Contextual centrality: going beyond network structure
Texte intégral
Figure
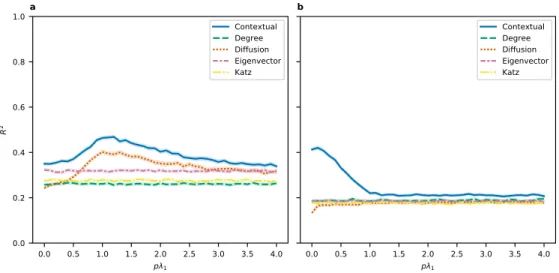
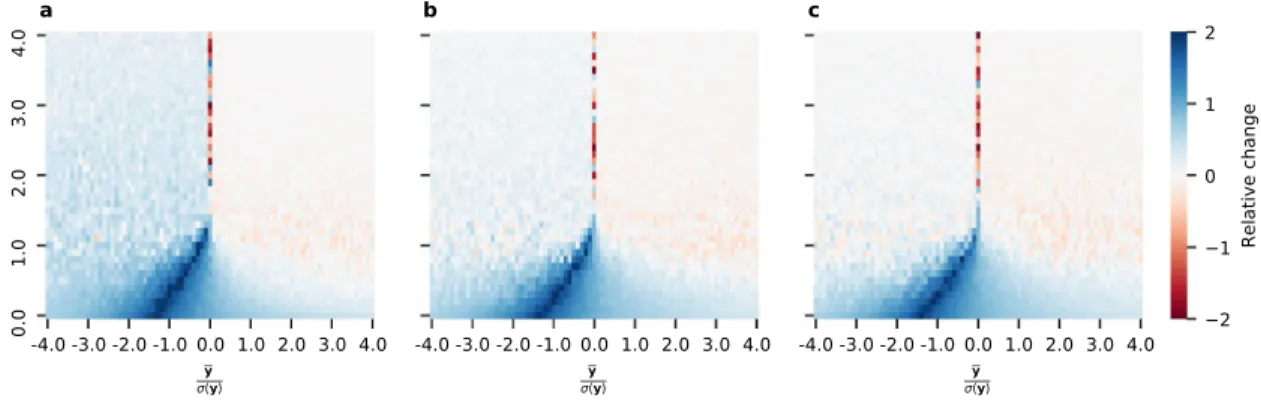

Documents relatifs
We conducted two types of experiments: in the first type we evaluate the quality of the solution produced by the greedy algorithm by measuring the approxi- mation ratio on
In order to evaluate the proposed centrality measure we computed the mint centrality for the first 200,000 blocks of the public bitcoin blockchain.. We then inspected the 50
To determine a variation of betweenness centrality we will use the methods of cooperative game theory using the model of the communication game developed by Myerson.. Cooperative
The well known concept of eingenvector centrality for graphs is extended to weighted multi-hypergraphs and we present a model instantiation for centrality analysis in
Section 3 introduces principles of net- work’s dynamic, dynamic evaluation of the neighbourhood of the selected author and our approach in the directed network created from DBLP
The modulus of the Overlapping Modular Betweenness centrality performs better than the standard measure with an average gain that ranges between 39% and 47% in networks
In this section, we analyze the evolution of the number of clusters when both threshold and the fraction of the top ranked nodes are combined and the size of the network changes.
Simulation results on different synthetic and real-world networks show that it outperforms Degree, Betweenness and Comm centrality in term of the epidemic size in networks with