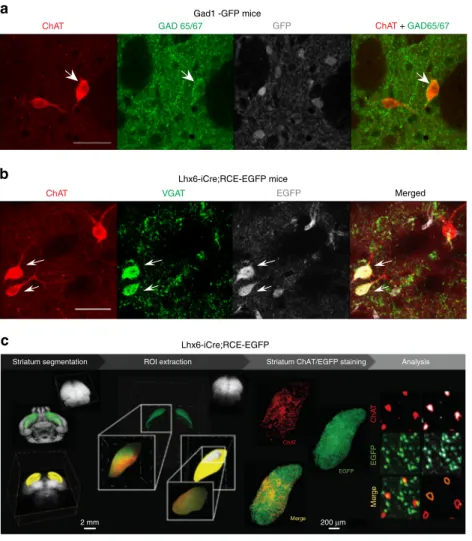
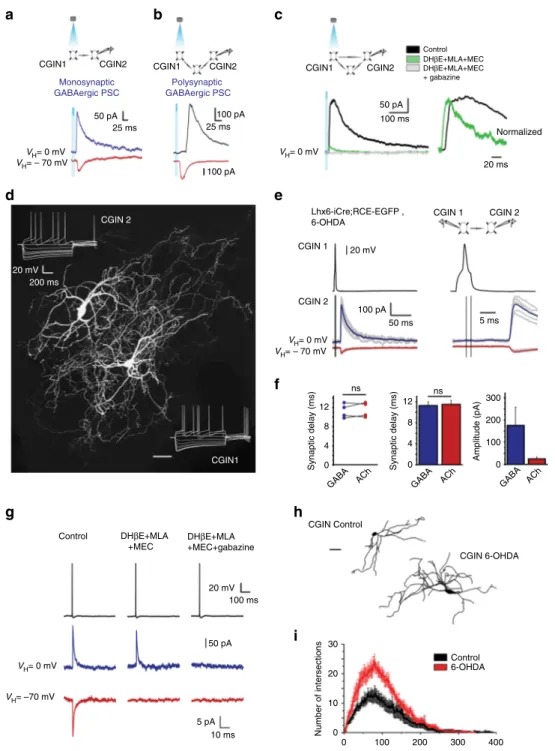
GABAergic inhibition in dual-transmission cholinergic and GABAergic striatal interneurons is abolished in Parkinson disease
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
In order to determine the concentration of selected genes within a biological sample, the hybridization experiments were performed under identical conditions to those described for
On average, FSI input resistance measured with small current steps in the presence of ethanol was, again, not significantly different from that observed in control solution
L’accès à ce site Web et l’utilisation de son contenu sont assujettis aux conditions présentées dans le site LISEZ CES CONDITIONS ATTENTIVEMENT AVANT D’UTILISER CE SITE WEB.
To sum up, the contributions of our paper are as follow: (i) we identify errors in previous work of Partush and Yahav [12]; (ii) we propose a new sound algorithm for the production of
coronal brain section of a VIPcre/tdTomato/GIN mouse shows VIP neurons in red, Martinotti cells in green and calretinin in blue in the primary somatosensory cortex (S1Tr).. (A)
More recently, it as been shown that the three types of striatal interneurons, choliner- gic, fast-spiking GABAergic and nNOS interneurons, were able to develop long-term
On the macroscopic scale, the in fl uence of CINs on behavior can be either immediate, due to the modulation of striatal output by CINs, or delayed/persistent, due to
This review will focus on the specific interaction between striatal ChIs and DA systems and the mechanisms underlying the regulation of striatal and basal ganglia function