2D Static Resource Allocation for Compressed Linear Algebra and Communication Constraints
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
In a previous work, the geometric degree of nonconservativity of such systems, defined as the minimal number of kinematic constraints necessary to convert the initial system into
Data Allocation Strategies for Dense Linear Algebra Kernels on Heterogeneous Two-dimensional Grids Vincent Boudet, Antoine Petitet, Fabrice Rastello, Yves Robert.. To cite this
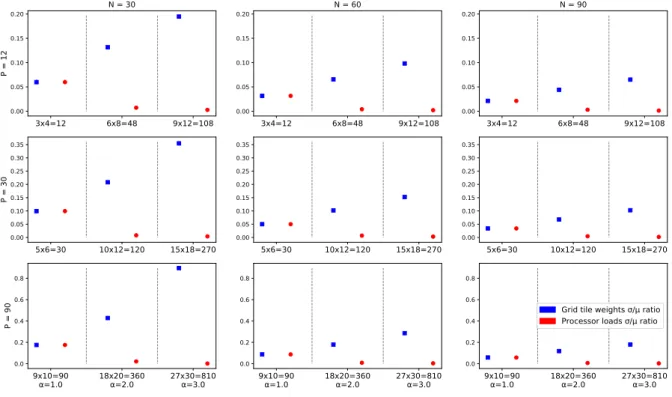
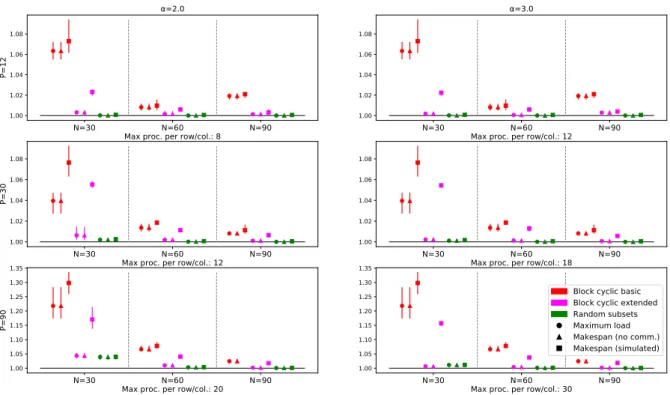
of queries is shown Fig. The speedup factor of the two strategies is illustrated in Fig. Not surprisingly, we find that the speedup factor is more significant when there
In the following subsections, we will compare the performance of the static and dynamic allocations for both codes C1 and C2, by measuring their execution time, number of
More importantly, we have shown that there does not exist any algorithm that is simultaneously an approximation algorithm for both makespan minimization and peak memory
The previous heuristic ParInnerFirst is motivated by good memory results for sequential postorder. Going the opposite direction, a heuristic objective can be the minimization of
These methods are based on the idea that to solve a robust optimization problem we can decompose the problem into a master problem (MP) and several adversarial separation