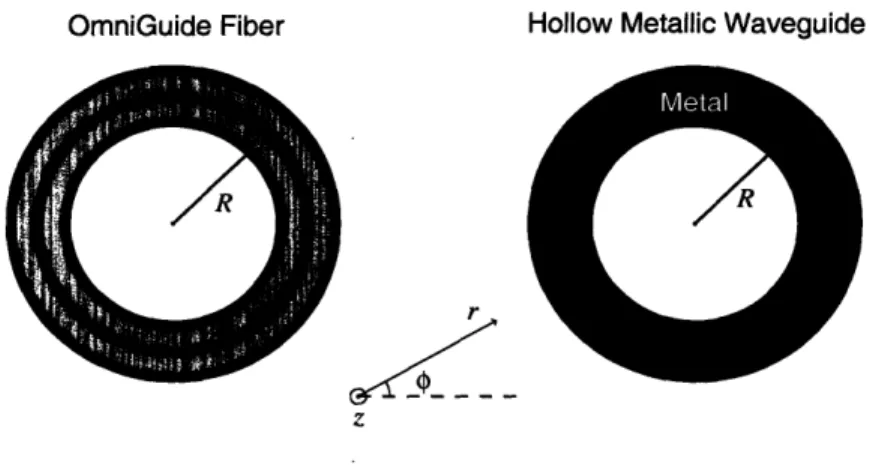
Documents relatifs
18–21 As we will show, it is pos- sible to design photonic materials based on dense assemblies of high refractive index, strongly correlated spherical par- ticles for which
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
In fact, the spatial averaging implicitly results in non-local macroscopic quantities in the sense that the macroscopic polarization at any given point does not depend only on
Fig. T is the period of the photonic crystal in both vertical and horizontal directions. R is the radius of the cylinders. b) Notations used in the text. ”A p ” referred to the p
Abstract—A high Q optical resonator and ultra-low losses of a silicon suspended waveguide, are experimentally measured and presented, in order to demonstrate the working of a
Abstract We study the spectral and scattering theory of light transmission in a system consisting of two asymptotically periodic waveguides, also known as one-dimensional
In this work we demonstrate an external optical control over the dissipative optomechanical coupling strength mediated by the modulation of the absorption of a quantum dot layer in
In the weakly resonant case the radiation is described by a transverse wave (dispersive) equation with moving source term localized where the main pulse is and which is responsible