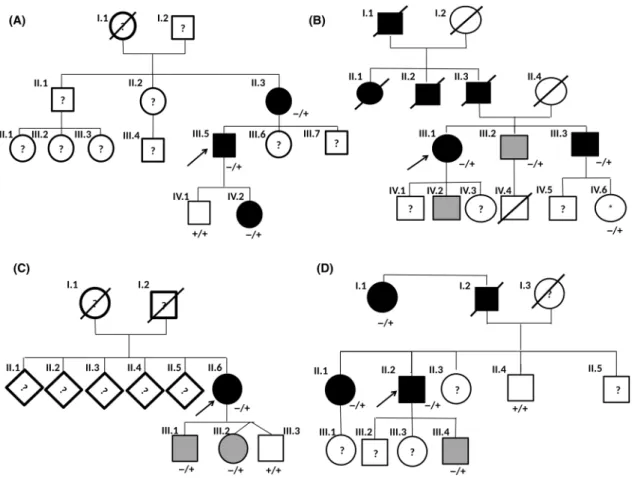
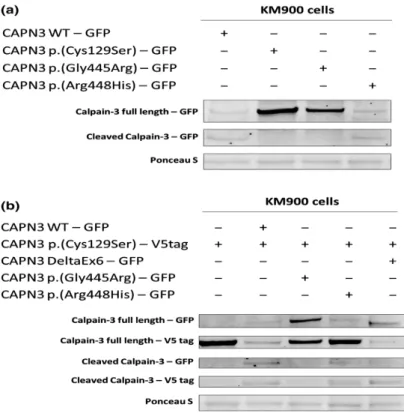
Novel CAPN3 variant associated with an autosomal dominant calpainopathy
Texte intégral
Figure
![Table 2. Summary of all previously identified cases associated with the c.1333G > A CAPN3 variant CAPN3 (NM_000070.2): c.1333G > A [p.(Gly445Arg)]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14415045.512494/10.892.79.787.175.967/table-summary-previously-identified-cases-associated-capn-variant.webp)

Documents relatifs
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
2) Régime isotonique concentrique : force générée par le muscle supérieur à la force de traction générée par muscle supérieur à la force de traction générée
Descriptive evidence suggests the upstream involvment of the phosphotransfer enzyme FAK (focal adhesion kinase) in the molecular control of load-dependent muscle plasticity..
Ainsi, lorsque le gène codant pour la �-dystroglycane, une des protéines du doublet de 43 kDa, a été cloné [19] , sa séquence en acides aminés a été
Plage en hyper signal T2 Fat sat au sein du muscle , en regard de cette zone épaissie : infiltration hématique et inflammatoire... Ax
To conclude, we hypothesise that an increased Plin2 expression in the muscle has different effects according to the age and the level of activity of the subjects: while
Experiments were performed at an early state of the disease process and our results show an impaired mitochondrial energy production accompanied by a faster
FIGURE 1 | Relationship between muscle volume and maximal joint torque for four lower limb joint movements in children with a typical development (TD) and with spastic cerebral