Frictional stress formulation for solid-liquid two-phase flows
Texte intégral
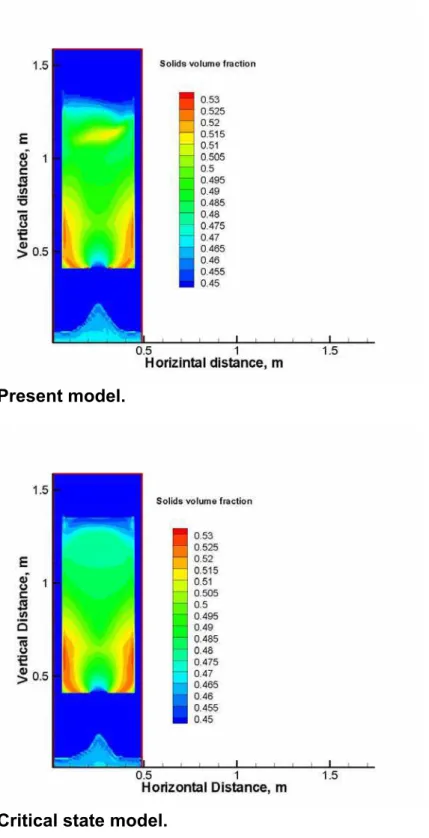
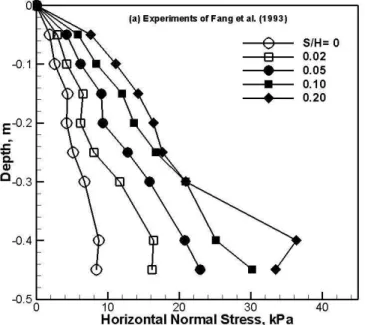
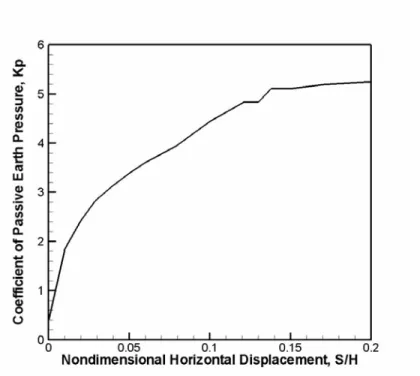
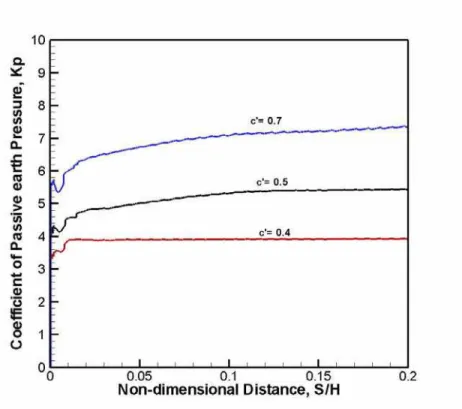
Figure

Documents relatifs
In this brief paper, we have provided an alternative derivation for the Green-Kubo relationship for the solid- liquid friction coefficient, based on a Langevin approach for the
The Canadian Primary Care Sentinel Surveillance Network, a Pan-Canadian project led by the CFPC that conducts standardized surveillance on selected chronic
In both linear empirical models and self- consistent nonlinear mean-field models, the electronic state of the crystal at time t is described by a one-body density matrix γ (t)
Mr Koïchiro Matsuura welcomed the Chairperson of the first session of the General Assembly, the Chairperson of the Intergovernmental Committee and
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
We give an implicit finite volume scheme for such a two- phase flow, and we prove the convergence of the inducted discrete solutions to a weak solution.. Under assumption on the
Even if these two papers are dedicated to systems of conservation laws, the analysis relies on the use of the entropy (and equivalently in the conservation case, upon the symmetric
The present paper is devoted to the computation of two-phase flows using the two-fluid approach. The overall model is hyperbolic and has no conservative form. No instanta- neous