Microbial Diversity in Sulfate-Reducing Marine Sediment Enrichment Cultures Associated with Anaerobic Biotransformation of Coastal Stockpiled Phosphogypsum (Sfax, Tunisia)
Texte intégral
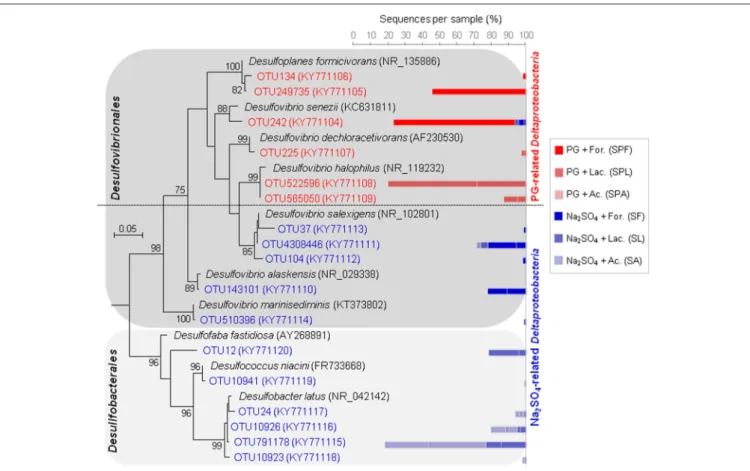
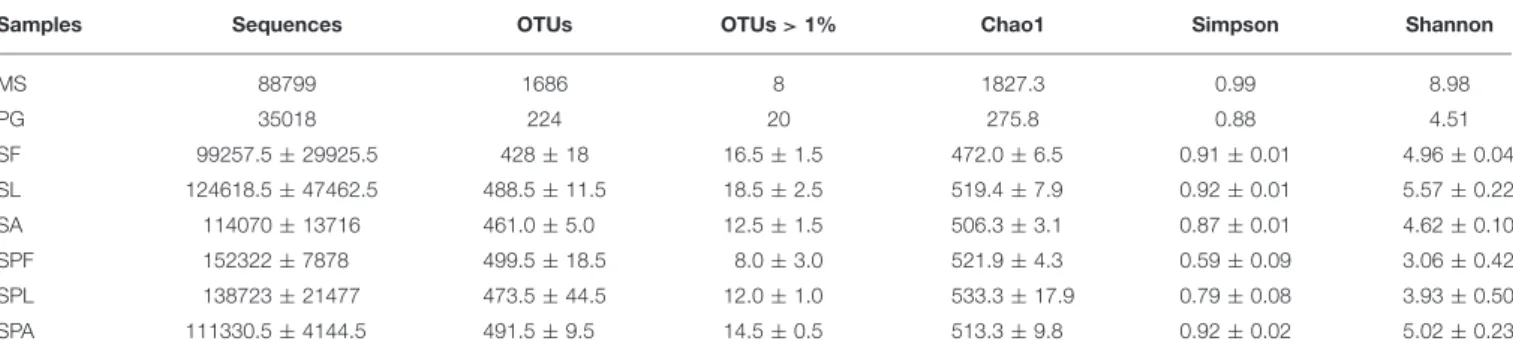
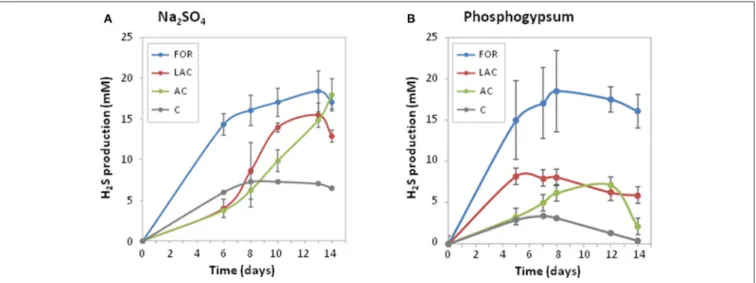
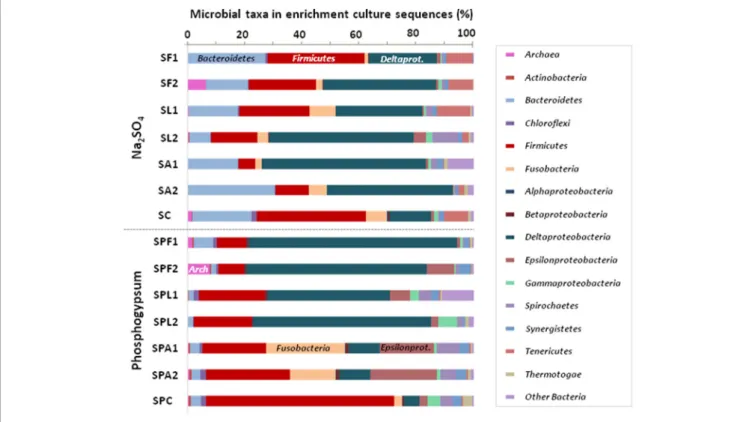
Figure

Documents relatifs
Depuis des années, l’infection urinaire est l’infection bactérienne la plus commune et cause un lourd fardeau pour les ressources du système de santé, car elle
Clearly, the Portilla-Simoncelli model allows many ambiguities about the visual information it tries to represent in the examples presented in this section.
THE COSTS OF A PURELY MONETARY DISINFLATION POLICY: THE CASE OF LONG-RUN INVOLUNTARY UNEMPLOYMENT.. by
In this study we describe the development of new lipophilic and biocompatible benzothiazole-based push-pull fluorophores as potent fluorogenic probes for the specific staining
:اضيأ فرعت امك نيب تابيترت لثمت دوقعلا عاونأ رئاسك دوقع يه امن او ةيلام لاو ةينيع لوصأ تسيل اهنأ أ نيفرط دقنلا قودنص رايتخا هيلع عقو يذلا فيرعتلا
As observed for the water column in lagoon and offshore waters, sediment contamination in the channel station exhibited clear seasonal variations, especially for PAH concentrations
From our experimental results, it could be possible that sea spray derived from waters with a higher concentration of marine microorganisms than normal (i.e. a bloom) blown onto
Microstructure of natural sediment after triaxial loading: (a) MIP cumulative volume results; (b) MIP incremental volume results; (c) SEM photo at 40 kPa loading; (d) SEM photo at